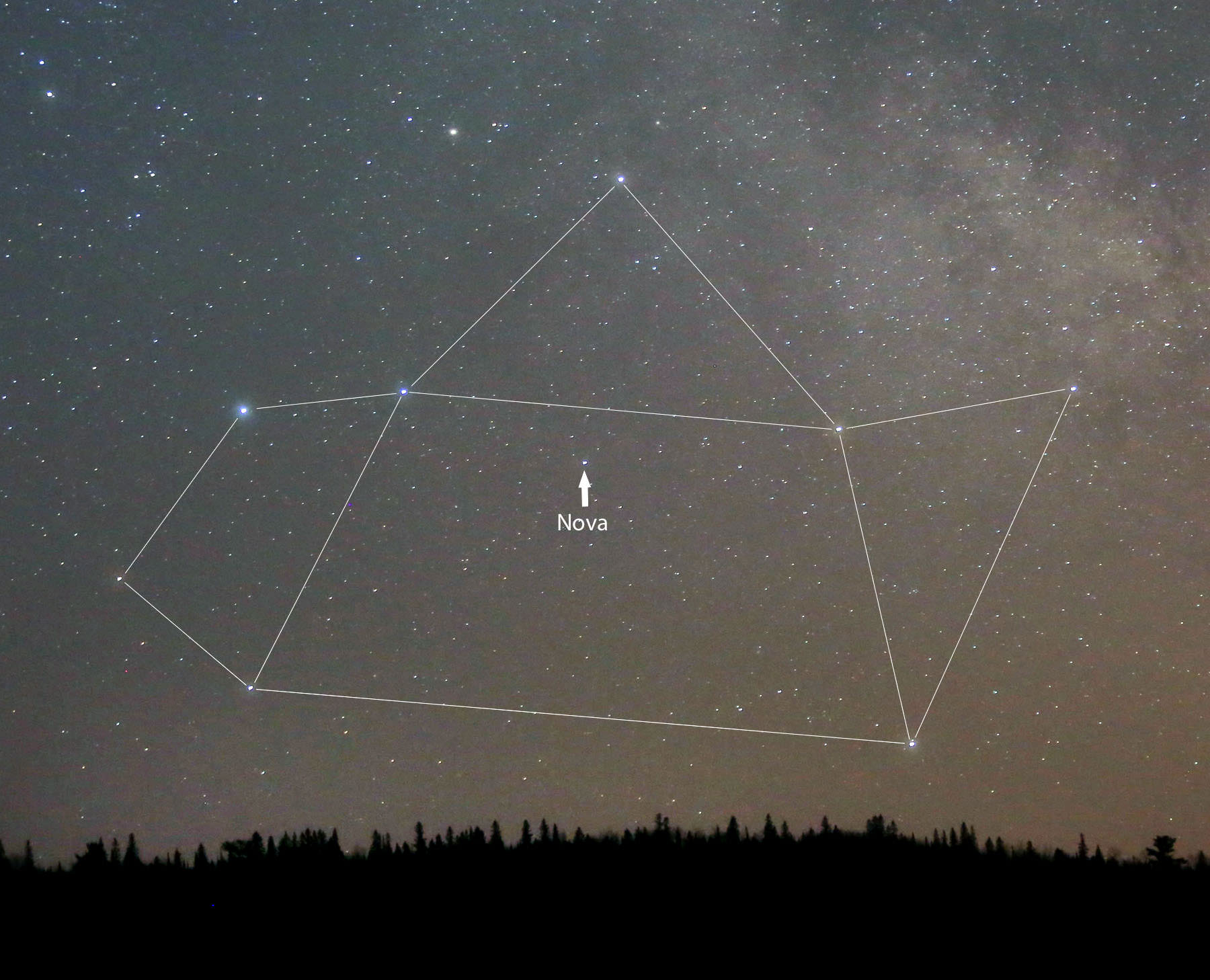
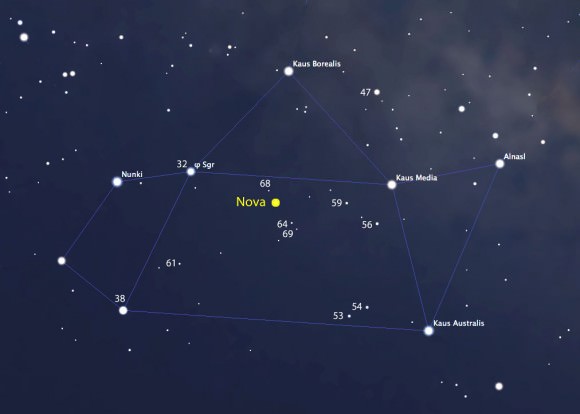
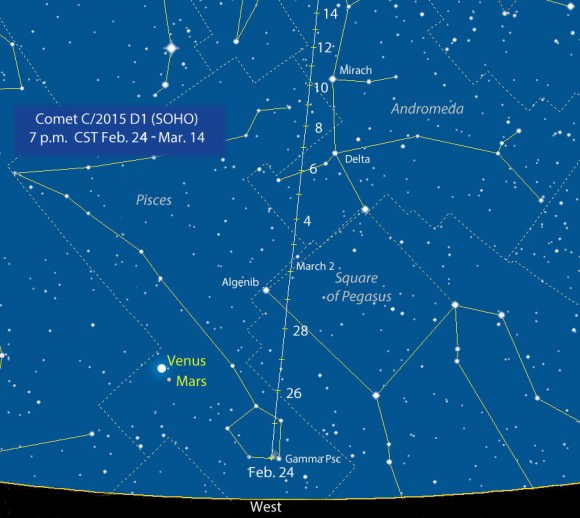
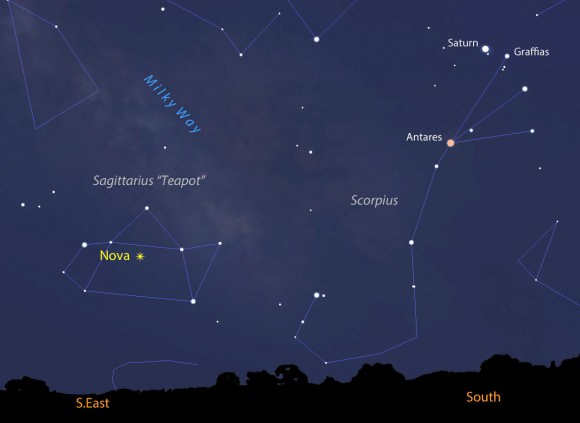
Great news about that new nova in Sagittarius. It’s still climbing in brightness and now ranks as the brightest nova seen from mid-northern latitudes in nearly two years. Even from the northern states, where Sagittarius hangs low in the sky before dawn, the “new star” was easy to spy this morning at magnitude +4.4.
While not as rare as hen’s teeth, novae aren’t common and those visible without optical aid even less so. The last naked eye nova seen