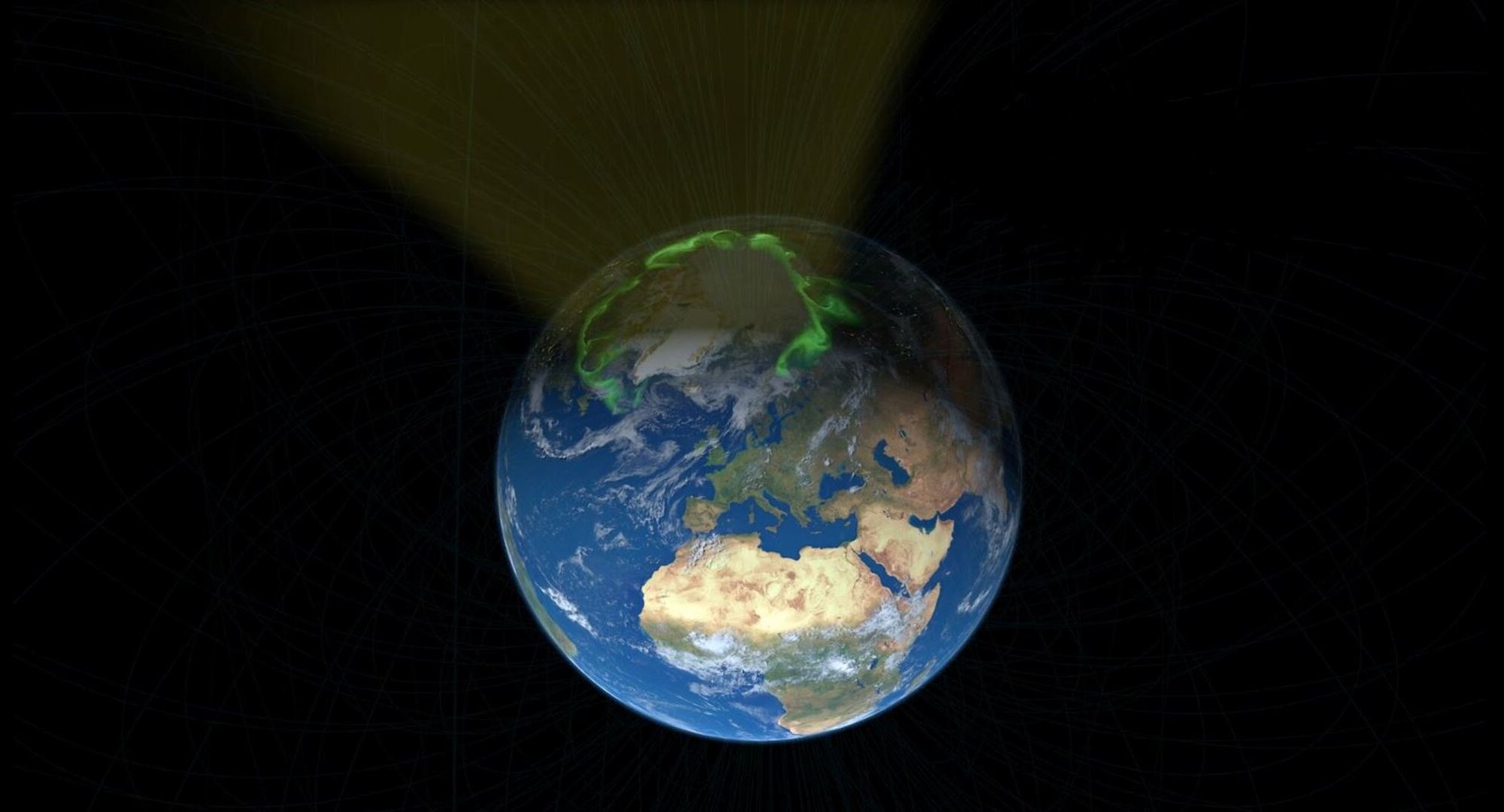
Likely the most well-known result of the Earth’s magnetic field are the Aurora Borealis and Australis (Northern and Southern Lights). When chargers particles from the solar wind run into the Earth’s magnetic field, they can occasionally elicit spectacular light displays. For years now, scientists have thought that the charged particles that cause those displays were sent in equal numbers toward the north and south pole. However, recent research from a team led by scientists from the University of Alberta, have shown that there are actually more charged particles heading north rather than south. The question now is why?
