The all-female astronaut walk is back on.
Back on March 26th, 2019, NASA was forced to cancel the first all-female spacewalk because they didn’t have the right spacesuits available on the ISS. There was a short-lived social media storm over that development, as some claimed it was evidence of sexism on the part of NASA. But that small storm didn’t have legs and it died out, because no serious-minded observer thinks that NASA is actually sexist.
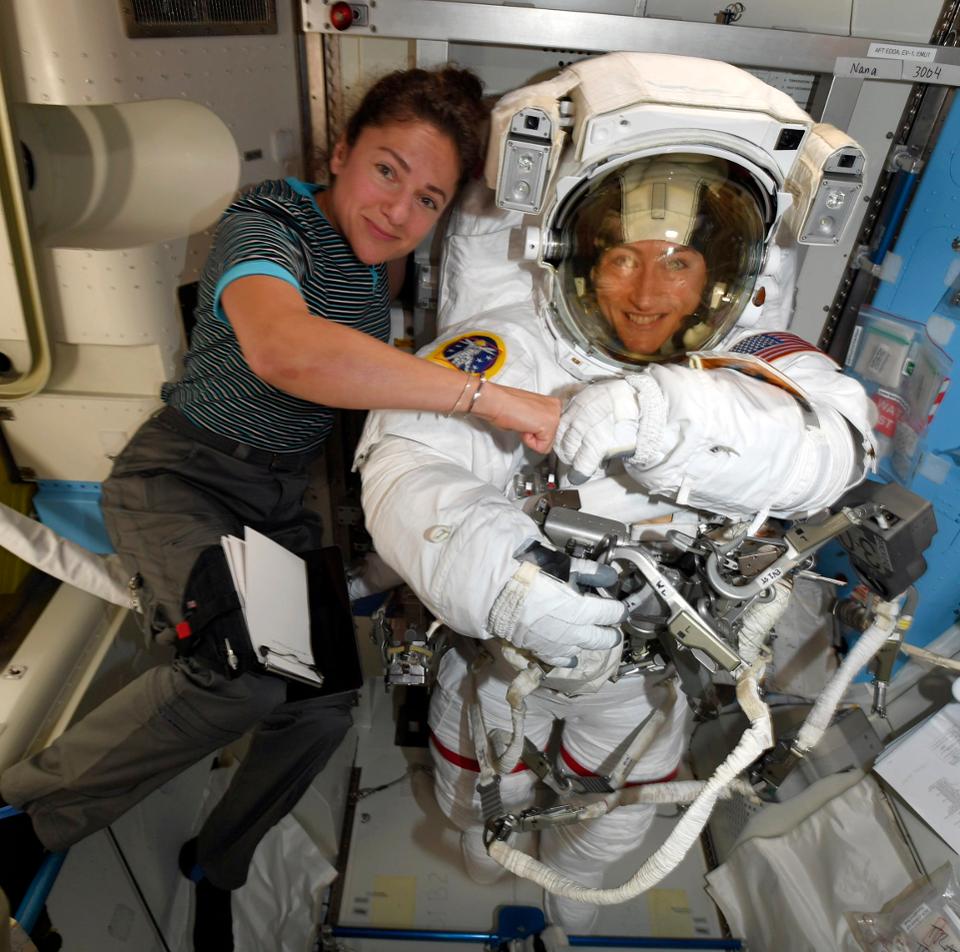
Now, the problem has been worked out, and the spacewalk will happen on October 21st, when astronauts Christina Koch and Jessica Meir will walk outside the ISS and install new lithium-ion batteries. Theirs is the first of five walks needed to complete the installation.
Continue reading “They’ve Got Spacesuits that Fit Now. Christina Koch and Jessica Meir Will Spacewalk on October 21st”