[/caption]
Take a good close look at the Moon today and consider this; Two new Moon’s just reached orbit.
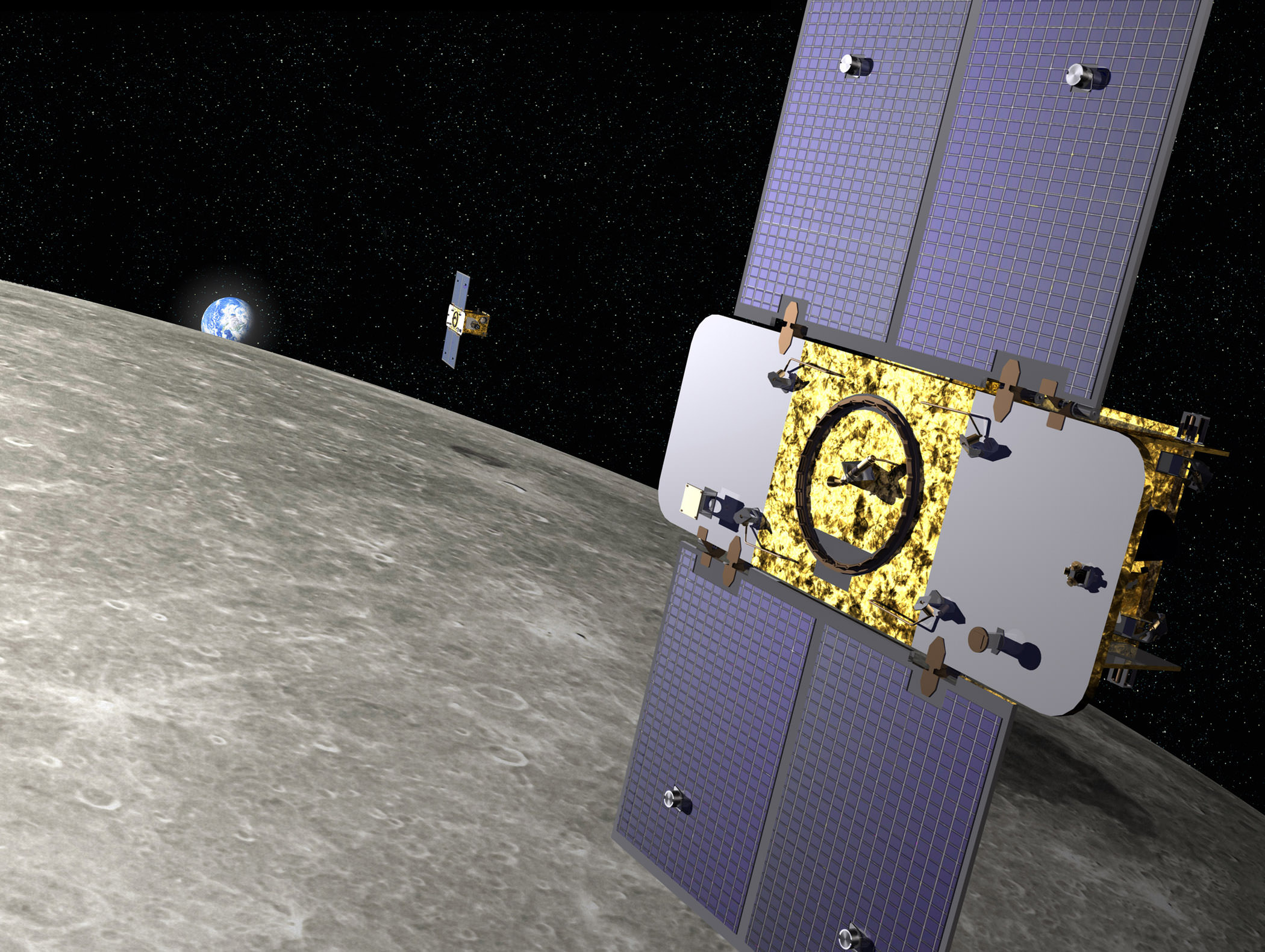
NASA is ringing in the New Year with a double dose of champagne toasts celebrating the back to back triumphal insertions of a pair of tiny probes into tandem lunar orbits this weekend that seek to unravel the hidden mysteries lurking deep inside the Moon and figure out how the inner solar system formed eons ago.