Continue reading “The Solar Wind is More Attracted to the Earth’s North Pole Than the South. Why?”The Magnetic Fields Swirling Within the Whirlpool Galaxy
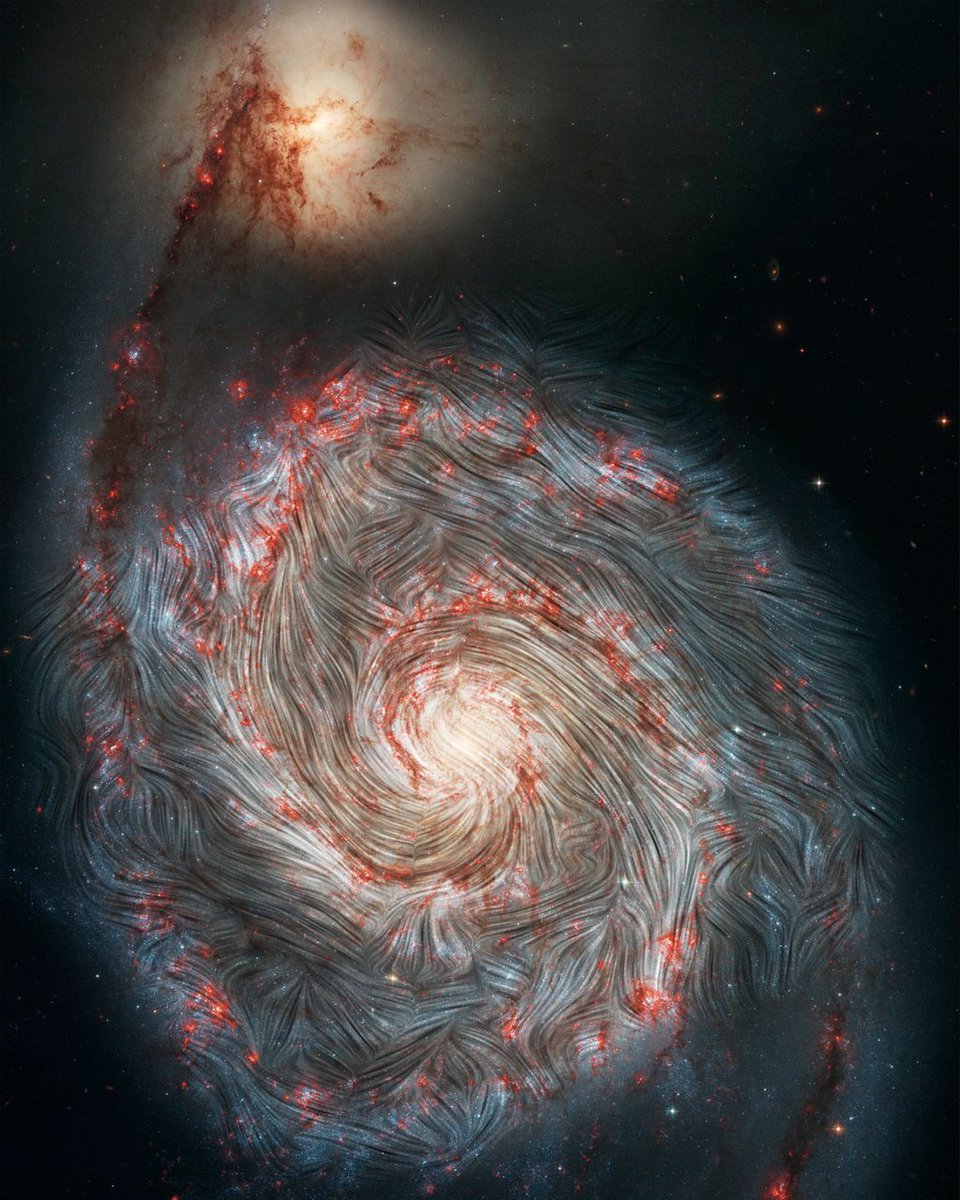
Messier objects are some of the most imaged objects in the universe. In part that’s because many of them are so visibly appealing. A good example of that is the Whirlpool galaxy, M51, which recently received an even more dramatic visual representation with a new photo released by NASA. In it, the magnetic fields that are holding the galaxy together and tearing it apart at the same time are clearly visible. And it is even more stunning to look at.
