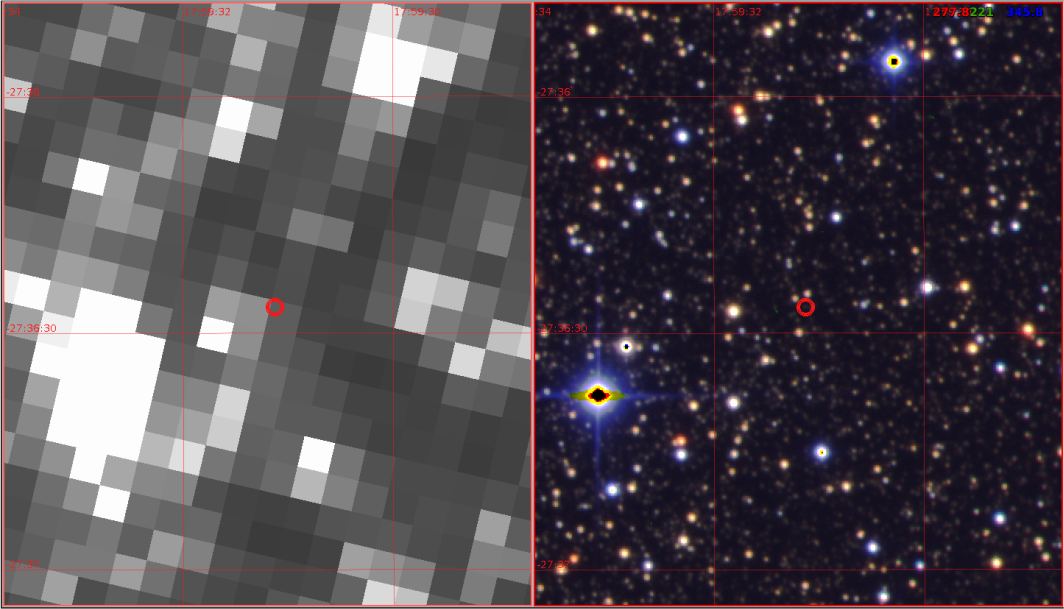
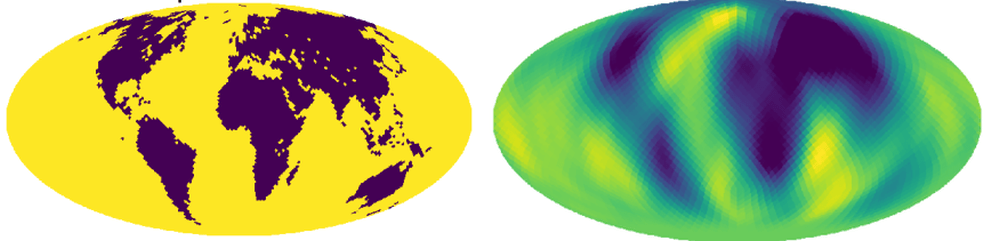
Direct images of exoplanets are rare and lack detail. Future observatories might change that, but for now, exoplanet images don’t tell researchers very much. They merely show the presence of the planets as blobs of light.
But a new study shows that only a few pixels can help us understand an exoplanet’s surface features.
Continue reading “Just a Few Pixels Would let Astronomers Map Surface Features on an Exoplanet Like Oceans and Deserts”