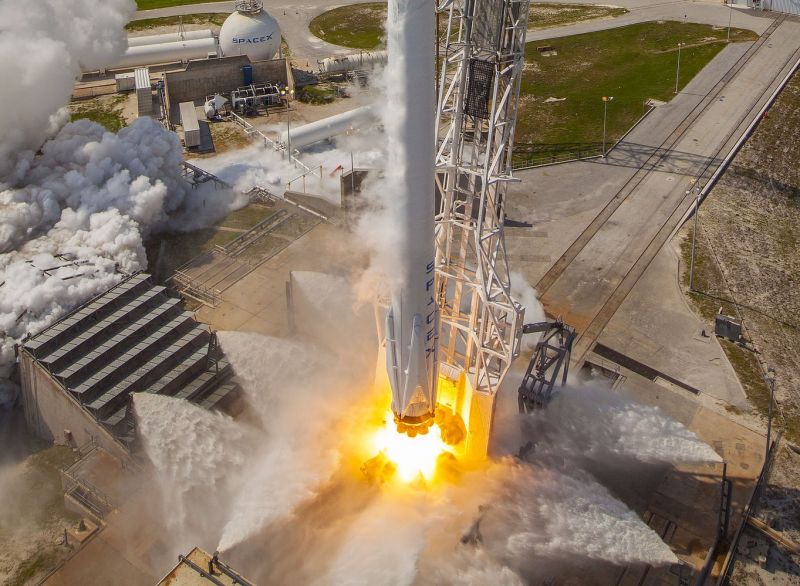
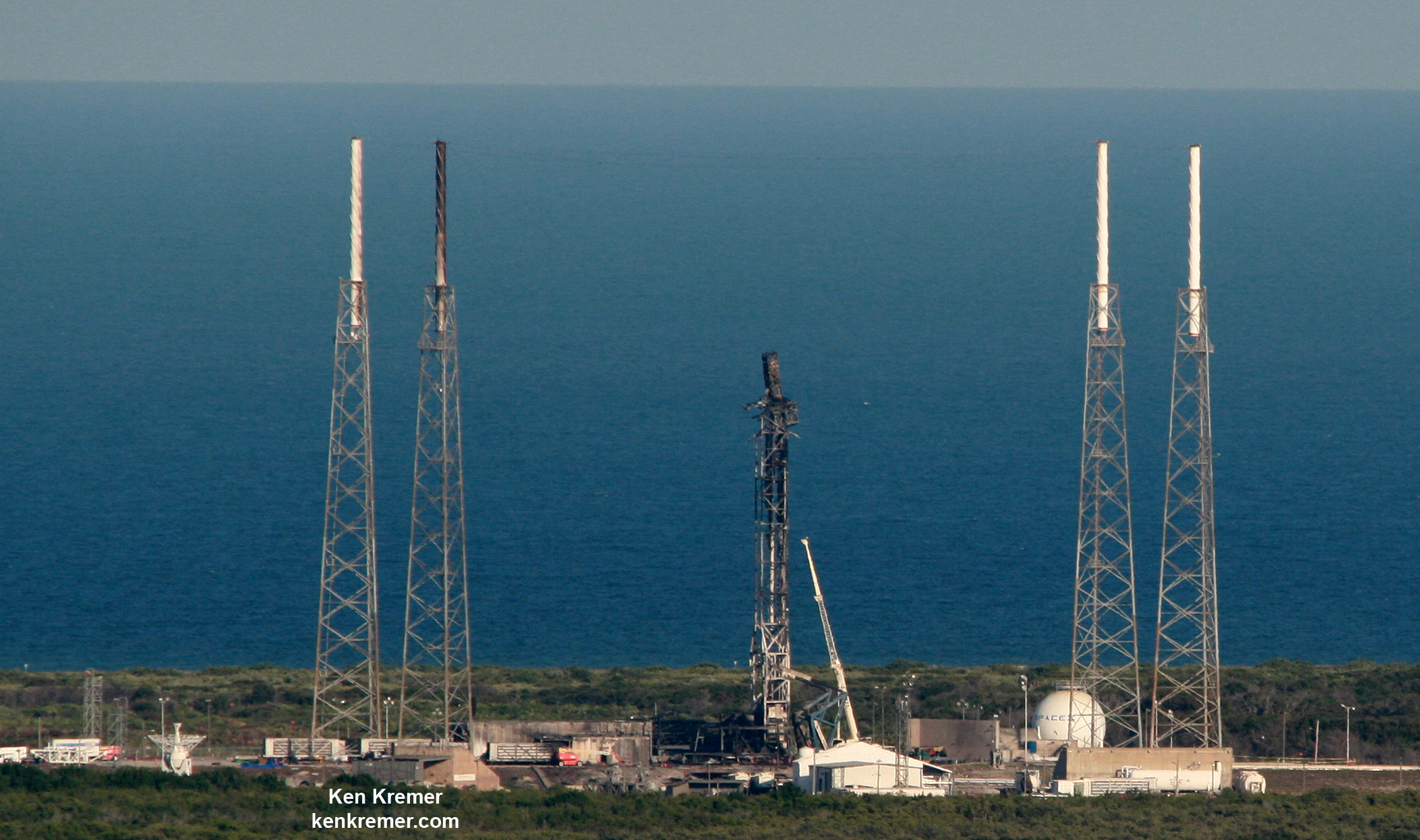
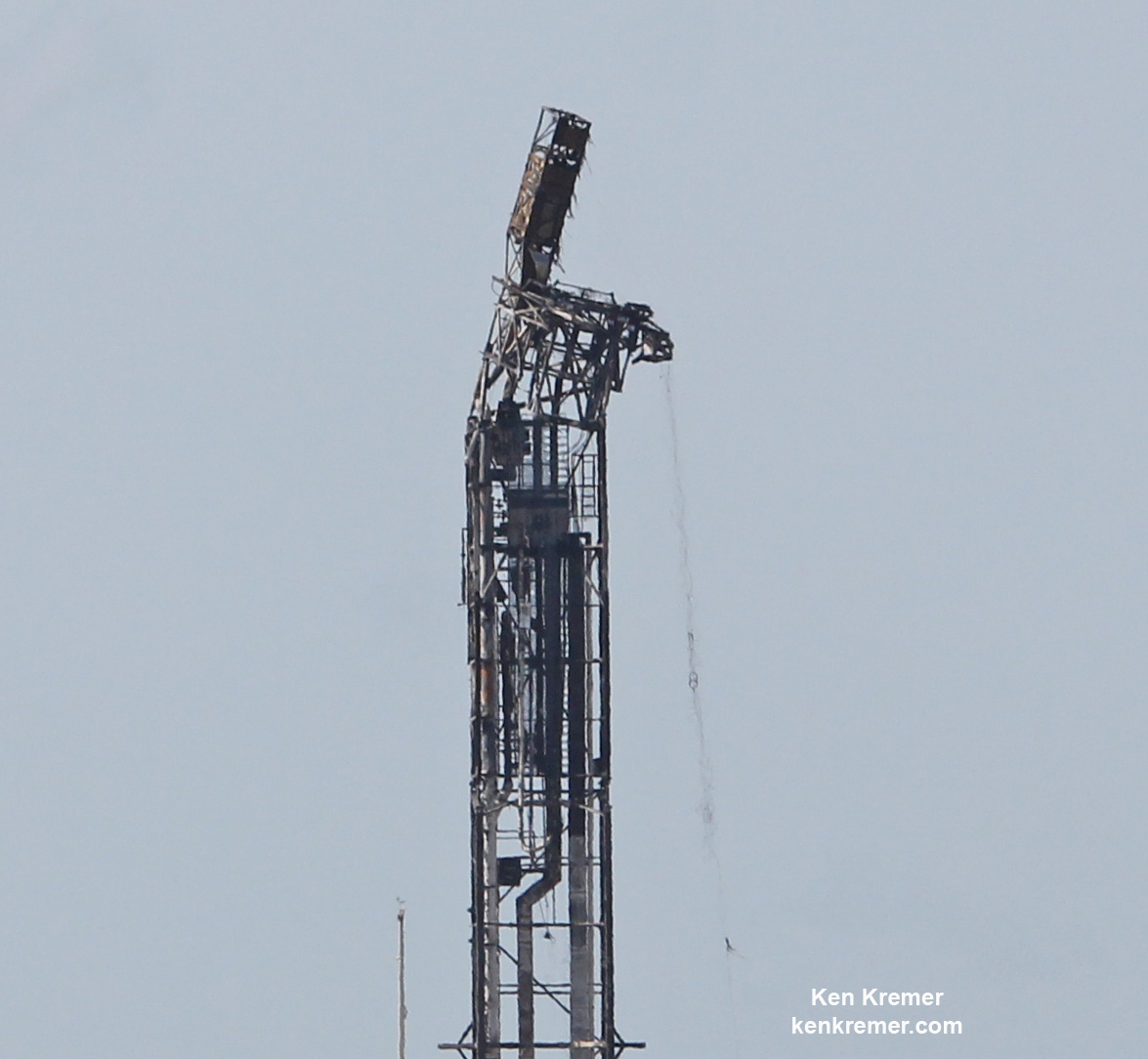
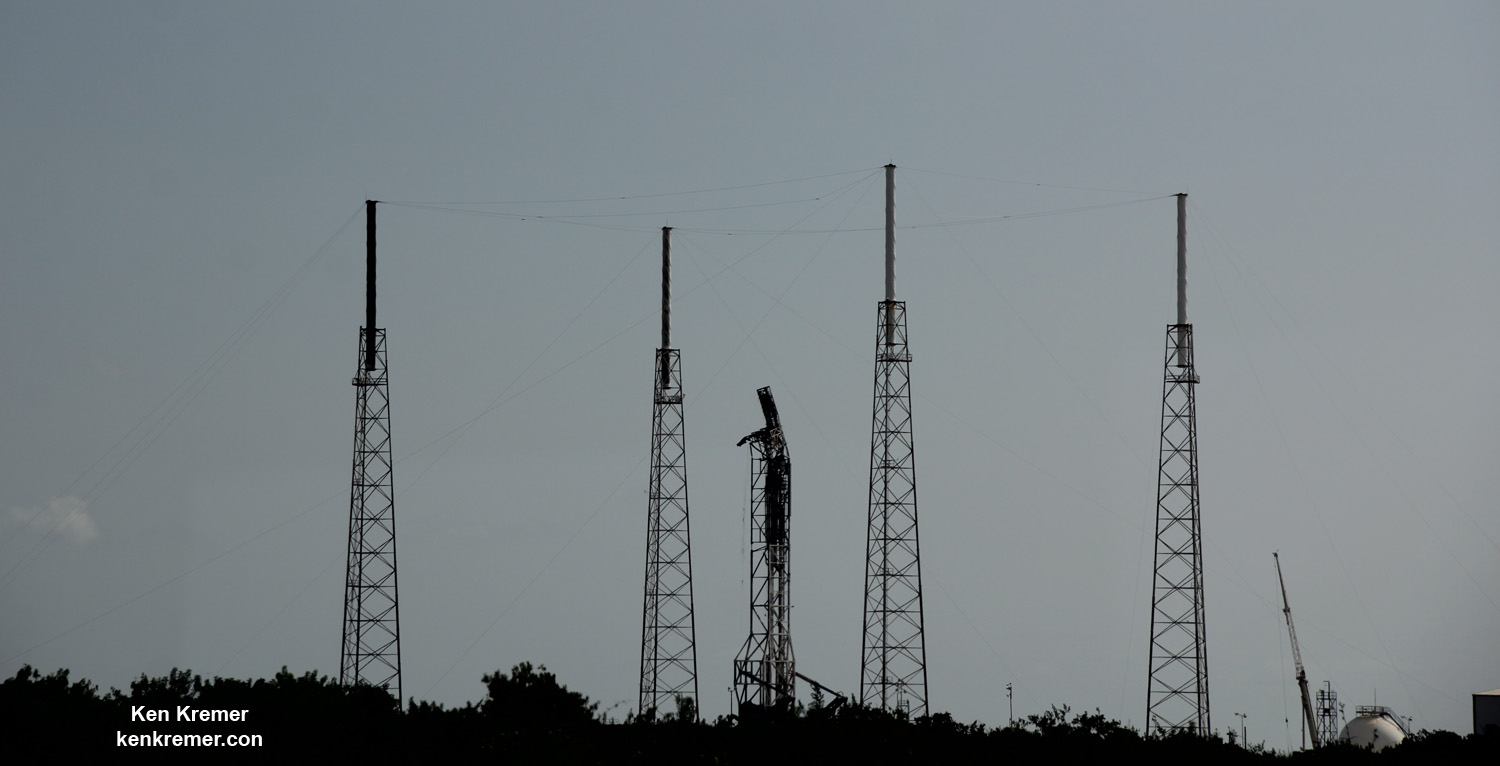
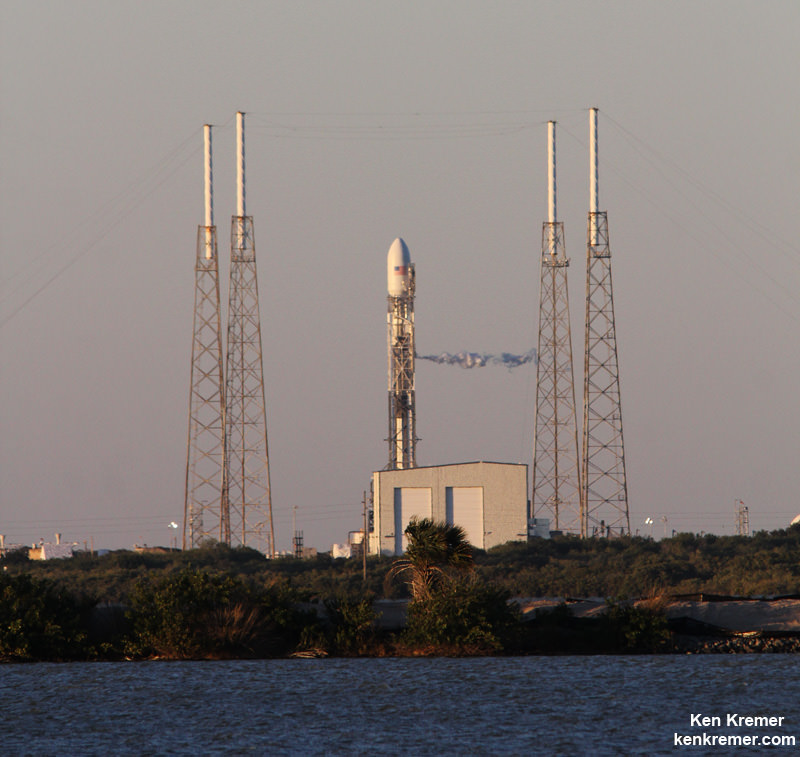
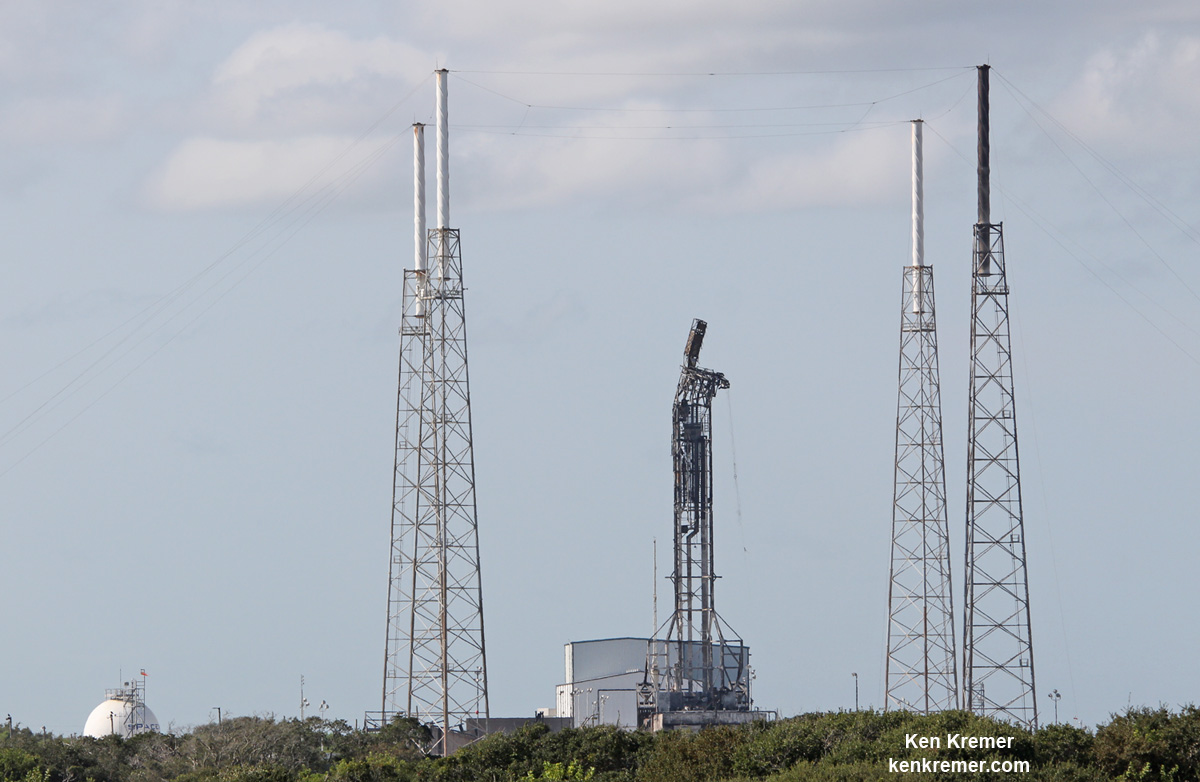
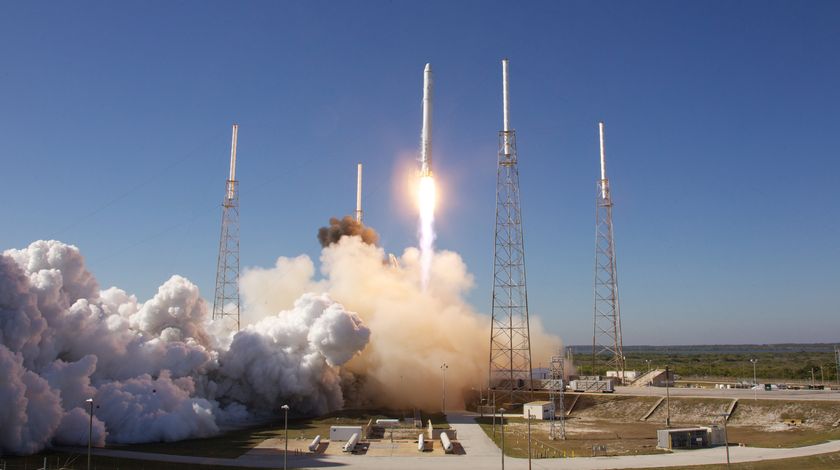
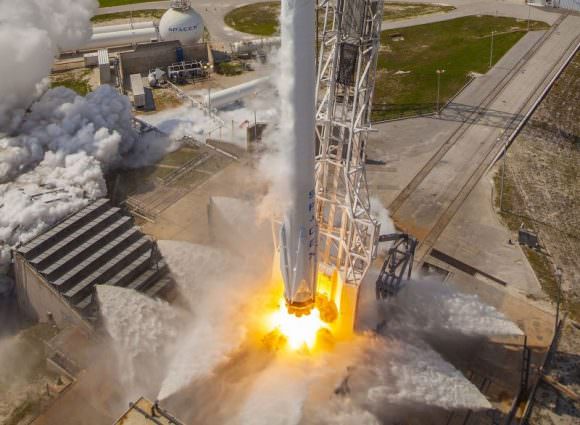
