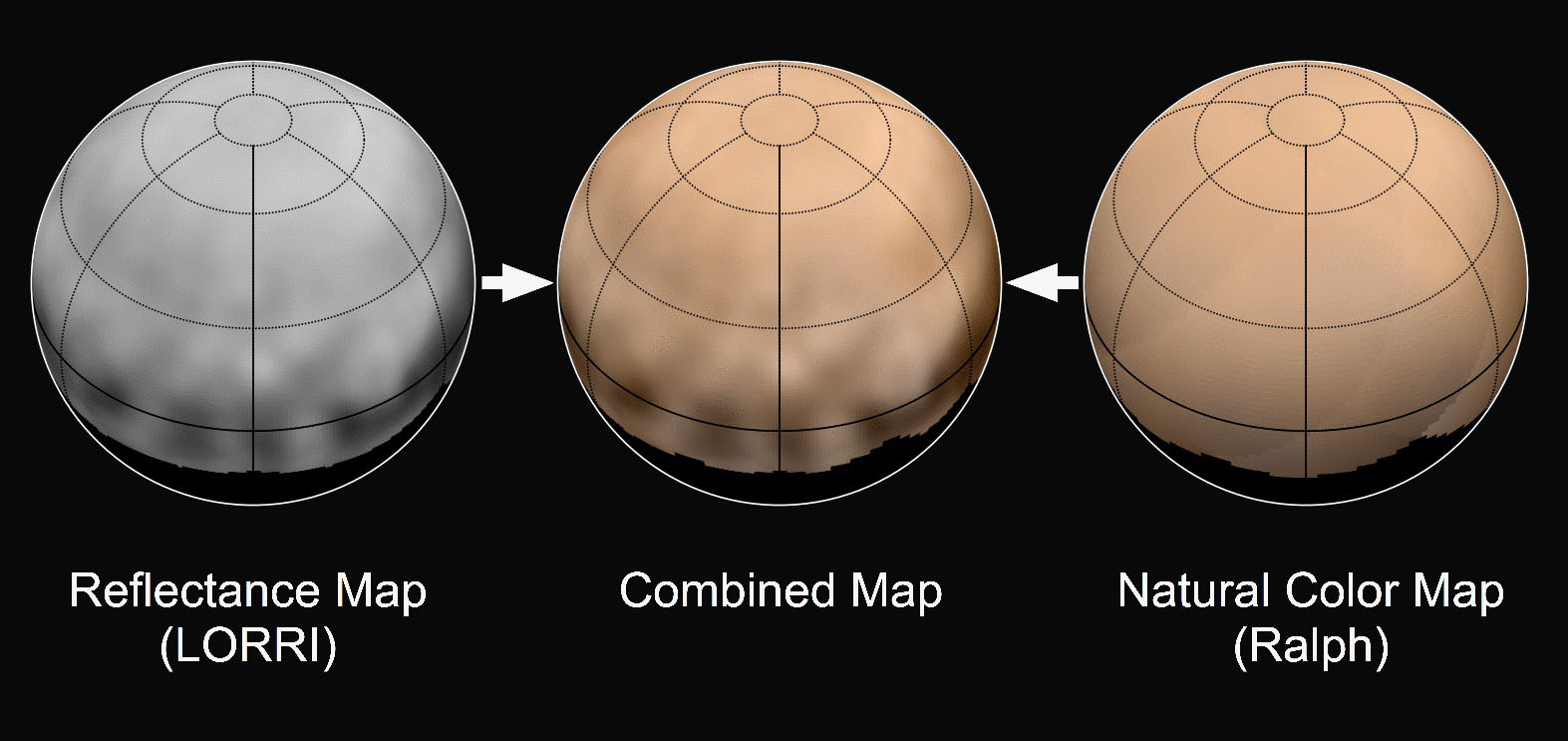
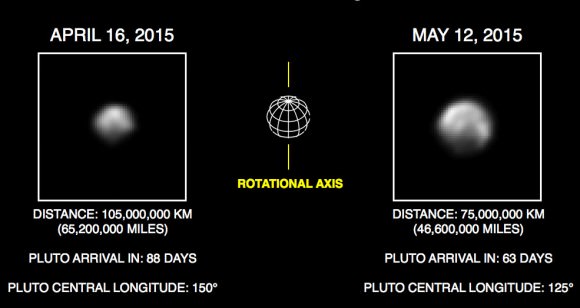
Hey, Mars, you’ve got company. Looks like there’s a second “red planet” in the Solar System — Pluto. Color images returned from NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft, now just 10 days from its encounter with the dwarf planet, show a distinctly ruddy surface with patchy markings that strongly resemble Mars’ appearance in a small telescope.
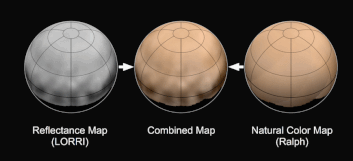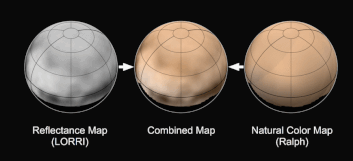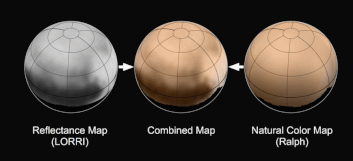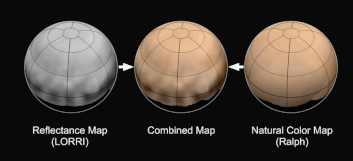
On Mars, iron oxide or rust colors the planet’s soil, while Pluto’s coloration is likely caused by hydrocarbon molecules called tholins that are formed when cosmic rays and solar ultraviolet light interact with methane in Pluto’s atmosphere and on its surface. Airborne tholins fall out of the atmosphere and coat the surface with a reddish gunk.

