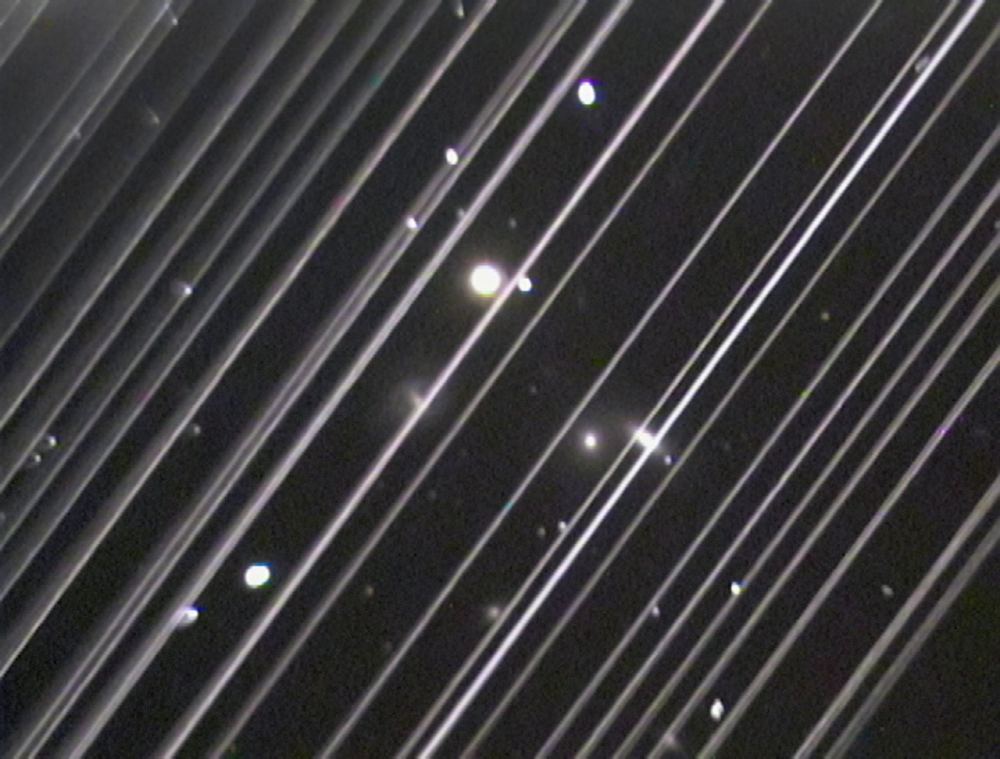
New research has found that as the number of satellites in Earth orbit continues to increase, their accumulated light pollution will brighten the night sky – making it much harder to do fundamental astronomy.
Continue reading “Satellites Have Brightened the Skies by About 10% Across the Entire Planet”Satellites Have Brightened the Skies by About 10% Across the Entire Planet