Continue reading “The Magnetic Fields Swirling Within the Whirlpool Galaxy”The First Cubesat With a Hall-Effect Thruster has Gone to Space
Student-led teams aren’t the only ones testing out novel electric propulsion techniques recently. Back in November, a company called Exotrail successfully tested a completely new kind of electric propulsion system in space – a small hall-effect thruster.
Continue reading “The First Cubesat With a Hall-Effect Thruster has Gone to Space”A New Satellite Is Going to Try to Maintain Low Earth Orbit Without Any Propellant
Staying afloat in space can be deceptively hard. Just ask the characters from Gravity, or any number of the hundreds of small satellites that fall into the atmosphere in a given year. Any object placed in low Earth orbit (LEO) must constantly fight against the drag caused by the small number of air molecules that make it up to that height.
Usually they counteract this force by using small amounts of propellant. However, smaller satellites don’t have the luxury of enough propellant to keep them afloat for any period of time. But now a team of students from the University of Michigan has launched a prototype satellite that attempts to stay afloat using a novel technique – magnetism.
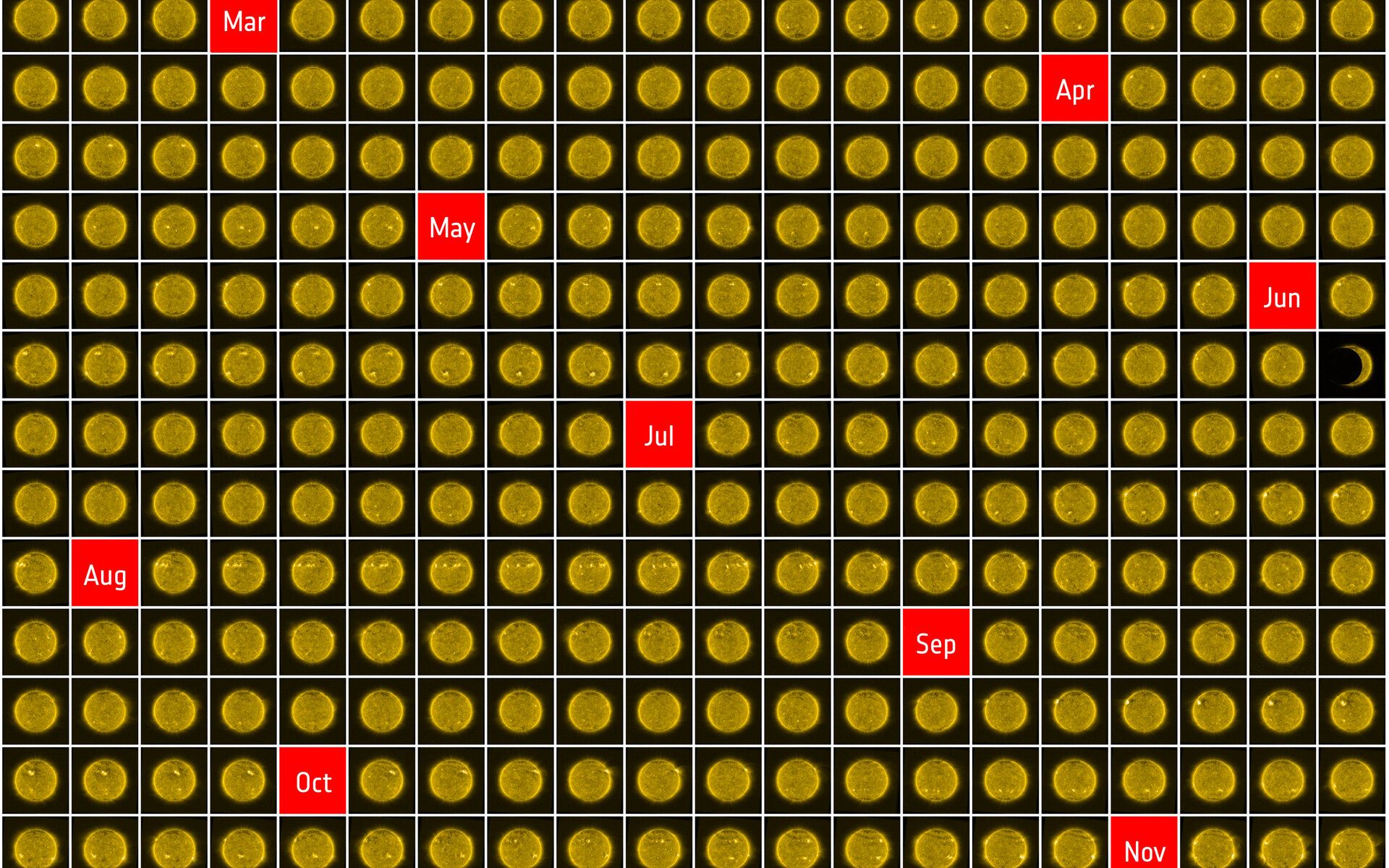
Continue reading “A New Satellite Is Going to Try to Maintain Low Earth Orbit Without Any Propellant”This is What the Sun Looked Like for Every Day in 2020
Have you ever seen the videos of people taking daily selfies of themselves over the course of years or even decades? Now the sun has started it’s own series of pictures – with 366 complete pictures from the year 2020, captured by the European Space Agency’s Proba-2 satellite.
