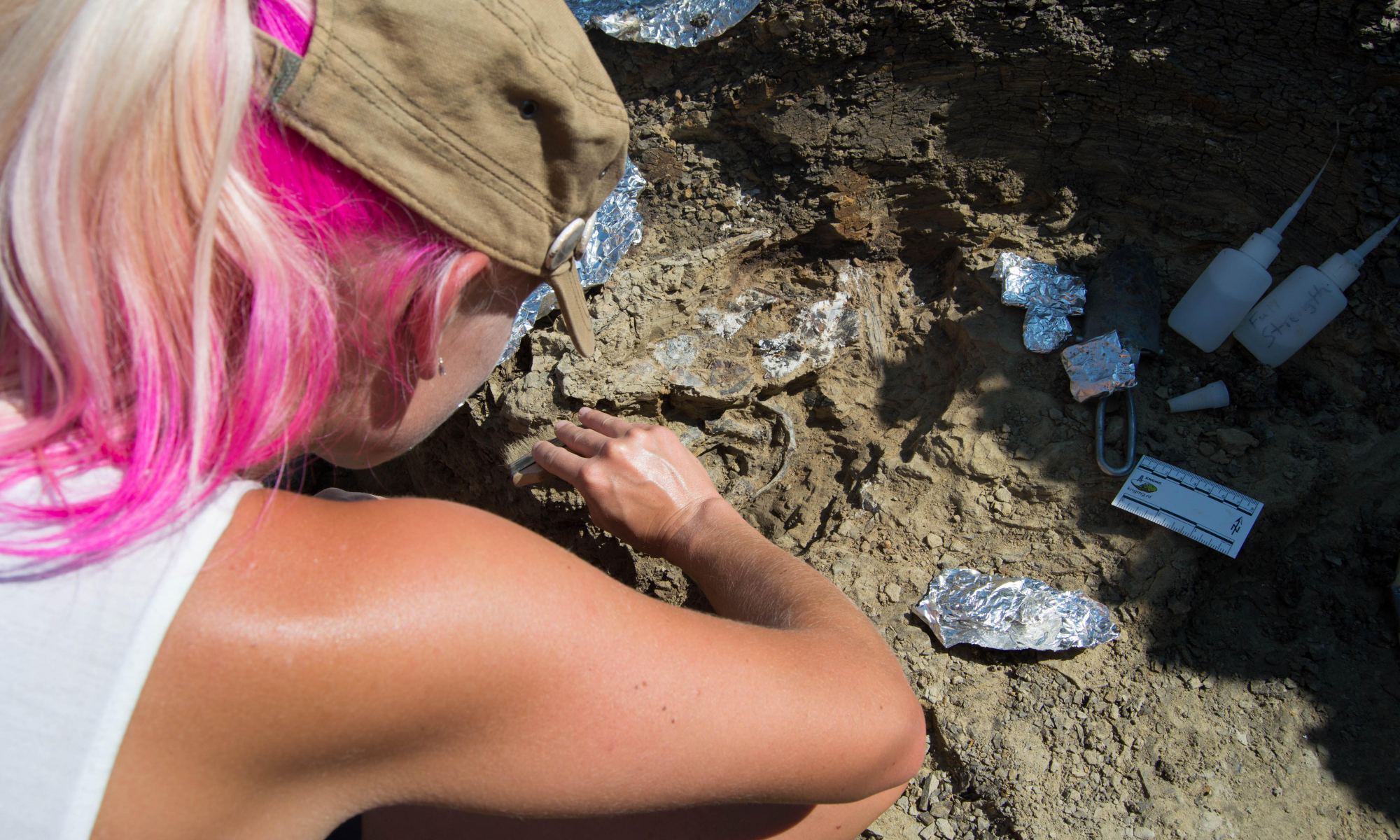
I must confess, I think asteroids and I think of movies like Deep Impact or Armageddon! Scientists think that an asteroid like the ones that appeared in the Hollywood blockbusters struck Mexico 66 million years ago and led to the extinction of the dinosaurs. It now seems they may not have been the only ones that were wiped from our planet. Ammonites are marine mollusks that flourished for 350 million years but they were wiped out too. Some research suggests they were struggling in North America but thriving in other parts of the world.
