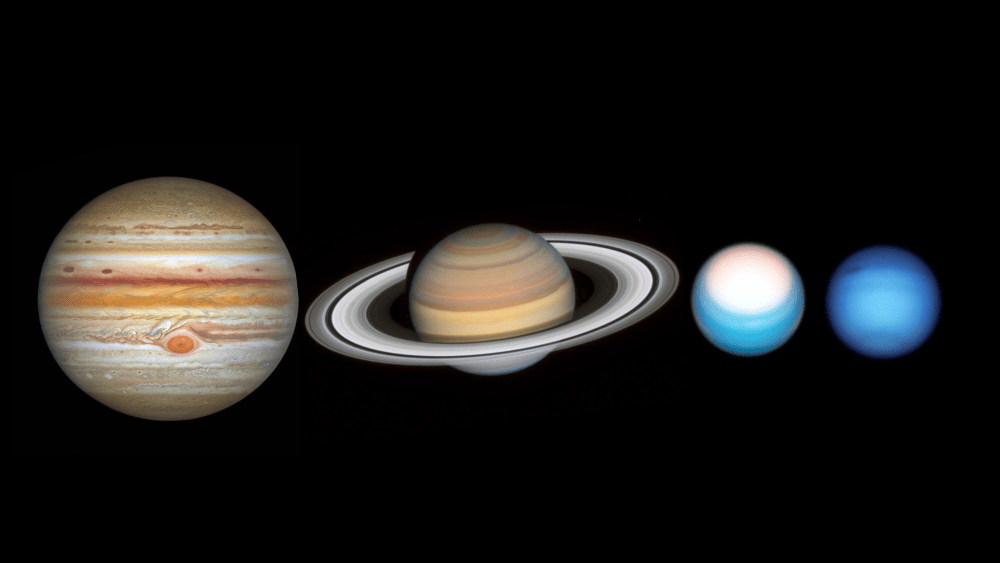
If we had to rely solely on spacecraft to learn about the outer planets, we wouldn’t be making great progress. It takes a massive effort to get a spacecraft to the outer Solar System. But thanks to the Hubble Space Telescope, we can keep tabs on the gas giants without leaving Earth’s orbit.
Continue reading “Here are Hubble’s 2021 Photos of the Outer Solar System”Here are Hubble’s 2021 Photos of the Outer Solar System