Continue reading “This is What the Sun Looked Like for Every Day in 2020”Planetary Scientists Have Created a Map of Mars’ Entire Ancient River Systems
Navigating and mapping rivers has long been a central component in human exploration. Whether it was Powell exploring the Colorado’s canyons or Pizarro using the Amazon to try to find El Dorado, rivers, and our exploration of them, have been extremely important. Now, scientists have mapped out an entirely new, unique river basin. This one happens to be on an entirely different planet, and dried up billions of years ago.
Continue reading “Planetary Scientists Have Created a Map of Mars’ Entire Ancient River Systems”Astronomers Capture a Direct Image of a Brown Dwarf
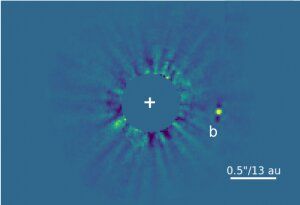
The field of exoplanet photography is just getting underway, with astronomers around the world striving to capture clear images of the more than 4000 exoplanets discovered to date. Some of these exoplanets are more interesting to image and research than others. That is certainly the case for a type of exoplanet called a brown dwarf. And now scientists have captured the first ever image of exactly that type of exoplanet.
Continue reading “Astronomers Capture a Direct Image of a Brown Dwarf”To Help Trudge Through the Snow, the Chang’e-5 Recovery Team Wore Powered Exoskeletons
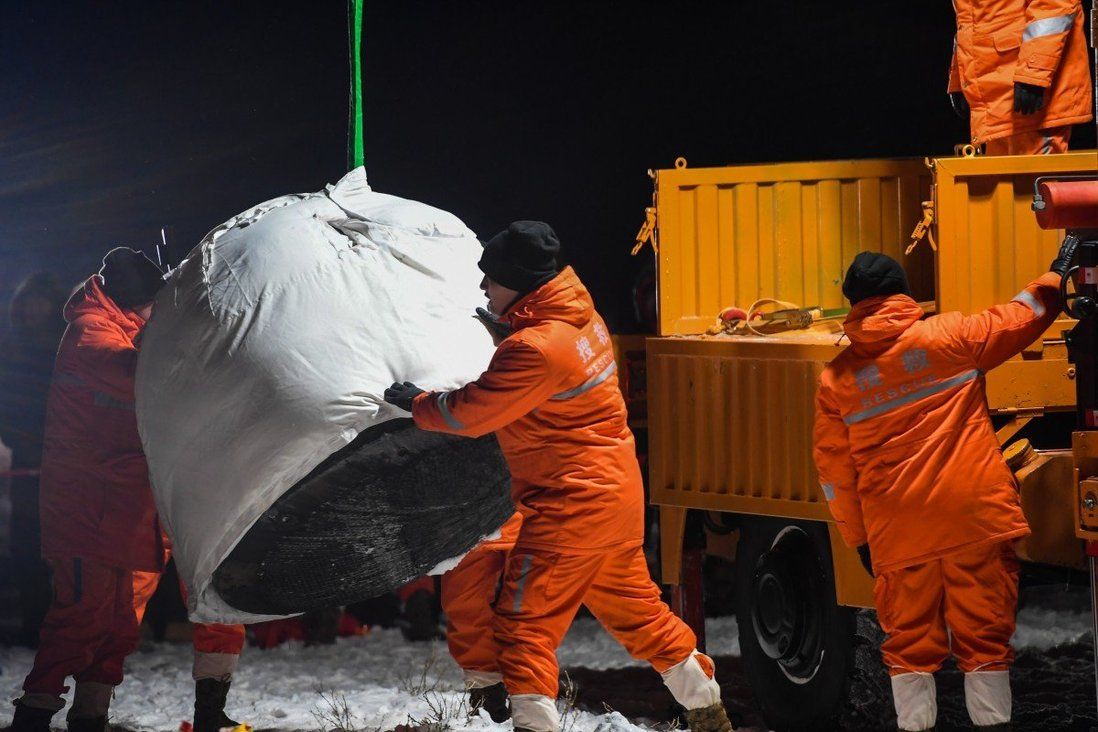
Other worlds aren’t the only difficult terrain personnel will have to traverse in humanity’s exploration of the solar system. There are some parts of our own planet that are inhospitable and hard to travel over. Inner Mongolia, a northern province of China, would certainly classify as one of those areas, especially in winter. But that’s exactly the terrain team members from the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASTC) had to traverse on December 16th to retrieve lunar samples from the Chang’e-5 mission. What was even more unique is that they did it with the help of exoskeletons.