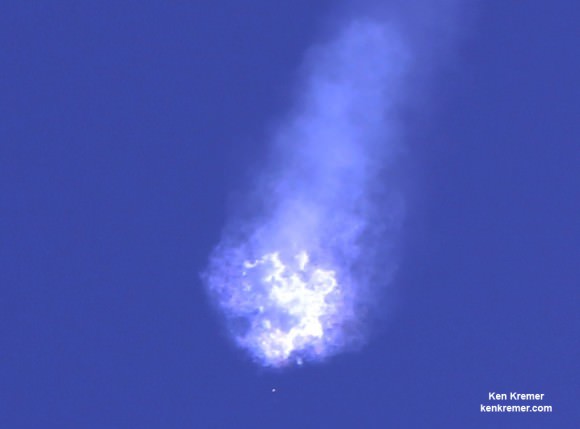
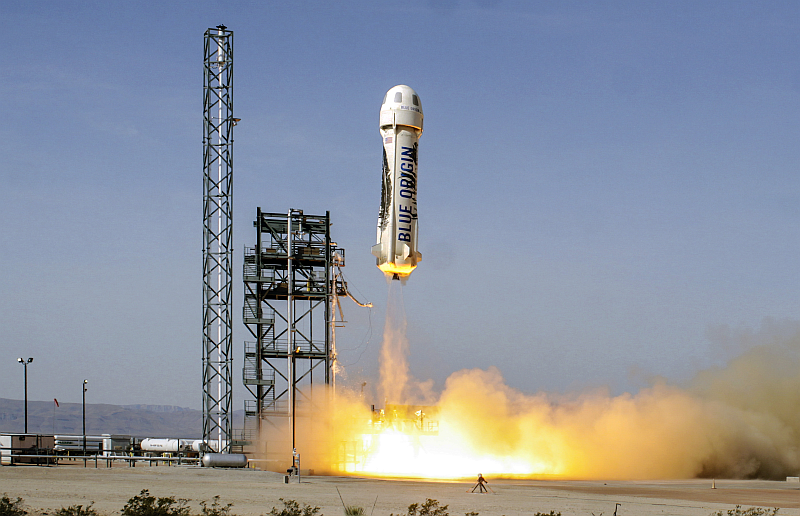
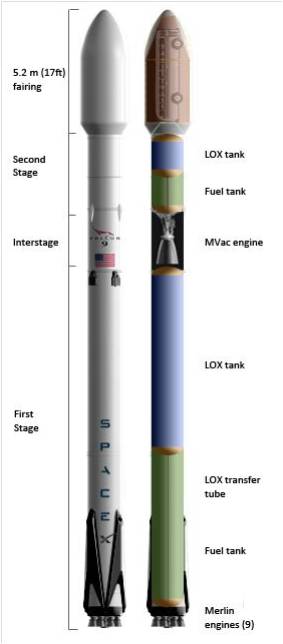
On September 1st, 2016, SpaceX experienced a rather public setback when one of their Falcon 9 rockets exploded on its launchpad at the Cape Canaveral Launch Complex in Florida. Though the accident resulted in no fatalities or injuries, this accident has since raised concerns over at NASA concerning the company’s safety standards.
Such was the conclusion reached by NASA’s Space Station Advisory Committee, which met on Monday, Oct. 31st, to discuss the accident and make recommendations. In a statement, the committee indicated that SpaceX’s policy of fueling rockets immediately before launch could pose a serious threat to crewed missions.
These concerns have been expressed before, but have become all the more relevant in light of the recent accident. At the time of the explosion, the rocket was already outfitted with its cargo capsule (which contained the Spacecom Amos-6 communications satellite). In the future, SpaceX hopes to send crewed missions into space, which means crews’ lives could be at risk in the event that a similar accident takes place during fueling.

Lt. General Thomas Stafford (USAF), who chaired the committee, was especially emphatic about the need for SpaceX to review its fueling policy. According to The Wall Street Journal, this is the second time that Lt. Gen. Stafford has expressed concerns. The last time was in 2015, when he sent a letter to NASA arguing that the company’s policy of fueling a rocket with its cargo already on board went against decades of procedure.