from outside the tropics was V339 Del (Nova Delphini), which peaked at +4.3 in August 2013. The new kid on the block could soon outshine it if this happy trend continues.
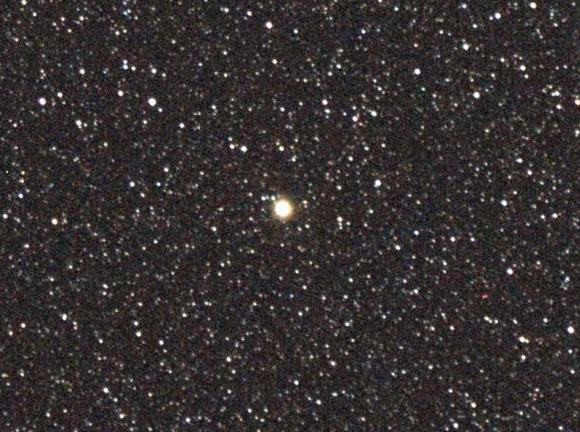
Now bearing the official title of Nova Sagittarii 2015 No. 2, the nova was discovered on March 15 by amateur astronomer and nova hunter John Seach of Chatsworth Island, NSW, Australia. At the time it glowed at the naked eye limit of magnitude +6. Until this morning I wasn’t able to see it with the naked eye, but from a dark sky site, it’s there for the picking. So long as you know exactly where to look.
