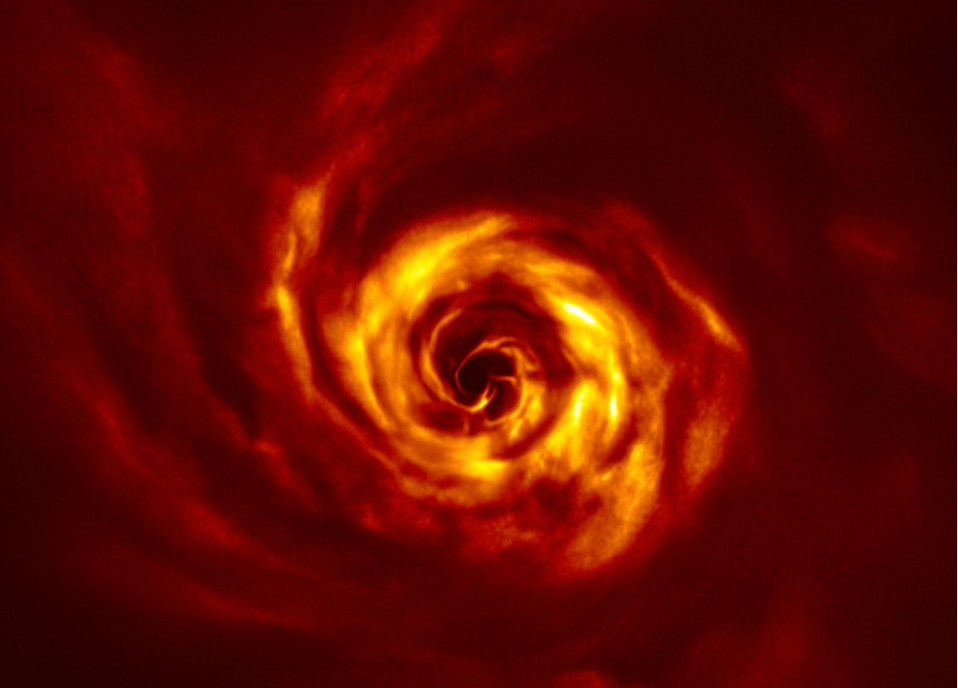
In 2017, astronomers used ALMA (Atacama Large Millimeter/sub-millimeter Array) to look at the star AB Aurigae. It’s a type of young star called a Herbig Ae star, and it’s less then 10 million years old. At that time, they found a dusty protoplanetary disk there, with tell-tale gaps indicating spiral arms.
Now they’ve taken another look, and found a very young planet forming there.
Continue reading “This is an Actual Image of a Planet-Forming Disc in a Distant Star System”