In the past, NASA has always maintained a policy where a rocket’s cargo is added only after the rocket is fueled. The same goes for crewed missions, where astronauts would board the rocket or Shuttle only after all pre-flight procedures were finished. But in the age of NewSpace, and with private companies offering launch services, things work a little differently.
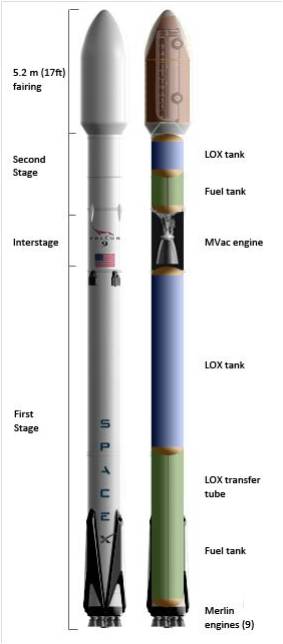
For example, SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket relies on a combination of liquid oxygen and rocket-grade kerosene propellant, which has less mass than conventional rocket fuel. This lets them pack more fuel into their rockets, and to be able to place larger payloads into orbit. However, this method requires that the rocket be immediately fueled before launch so that the fuel does not have time to warm up and expand.
As a result, future missions – which include crewed ones – will have to be fueled immediately before launch in order to ensure that the rocket’s fuel and lift capacity are not compromised. The Advisory Committee’s recommendations could therefore have a significant impact on how SpaceX does business. However, there recommendations might be a bit premature as far as crewed missions go.
For instance, the Dragon V2 has a crew abort system that was specifically designed for this kind of situation. Relying on the capsule’s eight side-mounted SuperDraco engines, this system is programmed to conduct a propulsive firing in the event of a catastrophic failure on the launchpad. The capsule also comes with a landing chute which will deploy once the rockets are depleted to ensure that it makes a soft landing.
In May of 2015, the company tested this system at the Cape Canaveral Launch Complex, followed by a “propulsive hovering test” in November of that same year. Both tests were successful and demonstrated how the SuperDraco engines are capable of launching the capsule to safety, and that they were capable of keeping the capsule in a state of equilibrium above the ground (see video above).
In addition, SpaceX responded to news of the Advisory Panel and expressed confidence in its procedures, which included fueling and their launch abort system. In an official statement, the full text of which was procured by Universe Today via email, the company said that:
“SpaceX has designed a reliable fueling and launch process that minimizes the duration and number of personnel exposed to the hazards of launching a rocket. As part of this process, the crew will safely board the Crew Dragon, ground personnel will depart, propellants will be carefully loaded over a short period, and then the vehicle will launch. During this time the Crew Dragon launch abort system will be enabled. Over the last year and a half, NASA and SpaceX have performed a detailed analysis of all potential hazards with this process.”

In addition, they cited that prior to the Sept.1st accident, all safety protocols had been followed and NASA had signed off on the launch. But of course, they also expressed that they would continue to comply with all safety procedures, which could include any changes based on the Advisory Committee’s recommendations:
“The hazard report documenting the controls was approved by the NASA’s Safety Technical Review Board in July 2016. As with all hazard analyses across the entire system and operations, controls against those hazards have been identified, and will be implemented and carefully verified prior to certification. There will be continued work ahead to show that all of these controls are in place for crewed operations and that the verifications meet NASA requirements. These analyses and controls will be carefully evaluated in light of all data and corrective actions resulting from the anomaly investigation. As needed, any additional controls will be put in place to ensure crew safety, from the moment the astronauts reach the pad, through fueling, launch, and spaceflight, and until they are brought safely home.”
In the meantime, SpaceX investigators are still attempting to find out exactly what went wrong with the Sept.1st launch. The most recent update (which was made on Oct. 28th) indicated that the company is making headway, and hoping to return to normal operations during the month of November.
“SpaceX’s efforts are now focused on two areas – finding the exact root cause, and developing improved helium loading conditions that allow SpaceX to reliably load Falcon 9,” it states. “With the advanced state of the investigation, we also plan to resume stage testing in Texas in the coming days, while continuing to focus on completion of the investigation.”
Further Reading: WSJ