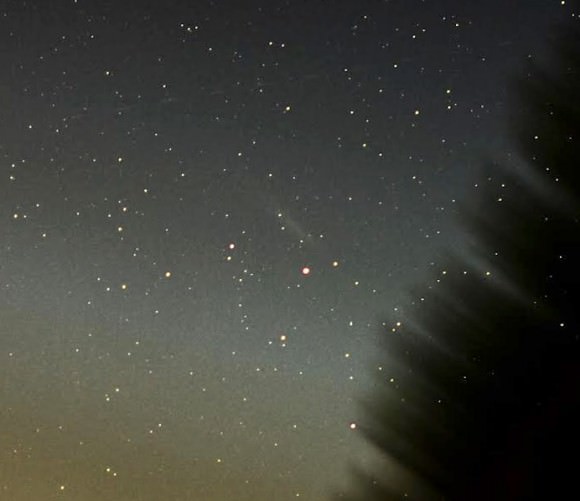
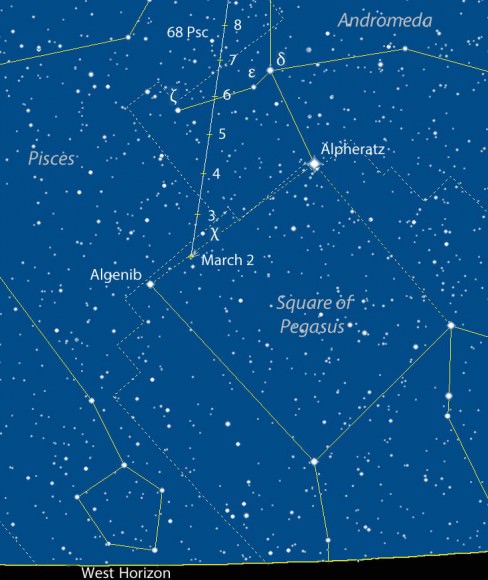
The chart and photo above will help guide you there. At the moment, the star’s about 15° high at dawn’s start, but it rises a little higher and becomes easier to see with each passing day. Find your sunrise time HERE and then subtract an hour and 45 minutes. That will bring you to the beginning of astronomical twilight, an ideal time to catch the nova at its highest in a dark sky.
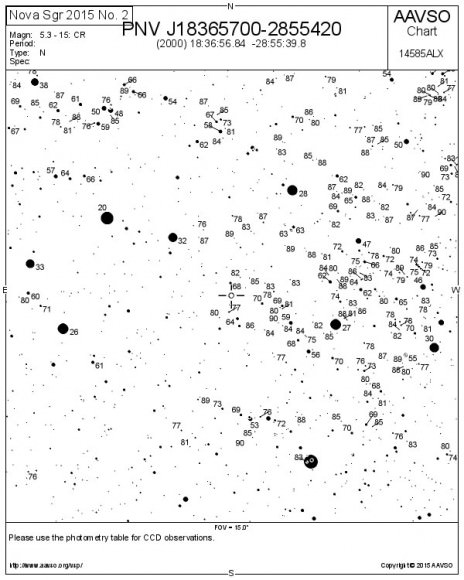
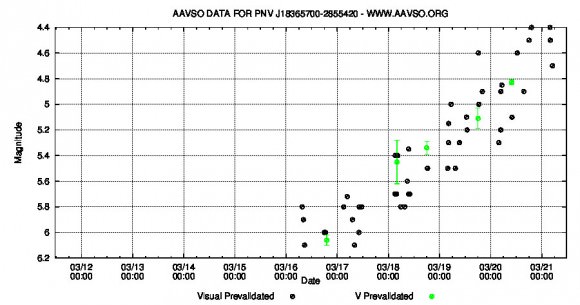
To see it with the naked eye, identify the star with binoculars first and then aim your gaze there. I hope you’ll be as pleasantly surprised as I was to see it. To check on the nova’s ups and downs, drop by the American Association Variable Star Observers (AAVSO) list of recent observations.
