We found our first exoplanets orbiting a pulsar in 1992. Since then, we’ve discovered many thousands more. Those were the first steps in identifying other worlds that could harbour life.
Now planetary scientists want to take the next step: studying exoplanet atmospheres.
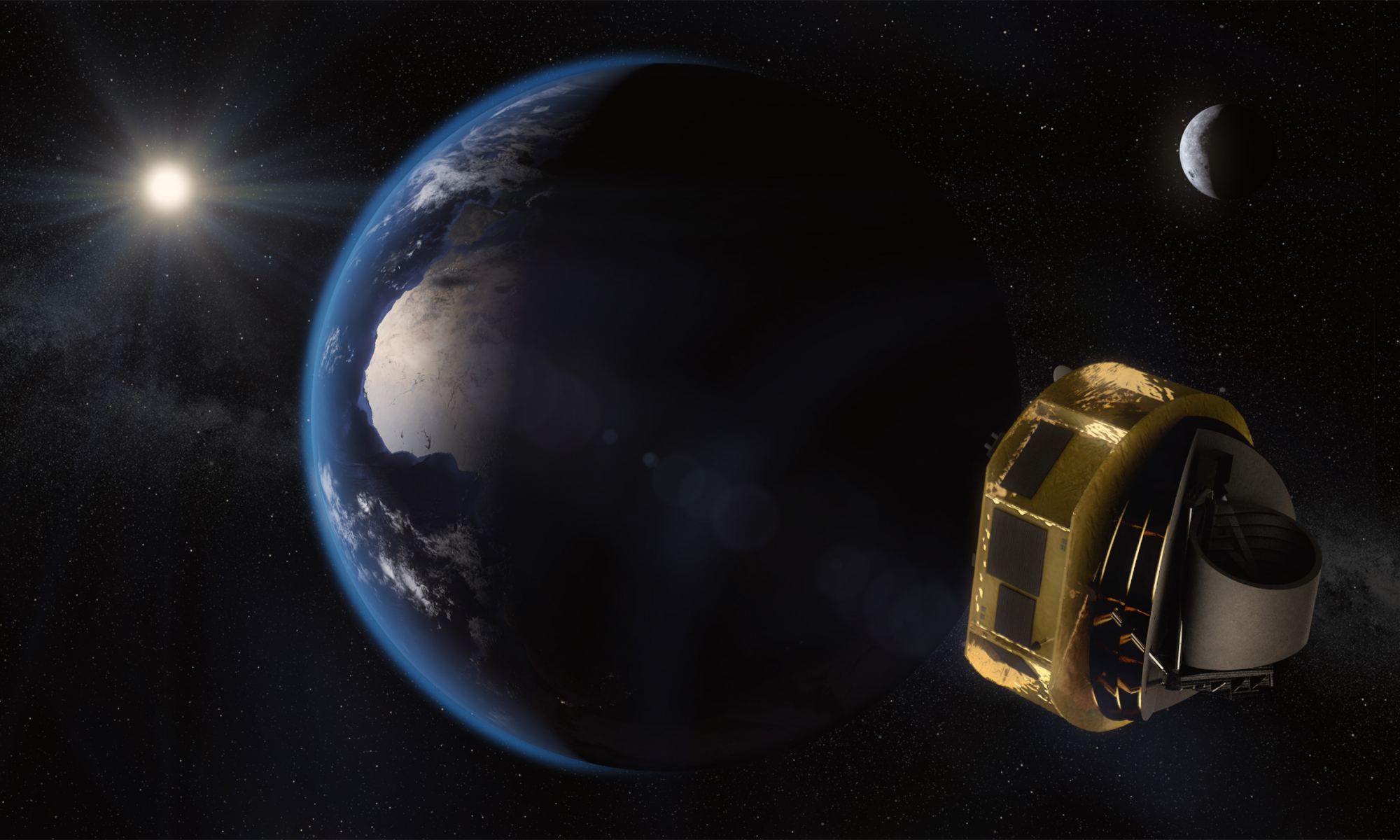
The ESA’s ARIEL mission will be a powerful tool.
Continue reading “ESA’s ARIEL Mission Will Study the Atmospheres of More Than 1,000 Exoplanets”