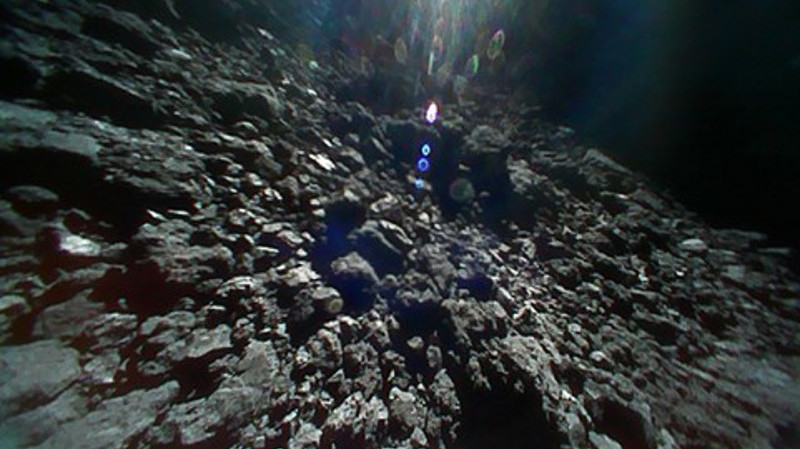
In December of 2014, the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) launched the Hayabusa2 mission. As the second spacecraft to bear this name, Hayabusa2 was deployed by JAXA to conduct a sample-return mission with an asteroid. By studying samples of the near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, scientists hope to shed new light on the history of the early Solar System
The spacecraft arrived in orbit around Ryugu in July of 2018, where it will spend a total of a year and a half surveying the asteroid before returning to Earth. On September 23rd, the satellite deployed its onboard MINERVA-II rovers onto the surface of Ryugu. According to the latest updates from JAXA, both rovers are in good condition and have recently sent back photographs and a video of the asteroid’s surface.