Seeing the nova without optical aid took me back to the time before the telescope when a “new star” in the sky would have been met with great concern. Changes in the heavens in that pre-telescopic era were generally considered bad omens. They were also thought to occur either in Earth’s atmosphere or within the Solar System. The universe has grown by countless light years since then. Nowadays we sweat the small stuff – unseen asteroids – which were unknown in that time.
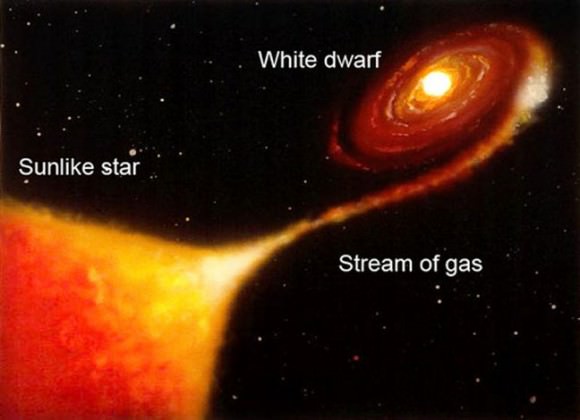
Novae occur in binary star systems where a tiny but gravitationally powerful white dwarf star pulls gases from a close companion star. The material piles up in a thin layer on the dwarf’s hot surface, fuses and burns explosively to create the explosion we dub a nova. Spectra of the expanding debris envelope reveal the imprint of hydrogen gas and as well as ionized iron.

Shortly after discovery, the nova’s debris shell was expanding at the rate of ~1,740 miles per second (2,800 km/sec) or more than 6.2 million mph (10 million mph). It’s since slowed to about half that rate. Through a telescope the star glows pale yellow but watch for its color to deepen to yellow orange and even red. Right now, it’s still in the fireball phase, with the dwarf star hidden by an envelope of fiery hydrogen gas.
As novae evolve, they’ll often turn from white or yellow to red. Emission of deep red light from hydrogen atoms – called hydrogen alpha – gives them their warm, red color. Hydrogen, the most common element in stars, gets excited through intense radiation or collisions with atoms (heat) and re-emits a ruby red light when it returns to its rest state. Astronomers see the light as bright red emission line in the star’s spectrum. Spectra of the nova show additional emission lines of hydrogen beta or H-beta (blue light emitted by hydrogen) and iron.
There are actually several reasons why novae rouge up over time, according to former AAVSO director Arne Henden:
“Energy from the explosion gets absorbed by the surrounding material in a nova and re-emitted as H-alpha,” said Henden. Not only that but as the explosion expands over time, the same amount of energy is spread over a larger area.
“The temperature drops,” said Henden, “causing the fireball to cool and turn redder on its own.” As the eruption expands and cools, materials blasted into the surrounding space condense into a shell of soot that absorbs that reddens the nova much the same way dusty air reddens the Sun.
Nova Sagittarii’s current pale yellow color results from seeing a mix of light – blue from the explosion itself plus red from the expanding fireball. As for its distance from Earth, I haven’t heard, but given that the progenitor star was 15th magnitude or possibly fainter, we’re probably talking in the thousands of light years.