Credits: Chao He, Xinting Yu, Sydney Riemer, and Sarah Hörst, Johns Hopkins University
A particular color or wavelength of UV light called Lyman-alpha is most effective at stimulating the chemical reactions that build hydrocarbons at Pluto. Recent measurements with New Horizons’ Alice instrument reveal the diffuse glow of Lyman-alpha light all around the dwarf planet coming from all directions of space, not just the Sun.
Since one of the main sources of Lyman-alpha light besides the Sun are regions of vigorous star formation in young galaxies, Pluto’s cosmetic rouge may originate in events happening millions of light years away.

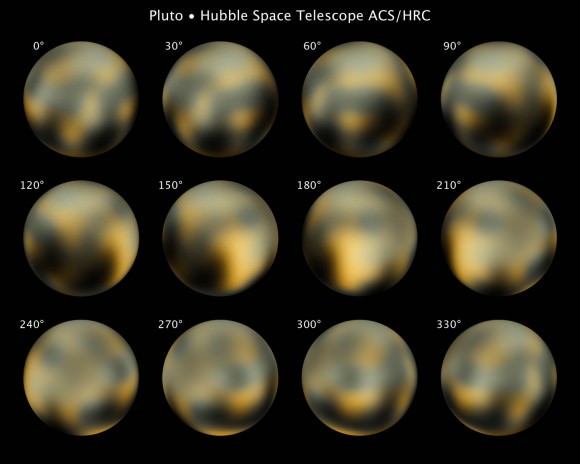
“Pluto’s reddish color has been known for decades, but New Horizons is now allowing us to correlate the color of different places on the surface with their geology and soon, with their compositions,” said New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute, Boulder, Colorado.
Tholins have been found on other bodies in the outer Solar System, including Titan and Triton, the largest moons of Saturn and Neptune, respectively, and made in laboratory experiments that simulate the atmospheres of those bodies.