Following closely on the heels of her twin sister, NASA’s GRAIL-B spacecraft ignited her main braking rockets precisely as planned on New Year’s Day (Jan.1) to go into a formation flying orbit around the Moon, chasing behind GRAIL-A which arrived on New Year’s Eve (Dec. 31).
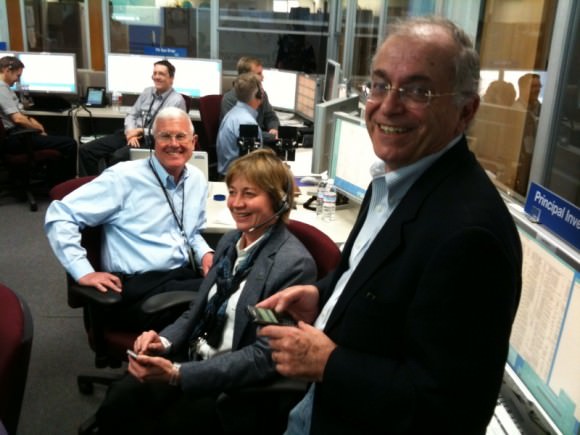
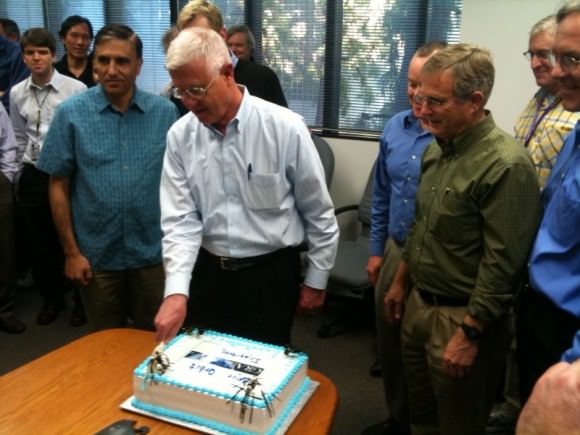
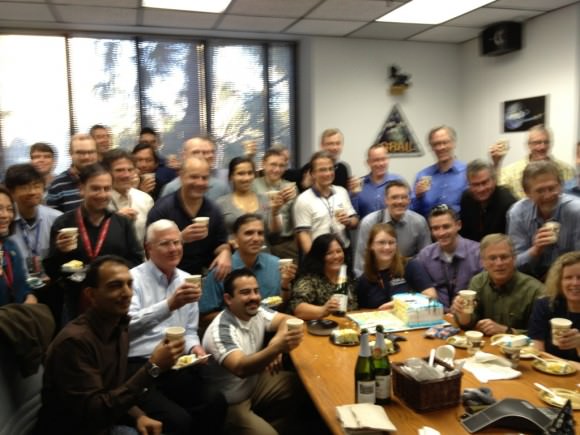
“Now we have them both in orbit. What a great feeling!!!!” NASA manager Jim Green told Universe Today just minutes after the thruster firing was done. Green is NASA’s Director of Planetary Science and witnessed the events inside Mission Control at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, Ca.
“It’s the best New Year’s ever!!” Green gushed with glee.

The new lunar arrivals of GRAIL-A and GRAIL-B capped a perfect year for NASA’s Planetary Science research in 2011.
“2011 began the Year of the Solar System – which is a Mars year (~670 Earth days long)… and includes Grail B insertion, Dawn leaving Vesta this summer … And the landing of MSL! ,” Green said.

Credit: Ken Kremer
“Cheers in JPL mission control as everything is looking good for GRAIL-B. It’s going to be a great 2012!!” JPL tweeted shortly after confirming the burn successfully placed GRAIL-B into the desired elliptical orbit.
After years of hard work, GRAIL principal investigator Maria Zuber of MIT told Universe Today that she was very “relieved”, soon after hearing the good news at JPL Mission Control.
“Since GRAIL was originally selected I’ve believed this day would come,” Zuber told me shortly after the GRAIL-B engine firing was declared a success on New Year’s Day.