Continue reading “Ammonites Were Doing Fine Until the Asteroid Hit”Devastating Clouds of Dust Helped End the Reign of the Dinosaurs

When a giant meteor crashed into Earth 66 million years ago, the impact pulverized cubic kilometers of rock and blasted the dust and debris into the Earth’s atmosphere. It was previously believed that sulfur from the impact and soot from the global fires that followed drove a global “impact winter” that killed off 75% of species on Earth, including the dinosaurs.
A new geology paper says that the die-off was additionally fueled by ultrafine dust created by the impact which filled the atmosphere and blocked sunlight for as long as 15 years. Plants were unable to photosynthesize and global temperatures were lowered by 15 degrees C (59 F).
Continue reading “Devastating Clouds of Dust Helped End the Reign of the Dinosaurs”Earth’s First Known Mass Extinction Event Starved Life of Oxygen
650 million years ago, Earth was completely or almost completely frozen, according to the Snowball Earth Hypothesis. As the atmosphere changed and Earth warmed up, it heralded the beginning of the Ediacaran Period. The Ediacaran Period marks the first time multicellular life was widespread on the planet. It predates the more well-known Cambrian Period, when more complex life emerged, diversified, and flourished.
Life during the Ediacaran Period faced a mass extinction, and it was Earth’s first one.
What happened?
Continue reading “Earth’s First Known Mass Extinction Event Starved Life of Oxygen”We don’t Know Exactly When the Dinosaurs Died, but Now We Know it was in the Springtime
We’ve long known a disaster took place about 66 million years ago, where in a geological instant, 75% of the plants and animals on Earth were wiped out, including all the land-roaming dinosaurs. But here’s a new detail about that event: Even though we can’t pinpoint exactly what year this disaster took place, we now know it happened during the springtime.
Continue reading “We don’t Know Exactly When the Dinosaurs Died, but Now We Know it was in the Springtime”Scientists Think They Know What Caused the Deadliest Mass Extinction in the History of the Earth
![This illustration shows the percentage of marine animals that went extinct during Earth's worst extinction at the end of the Permian era by latitude, from the model (black line) and from the fossil record (blue dots).A greater percentage of marine animals survived in the tropics than at the poles. The color of the water shows the temperature change, with red being most severe warming and yellow less warming. At the top is the supercontinent Pangaea, with massive volcanic eruptions emitting carbon dioxide. The images below the line represent some of the 96 percent of marine species that died during the event. [Includes fossil drawings by Ernst Haeckel/Wikimedia; Blue crab photo by Wendy Kaveney/Flickr; Atlantic cod photo by Hans-Petter Fjeld/Wikimedia; Chambered nautilus photo by John White/CalPhotos.]Justin Penn and Curtis Deutsch/University of Washington](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/Penn_sumfig_final.jpg)
Humanity can have a love/hate relationship with itself, but there’s no denying that we’re the pinnacle of evolution on Earth as things stand now. But it took an awfully long time for evolution to produce beings such as we. Several times, life had to drag itself back from near annihilation.
The largest extinction setback was the Permian-Triassic extinction, also called the “Great Dying,” some 252 million years ago. Up to 96% of all marine species and 70% of terrestrial vertebrate species went extinct.
What happened?
Continue reading “Scientists Think They Know What Caused the Deadliest Mass Extinction in the History of the Earth”A New Mass Extinction has been Discovered, Wiping Out Life 233 Million Years Ago, and Leading to the Rise of the Dinosaurs
Most everybody knows that the dinosaurs perished rapidly in a tumultuous extinction, caused by an asteroid strike about 66 million years ago. But it looks like another extinction prior to the appearance of the dinosaurs paved the way for their long reign. That extinction took place about 233 million years ago.
And scientists have only now discovered it.
Continue reading “A New Mass Extinction has been Discovered, Wiping Out Life 233 Million Years Ago, and Leading to the Rise of the Dinosaurs”


