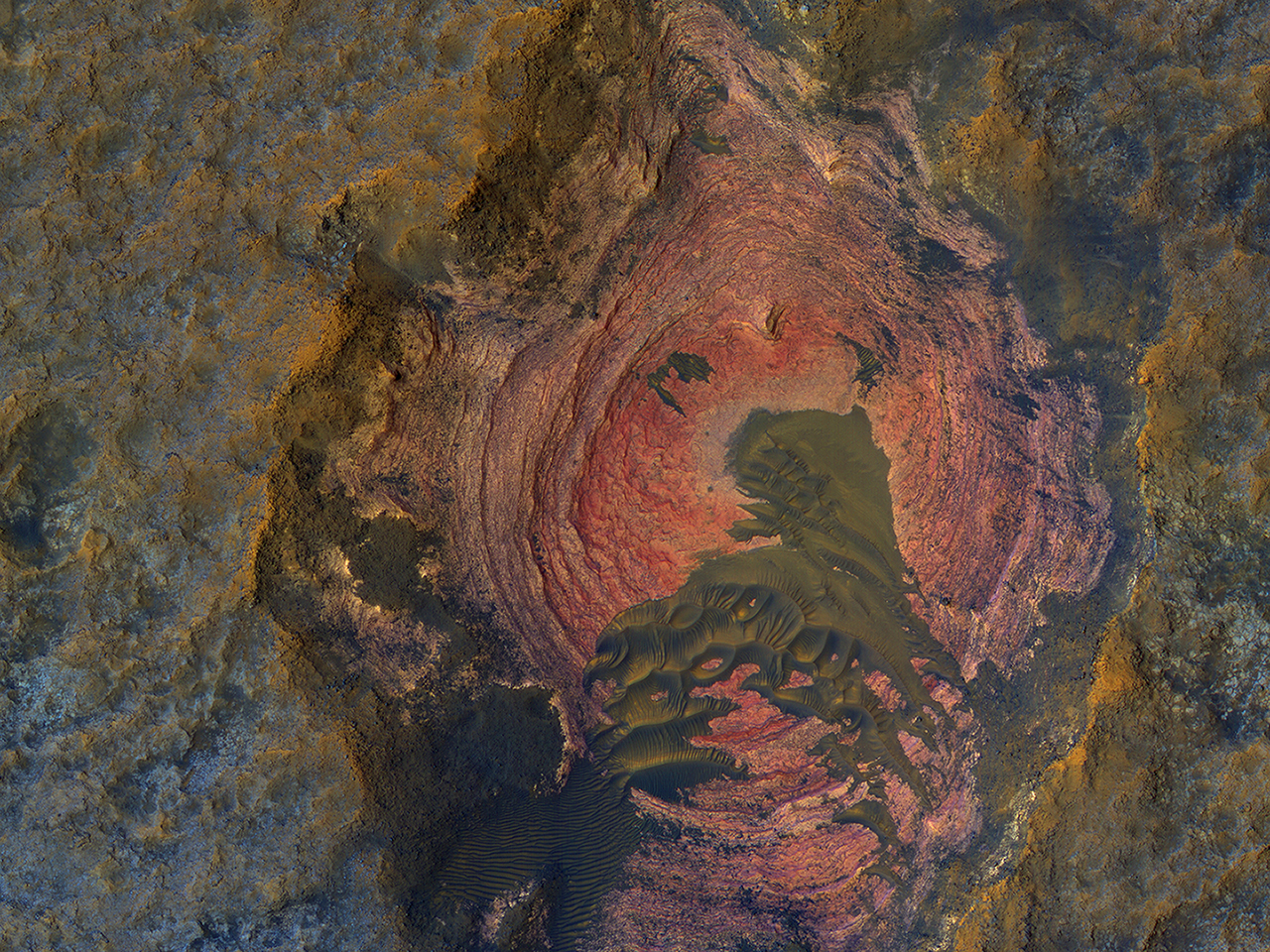
For a supposedly dead world, Mars sure provides a lot of eye candy. The High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRise) aboard NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) is our candy store for stunning images of Mars. Recently, HiRise gave us this stunning image (above) of colorful, layered bedrock on the surface of Mars. Notice the dunes in the center. The colors are enhanced, which makes the images more useful scientifically, but it’s still amazing.