“But it’s difficult to convey just how relieved I am right now. Time for the Science Team to start their engines !”
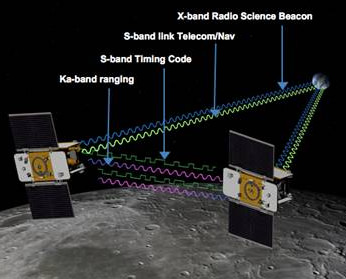
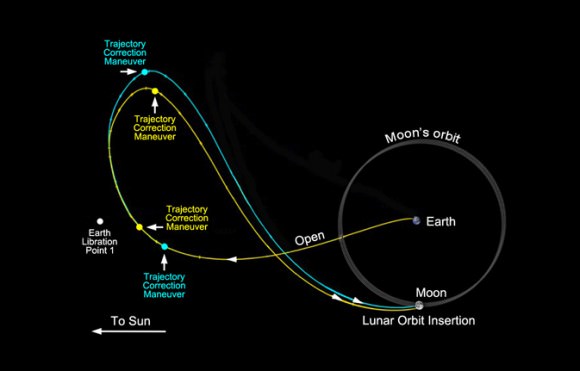
At 2:43 p.m. PST (5:43 p.m. EST) on New Year’s Day, the main thruster aboard GRAIL-B automatically commenced firing to slow down the spacecraft’s approach speed by about 430 MPH (691 kph) and allow it to be captured into orbit by the Moon’s gravity. The preprogrammed maneuver lasted about 39 minutes and was nearly identical to the GRAIL-A firing 25 hours earlier.
The hydrazine fueled main thrusters placed the dynamic spacecraft duo into near-polar, highly elliptical orbits.
Over the next two months, engineers will trim the orbits of both spacecraft to a near-polar, near-circular formation flying orientation. Their altitudes will be lowered to about 34 miles (55 kilometers) and the orbital periods trimmed from their initial 11.5 hour duration to about two hours.
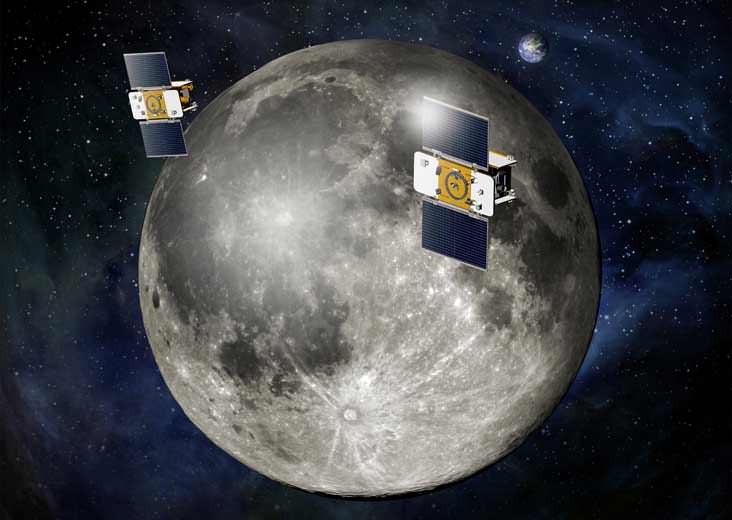
The science phase begins in March 2012. For 82 days, the mirror image GRAIL-A and GRAIL-B probes will be flying in tandem with an average separation of about 200 kilometers as the Moon rotates beneath.
