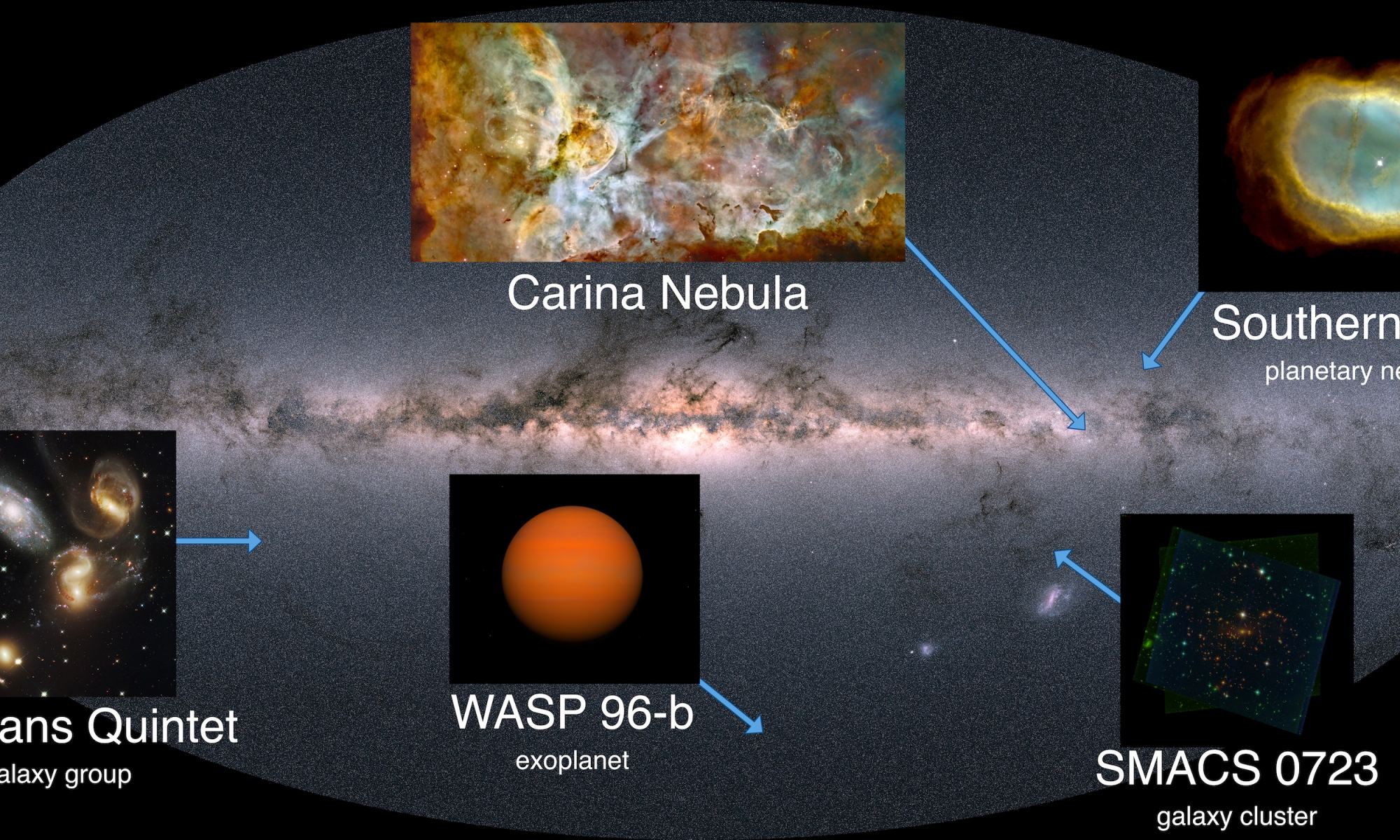
On the morning of Tuesday, July 12th, the world was treated to the first images captured by the James Webb Space Telescope – the most detailed images of the cosmos taken by the most powerful telescope ever! These featured familiar features from our galaxy, including updated images of the Carina Nebula, a nebula surrounding a stellar remnant (the Southern Ring), a collection of merging galaxies (Stephans Quintet), an exoplanet (WASP 96b), and a deep field image showing thousands of galaxies and gravitational lenses (SMACS 0723).
In anticipation of these images being released, a helpful space exploration ambassador shared a map that shows where these objects are located within (or in relation to) the Milky Way. The map was uploaded to the Reddit group Space on July 10th (two days before image release day) and is the work of data scientist Tony Rice (user name u/rtphokie). Rice is an information security engineer for a telecommunications company and a Solar System Ambassador with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Continue reading “Here are the Locations in the sky for the First JWST Images”