HiRise has done it before, of course. It’s keen vision has fed us a steady stream of downright jaw-dropping images of Elon Musk’s favorite planet. Check out this image of Gale Crater taken by HiRise to celebrate its 10 year anniversary orbiting Mars. This image was captured in March 2016.

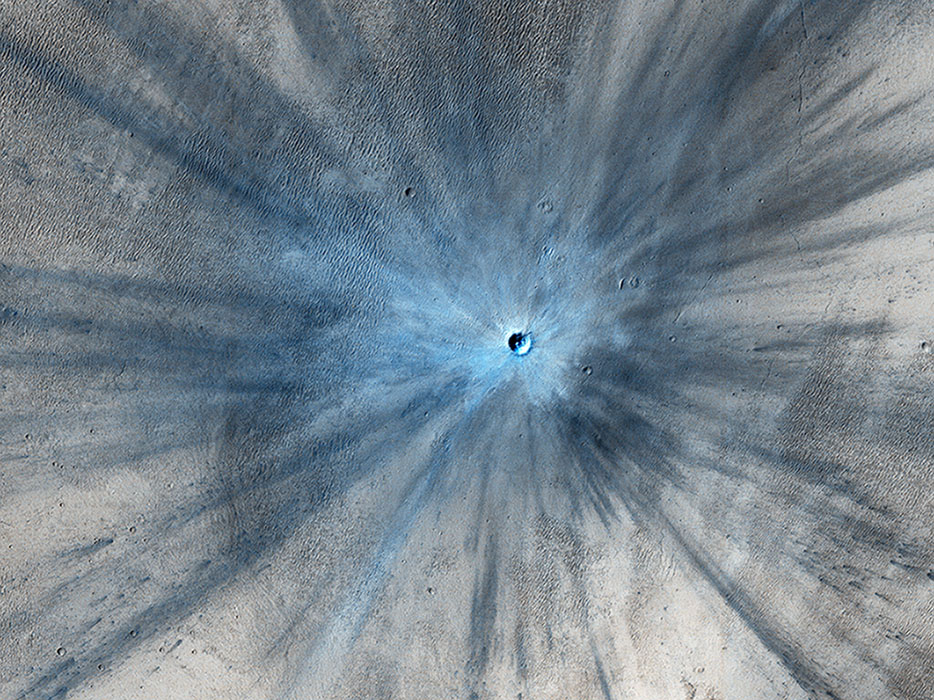
The MRO is approaching its 11 year anniversary around Mars. It has completed over 45,000 orbits and has taken over 216,000 images. The next image