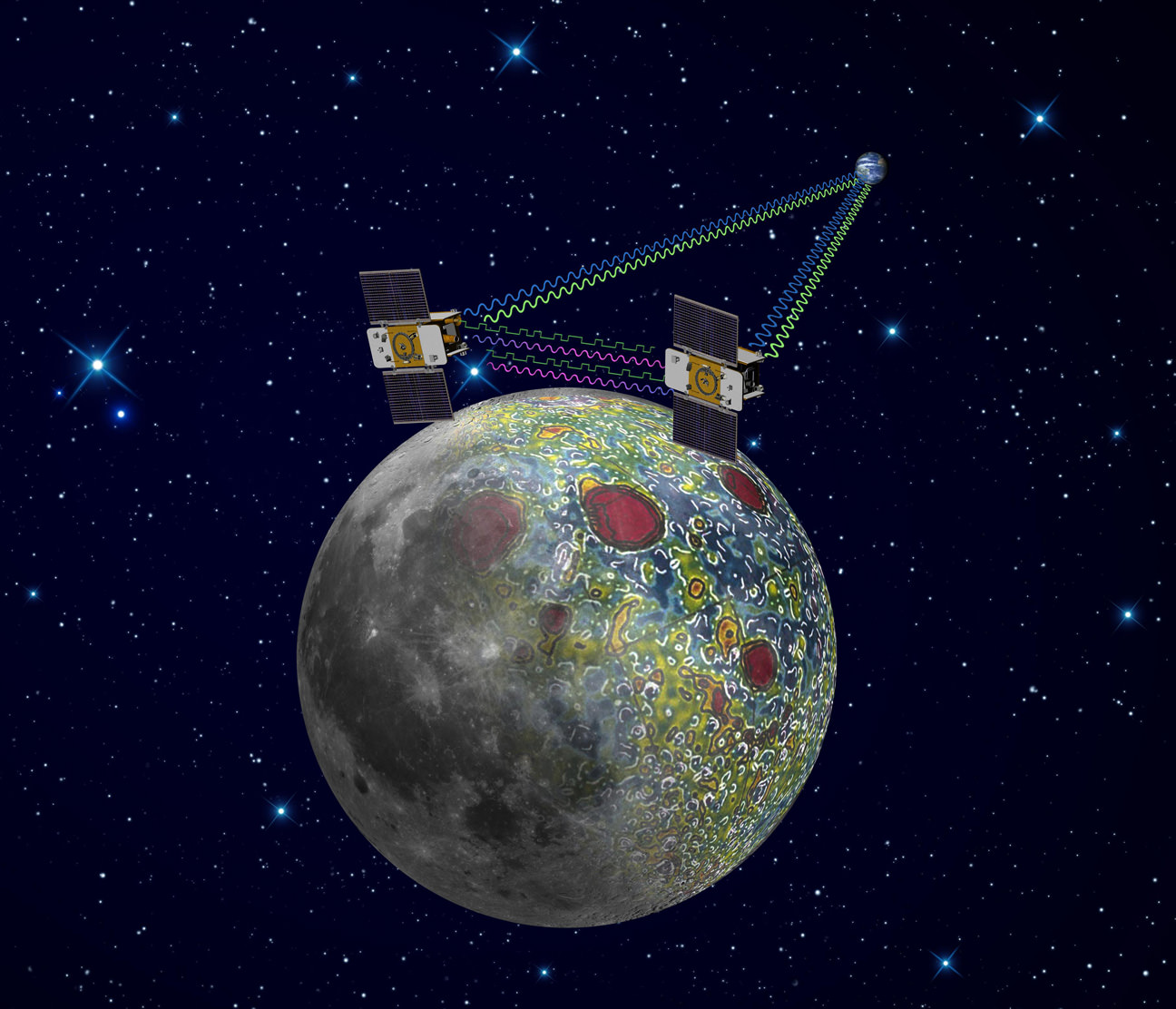
“GRAIL is a Journey to the Center of the Moon,” Zuber explained at a media briefing. “It will use exceedingly precise measurements of gravity to reveal what the inside of the Moon is like.”

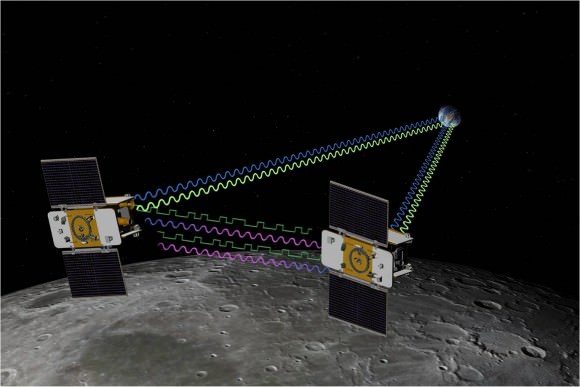
As one satellite follows the other, in the same orbit, they will perform high precision range-rate measurements to precisely measure the changing distance between each other to within 1 micron, the width of a red blood cell, using a Ka-band instrument.