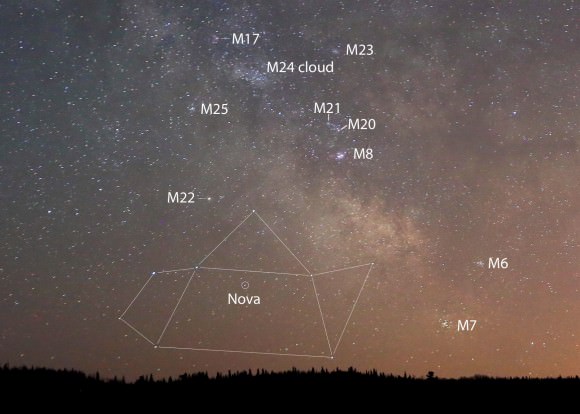
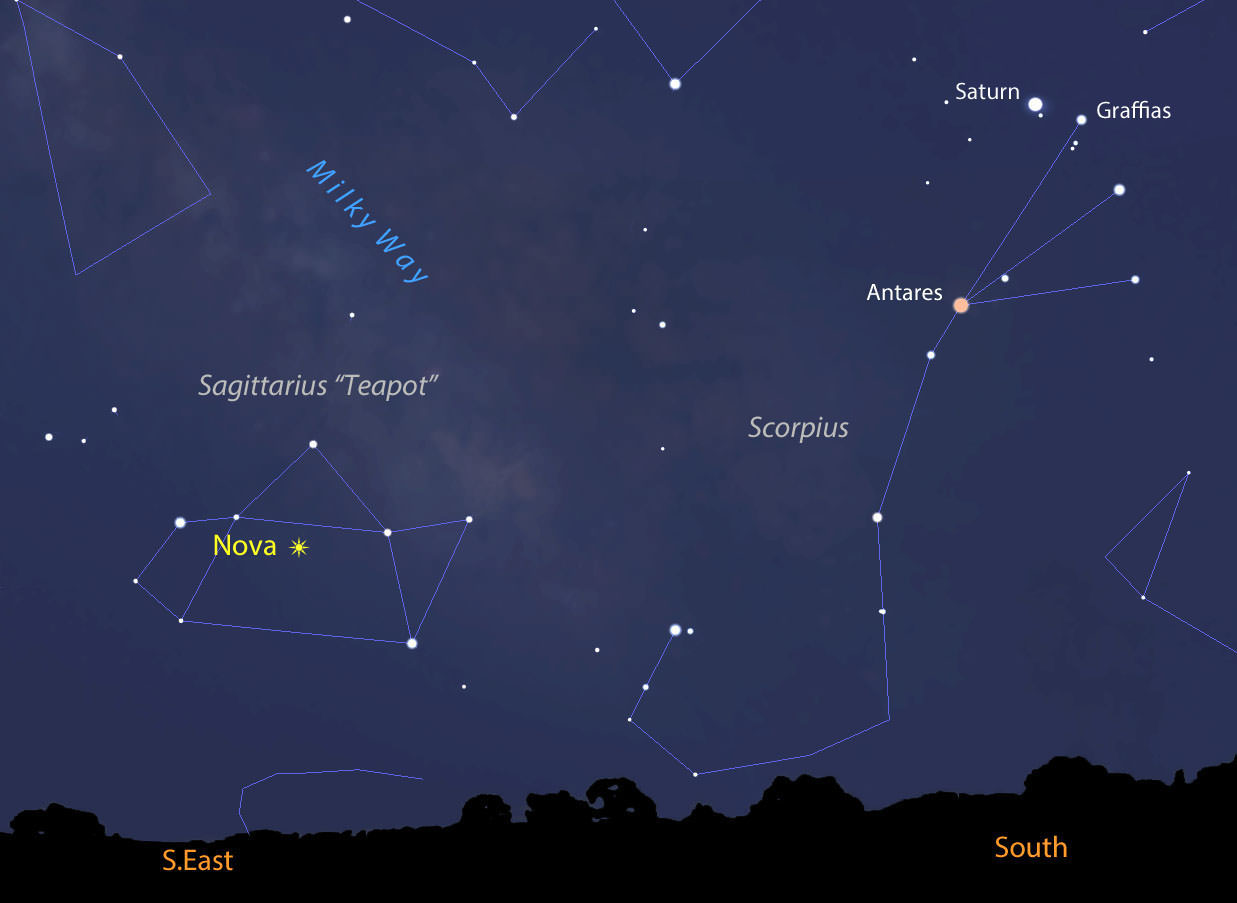
In an earlier article on the nova’s discovery I mentioned taking a look at Saturn as long as you made the effort the get up early. Here’s a photo of the Sagittarius region you can use to help you further your dawn binocular explorations. The entire region is rich with star clusters and nebula, many of which were cataloged long ago by French astronomer Charles Messier, hence the “M” numbers.