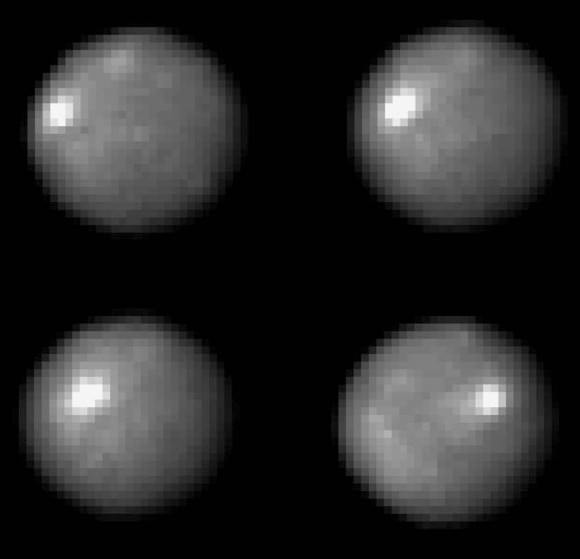
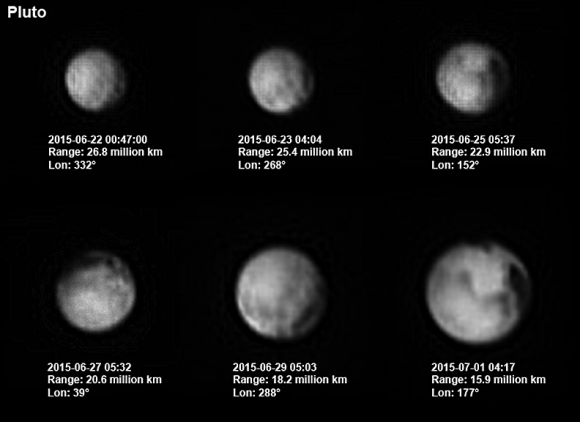
As you study the photos and animation, you’ll notice that Pluto’s largest dark spot is redder than the most of the surface; you also can’ help but wonder what’s going on with those four evenly-spaced dark streaks in the equatorial zone. When I first saw them, my reaction was “no way!” They look so neatly lined up I assumed it was an image artifact, but after seeing the rotating movie, maybe not. It’s more likely that low resolution enhances the appearance of alignment.
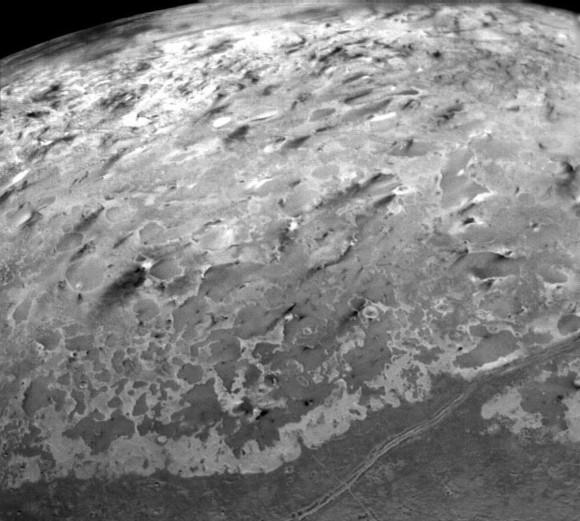
But what are they? Located as they are on the Charon-facing side of Pluto, they may be related to long-ago tidal stresses induced by each body on the other as they slowly settled into their current tidally-locked embrace or something as current as seasonal change.
Voyager 2 photographed cyrovolcanos at Triton during its 1989 flyby of the Neptune system. Nitrogen geysers and plumes of gas and ice as high as 5 miles (8 km) were seen erupting from active volcanoes, leaving dark streaks on its icy surface.


Seasonal heating from the Sun is the most likely cause for Triton’s eruptions; Pluto’s dark streaks may have a similar origin.

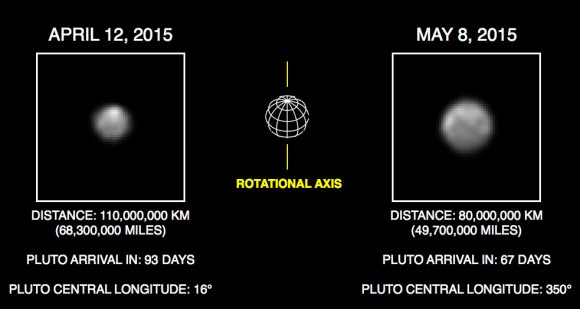
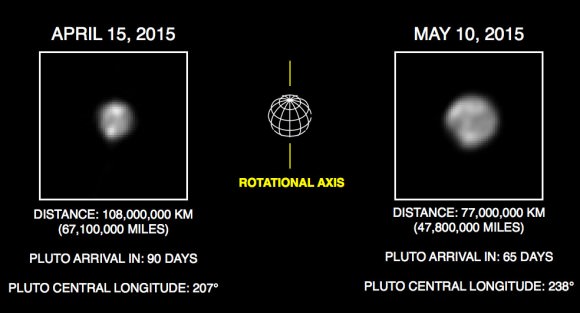
Today, New Horizons lies just 7.4 million miles (11.9 million km) from its target. Sharpness and detail visible will rapidly improve in just a few days.
“Even at this resolution, Pluto looks like no other world in our Solar System,” said mission scientist Marc Buie of the Southwest Research Institute, Boulder in a recent press release.
Indeed!