When the first satellite goes over a higher mass concentration, or higher gravity, it will speed up slightly. And that will increase the distance. Then as the second satellite goes over, that distance will close again.
The data returned will be translated into gravitational field maps of the Moon that will help unravel information about the makeup of the Moon’s mysterious core and interior composition. GRAIL will gather three complete gravity maps over the three month mission.
“There have been many missions that have gone to the Moon, orbited the Moon, landed on the Moon, brought back samples of the Moon,” said Zuber. “But the missing piece of the puzzle in trying to understand the Moon is what the deep interior is like.”
“Is there a core? How did the core form? How did the interior convect? What are the impact basins on the near-side flooded with magma and give us this Man-in-the-Moon shape whereas the back side of the Moon doesn’t have any of this? These are all mysteries that despite the fact we’ve studied the Moon before, we don’t understand how that has happened. GRAIL is a mission that is going to tell us that.”
“We think the answer is locked in the interior,” Zuber elaborated.
How will the twins be oriented in orbit to gather the data ?
“The probes will be pointed at one another to make the highly precise measurements,” said GRAIL co-investigator Sami Asmar of JPL to Universe Today. “The concept has heritage from the US/German GRACE earth orbiting satellites which mapped Earth’s gravity field. GRACE required the use of GPS satellites for exactly knowing the position, but there is no GPS at the Moon. So GRAIL was altered to compensate for no GPS at the Moon.”
GRAIL will map the gravity field by 100 to 1000 times better than ever before.
“We will learn more about the interior of the Moon with GRAIL than all previous lunar missions combined,” says Ed Weiler, the recently retired NASA Associate Administrator of the Science Mission Directorate in Washington, DC.
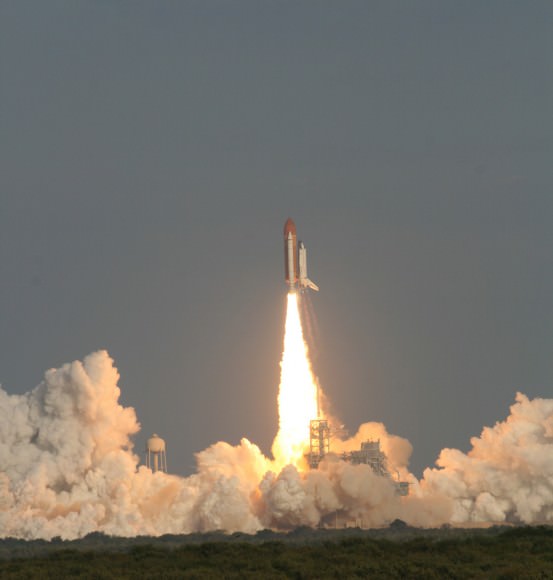
The GRAIL twins blasted off from Florida mounted side by side atop a Delta II booster on September 10, 2011 and took a circuitous 3.5 month low energy path to the Moon to minimize the overall costs.
So when you next look at the sky tonight and in the coming weeks just imagine those mirror image GRAIL twins circling about seeeking to determine how we all came to be !


Read continuing features about GRAIL by Ken Kremer here:
First GRAIL Twin Enters Lunar Orbit – NASA’s New Year’s Gift to Science
2011: Top Stories from the Best Year Ever for NASA Planetary Science!
NASA’s Unprecedented Science Twins are GO to Orbit our Moon on New Year’s Eve
Student Alert: GRAIL Naming Contest – Essay Deadline November 11
GRAIL Lunar Blastoff Gallery
GRAIL Twins Awesome Launch Videos – A Journey to the Center of the Moon
NASA launches Twin Lunar Probes to Unravel Moons Core
GRAIL Unveiled for Lunar Science Trek — Launch Reset to Sept. 10
Last Delta II Rocket to Launch Extraordinary Journey to the Center of the Moon on Sept. 8
NASAs Lunar Mapping Duo Encapsulated and Ready for Sept. 8 Liftoff
GRAIL Lunar Twins Mated to Delta Rocket at Launch Pad
GRAIL Twins ready for NASA Science Expedition to the Moon: Photo Gallery