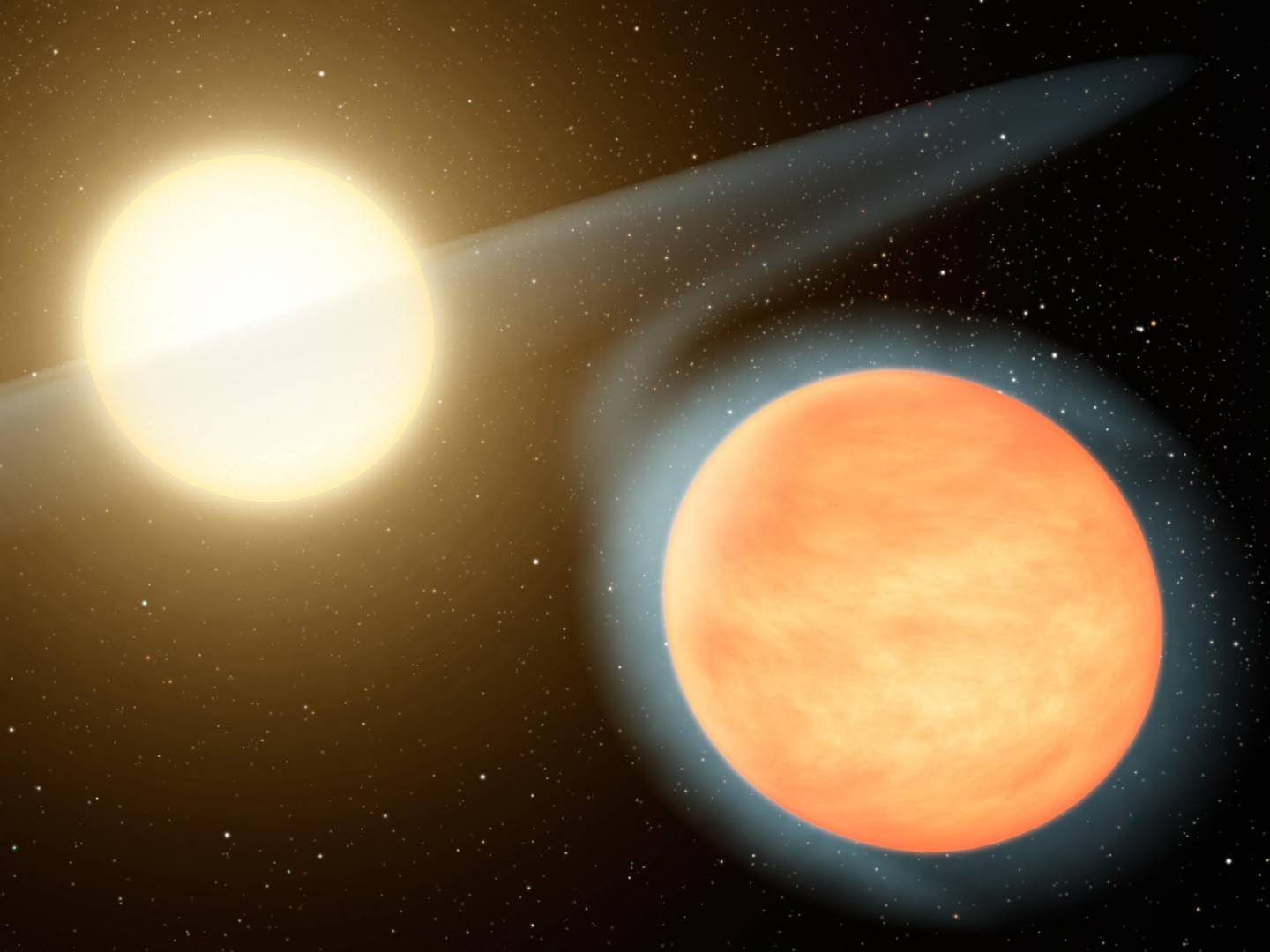
In 2008, astronomers with the SuperWASP survey spotted WASP-12b as it transited in front of its star. At the time, it was part of a new class of exoplanets (“Hot Jupiters”) discovered a little more than a decade before. However, subsequent observations revealed that WASP-12b was the first Hot Jupiter observed that orbits so closely to its parent star that it has become deformed. While several plausible scenarios have been suggested to explain these observations, a widely accepted theory is that the planet is being pulled apart as it slowly falls into its star.
Based on the observed rate of “tidal decay,” astronomers estimate that WASP-12b will fall into its parent star in about ten million years. In a recent study, astronomers with The Asiago Search for Transit Timing Variations of Exoplanets (TASTE) project presented an analysis that combines new spectral data from the Telescopio Nazionale Galileo (TNG) in La Palma with 12 years worth of unpublished transit light curves and archival data. Their results are consistent with previous observations that suggest WASP-12b is rapidly undergoing tidal dissipation and will be consumed by its star.
Continue reading “This Hot Jupiter is Doomed to Crash Into its Star in Just Three Million Years”