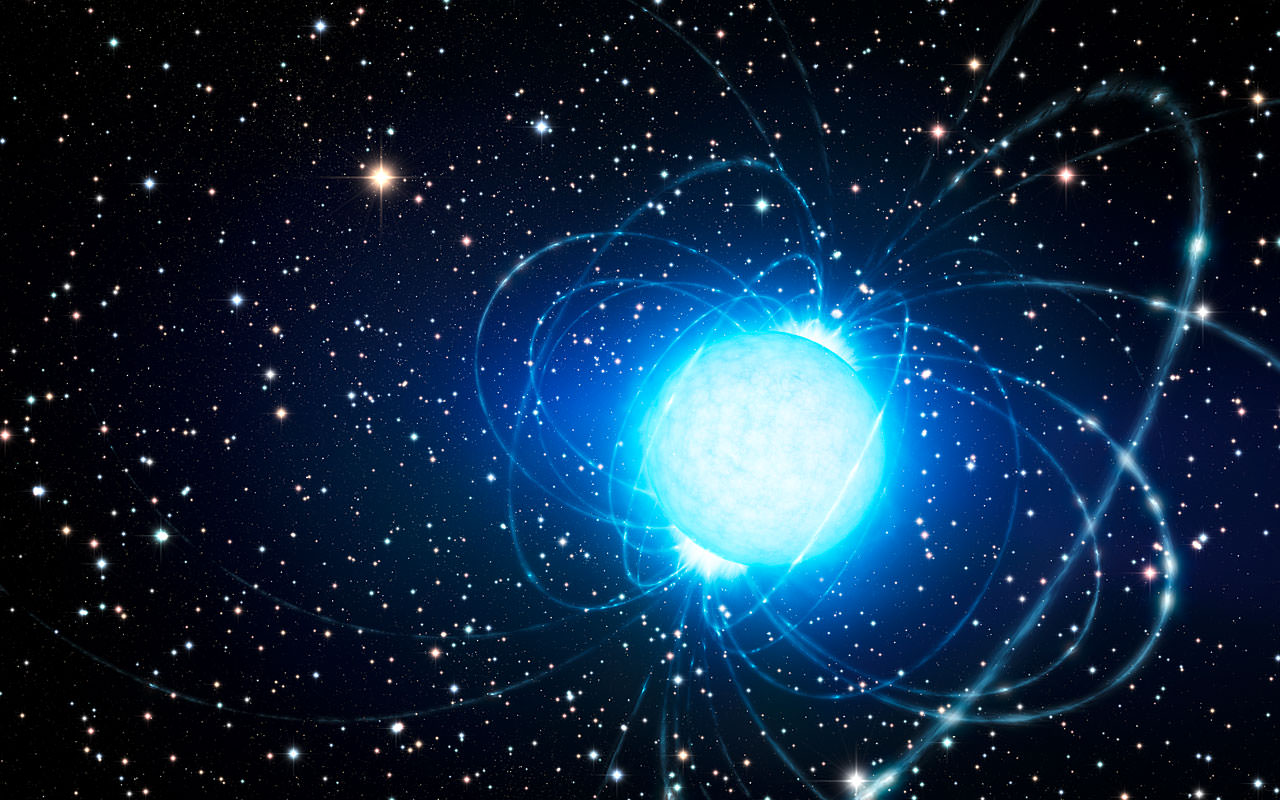
Can a star have a solid surface? It might sound counterintuitive. But human intuition is a response to our evolution on Earth, where up is up, down is down, and there are three states of matter. Intuition fails when it confronts the cosmos.
Continue reading “New Observations Confirm That a Magnetar has a Solid Surface and No Atmosphere”New Observations Confirm That a Magnetar has a Solid Surface and No Atmosphere