is of a fresh impact crater on the Martian surface that struck the planet sometime between July 2010 and May 2012. The impact was in a dusty area, and in this color-enhanced image the fresh crater looks blue because the impact removed the red dust.

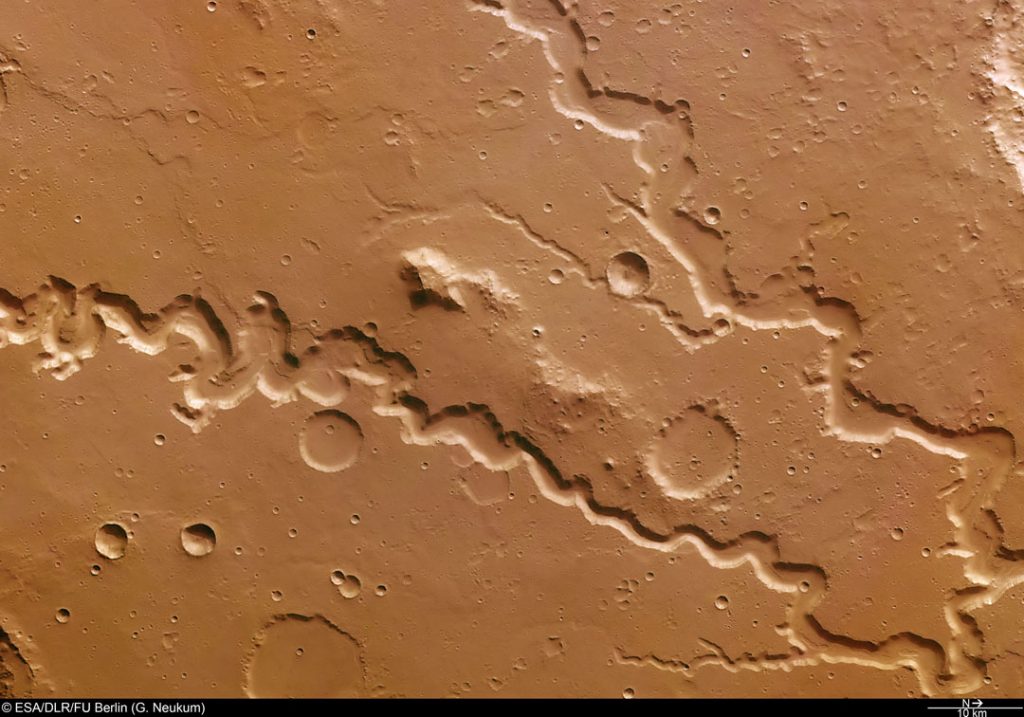
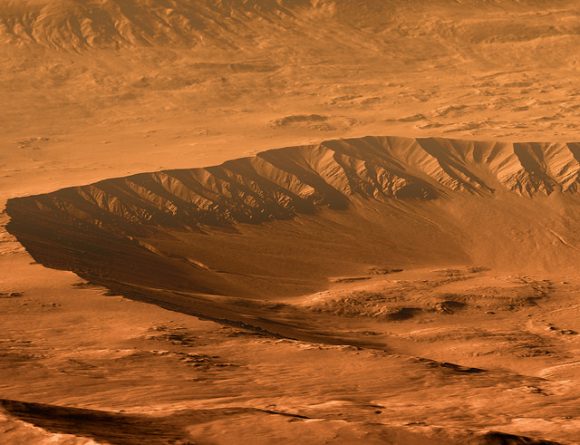
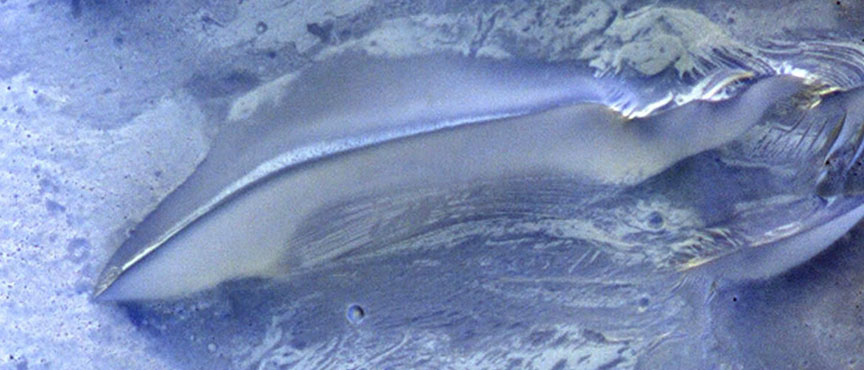
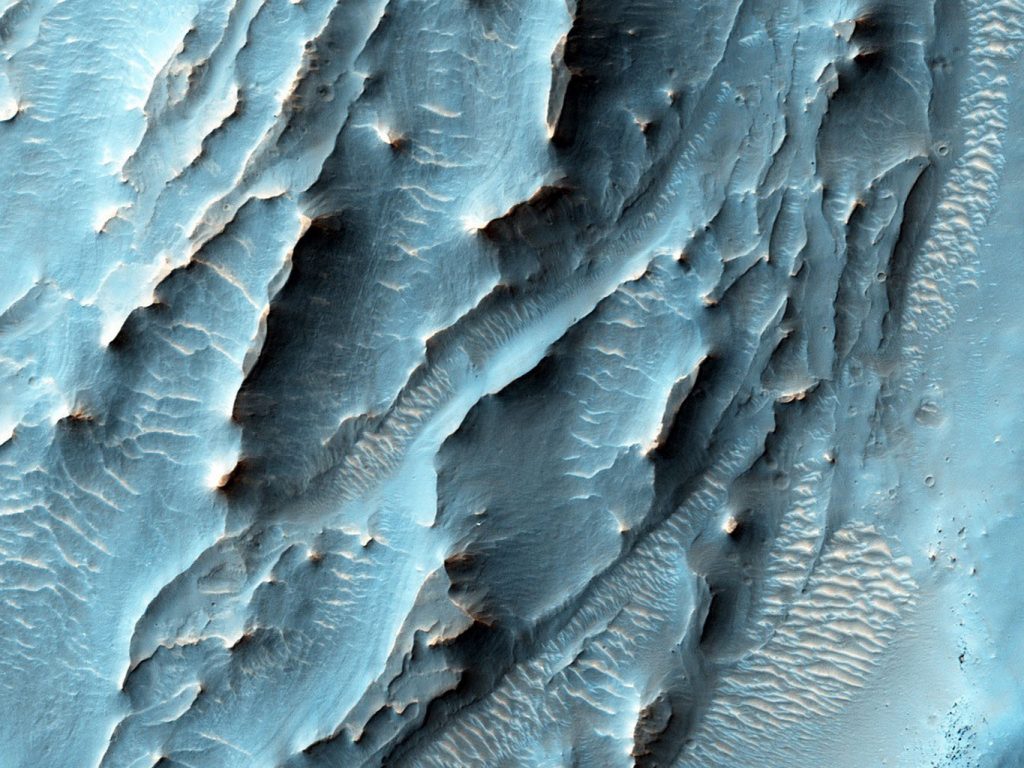
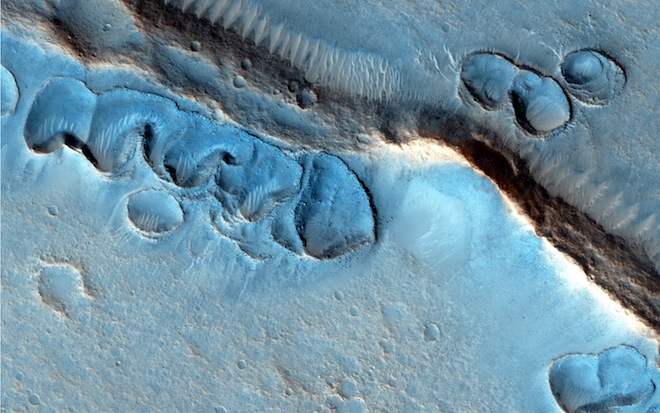
