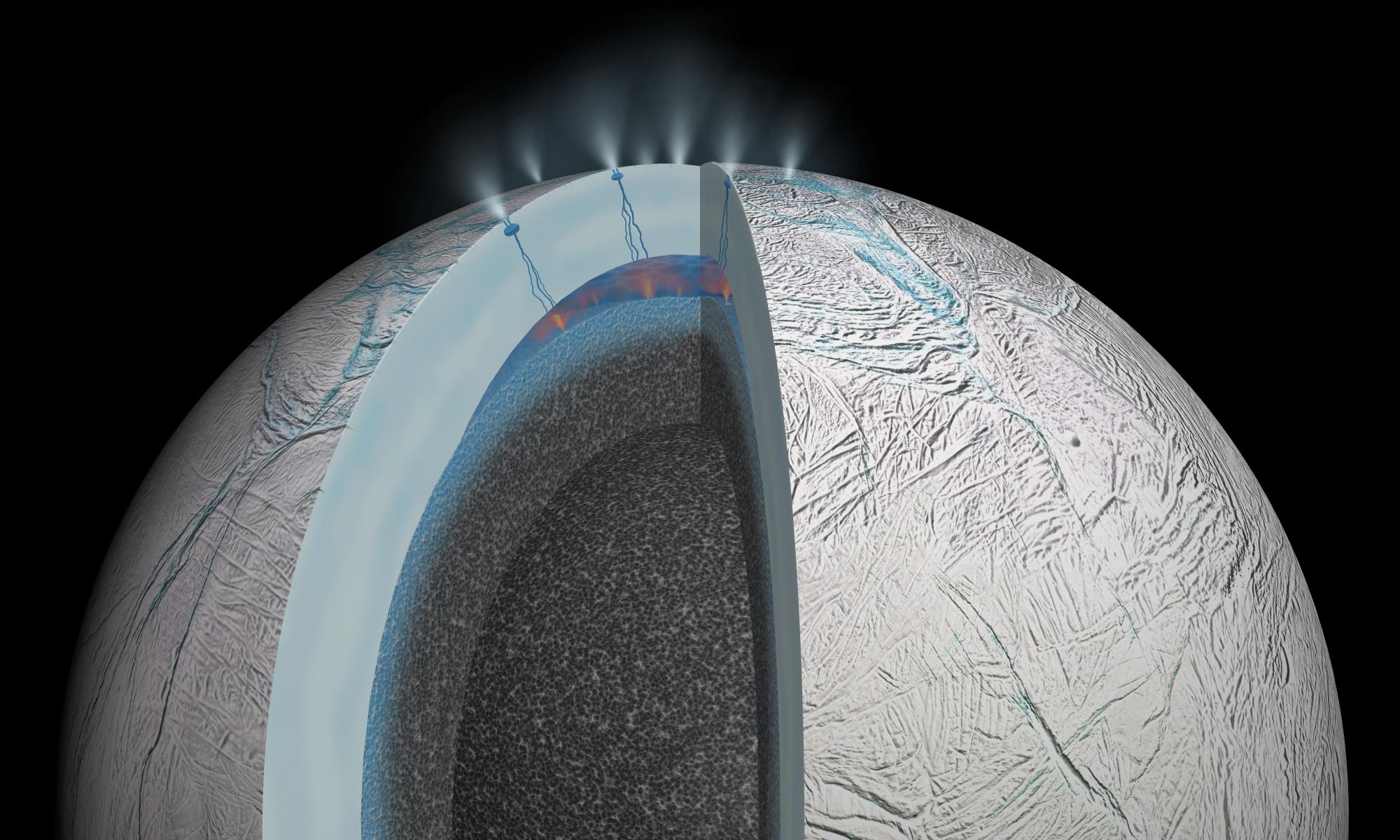
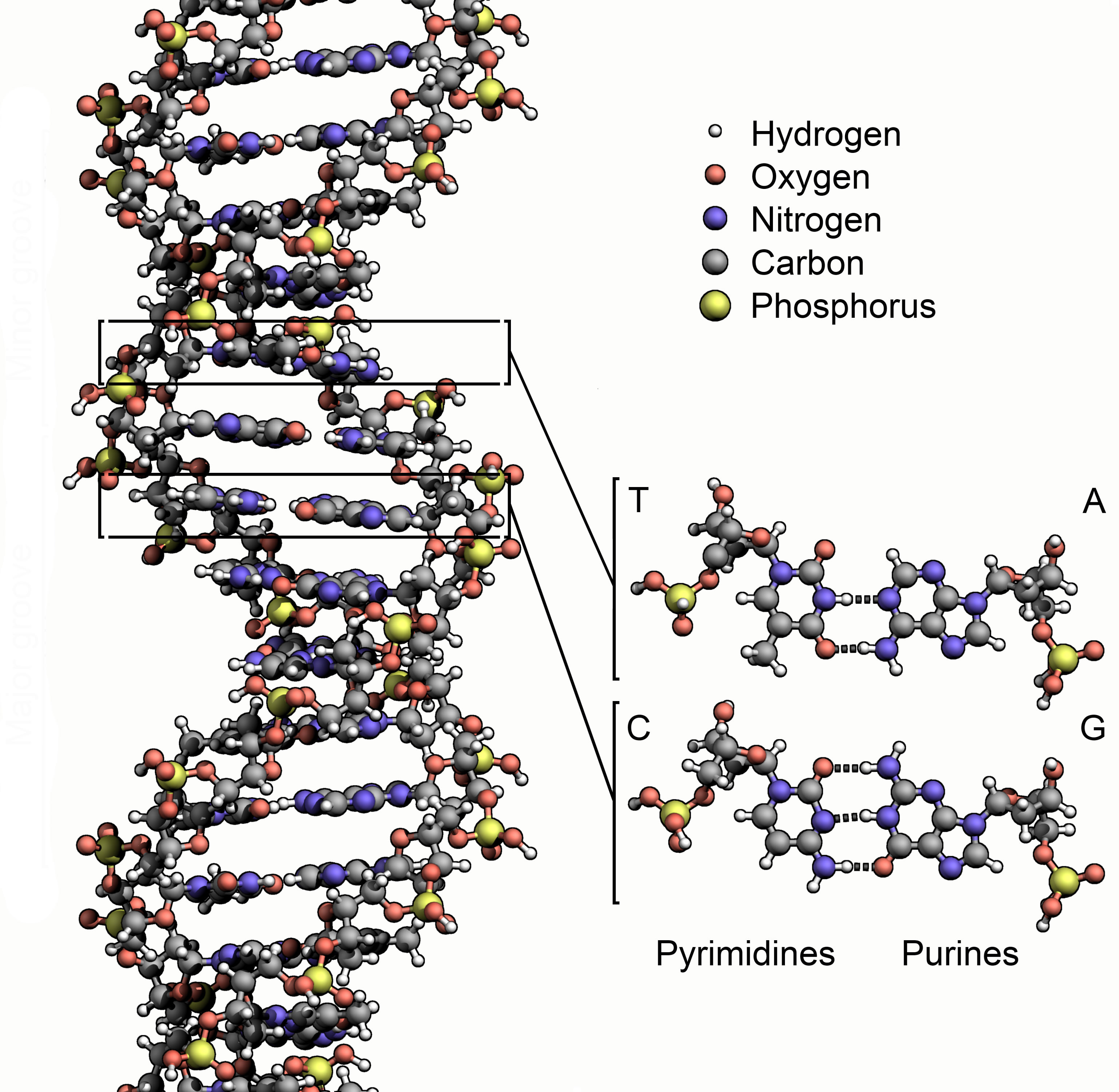
In many ways, stars are the engines of creation. Their energy drives a whole host of processes necessary for life. Scientists thought that stellar radiation is needed to create compounds like the amino acid glycine, one of the building blocks of life.
But a new study has found that glycine detected in comets formed in deep interstellar space when there was no stellar energy.
Continue reading “One of the Building Blocks of Life Can Form in the Harsh Environment of Deep Space Itself. No Star Required”