These landforms on the surface of Mars are still a bit of a mystery. It’s possible that they formed in the presence of an ancient Martian ocean, or perhaps glaciers. Whatever the case, they are mesmerizing to look at.

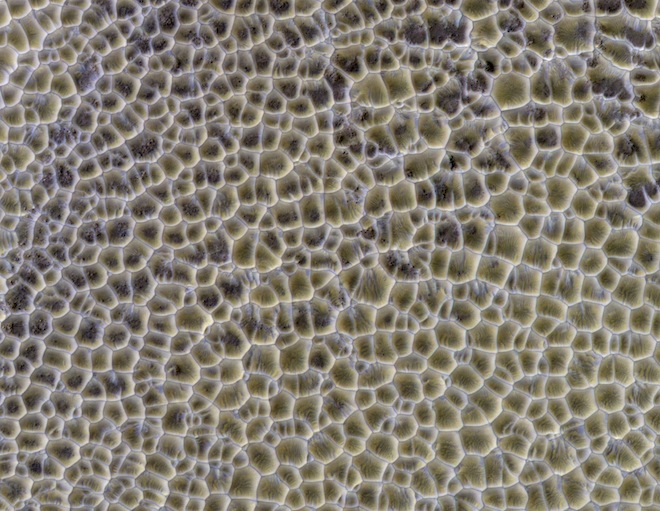
Many images of the Martian surface have confounded scientists, and some of them still do. But some, though they look puzzling and difficult to explain, have more prosaic explanations. The image below is a large area of intersecting sand dunes.
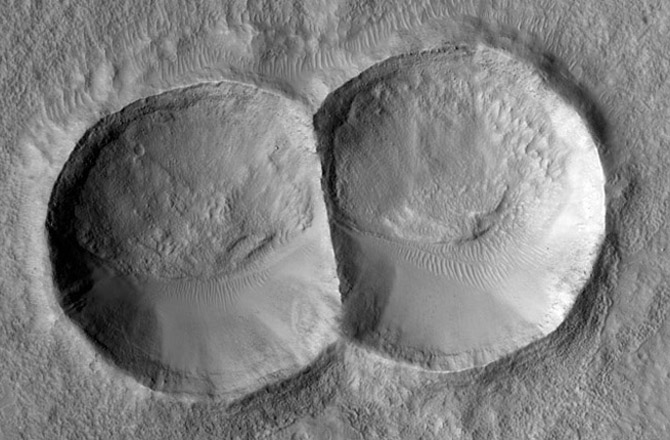
The surface of Mars is peppered with craters, and HiRise has imaged many of them. This double crater was caused by a meteorite that split in two before hitting the surface.
The image below shows gullies and dunes at the Russell Crater. In this image, the field of dunes is about 30 km long. This image was taken during the southern winter, when the carbon dioxide is frozen. You can see the frozen CO2 as white on the shaded side of the ridges. Scientists think that the gullies are formed when the CO2 melts in the summer.
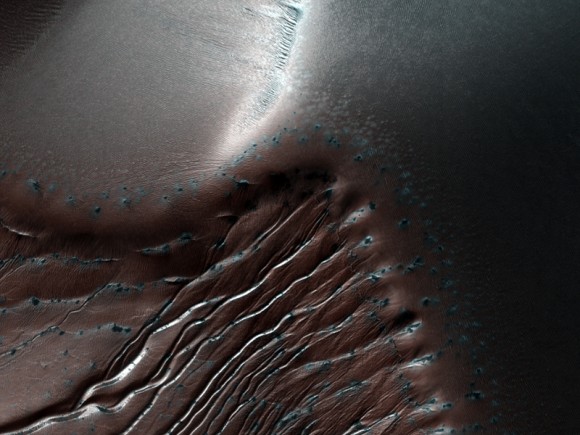
The next image is also the Russell Crater. It’s an area of study for the HiRise team, which means more Russell eye candy for us. This images shows the dunes, CO2 frost, and dust devil tracks that punctuate the area.
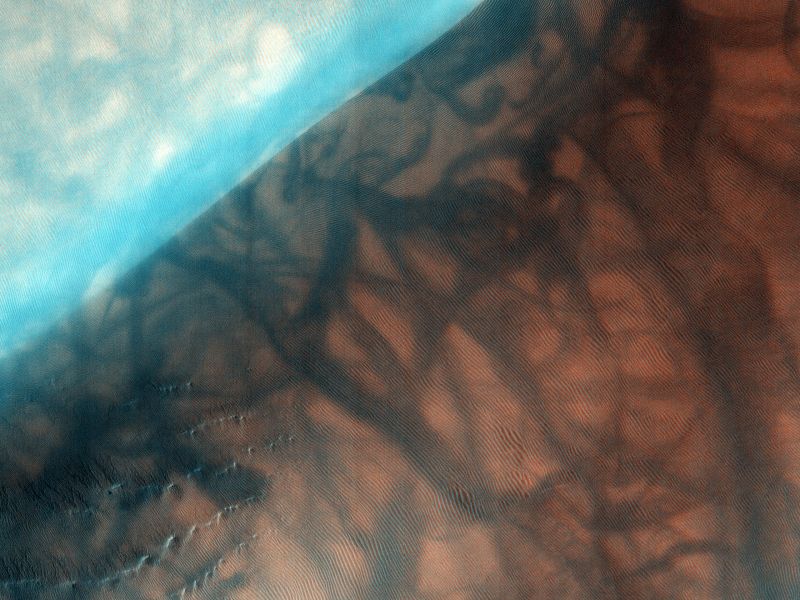

One of the main geological features on Mars is the Valles Marineris, the massive canyon system that dwarfs the Grand Canyon here on Earth. HiRise captured this image of delicate dune features inside Valles Marineris.

The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter is still going strong. In fact, it continues to act as a communications relay for surface rovers. The HiRise camera is along for the ride, and if the past is any indication, it will continue to provide astounding images of Mars.
And we can’t seem to get enough of them.