Continue reading “To Help Trudge Through the Snow, the Chang’e-5 Recovery Team Wore Powered Exoskeletons”One of the Largest, Most Complete Einstein Rings Ever Seen. Astronomers Call it the “Molten Ring”
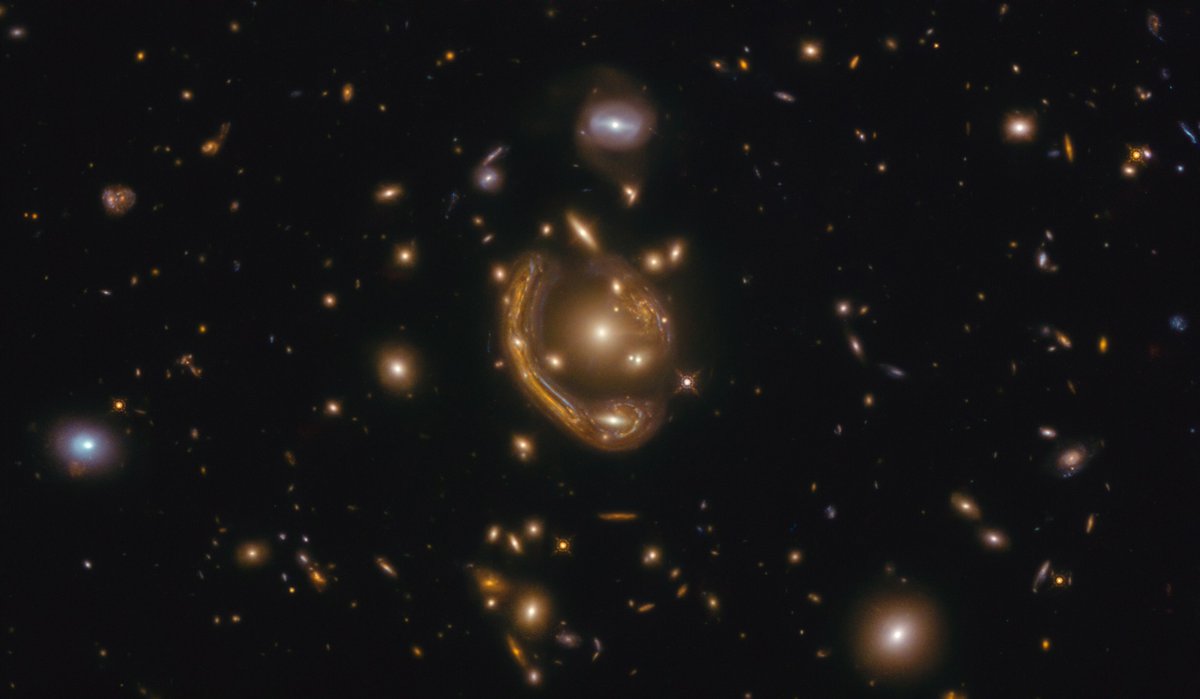
A very rare astronomical phenomenon has been in the headlines a lot recently, and for good reason. It will be hundreds of years until we can see Jupiter and Saturn this close to one another again. However, there are some even more “truly strange and very rare phenomena” that can currently be observed in our night sky. The only problem is that in order to observe this phenomena, you’ll need access to Hubble.
Continue reading “One of the Largest, Most Complete Einstein Rings Ever Seen. Astronomers Call it the “Molten Ring””A Single Filament of Gas Has Been Discovered That Stretches 50 Million Light-Years
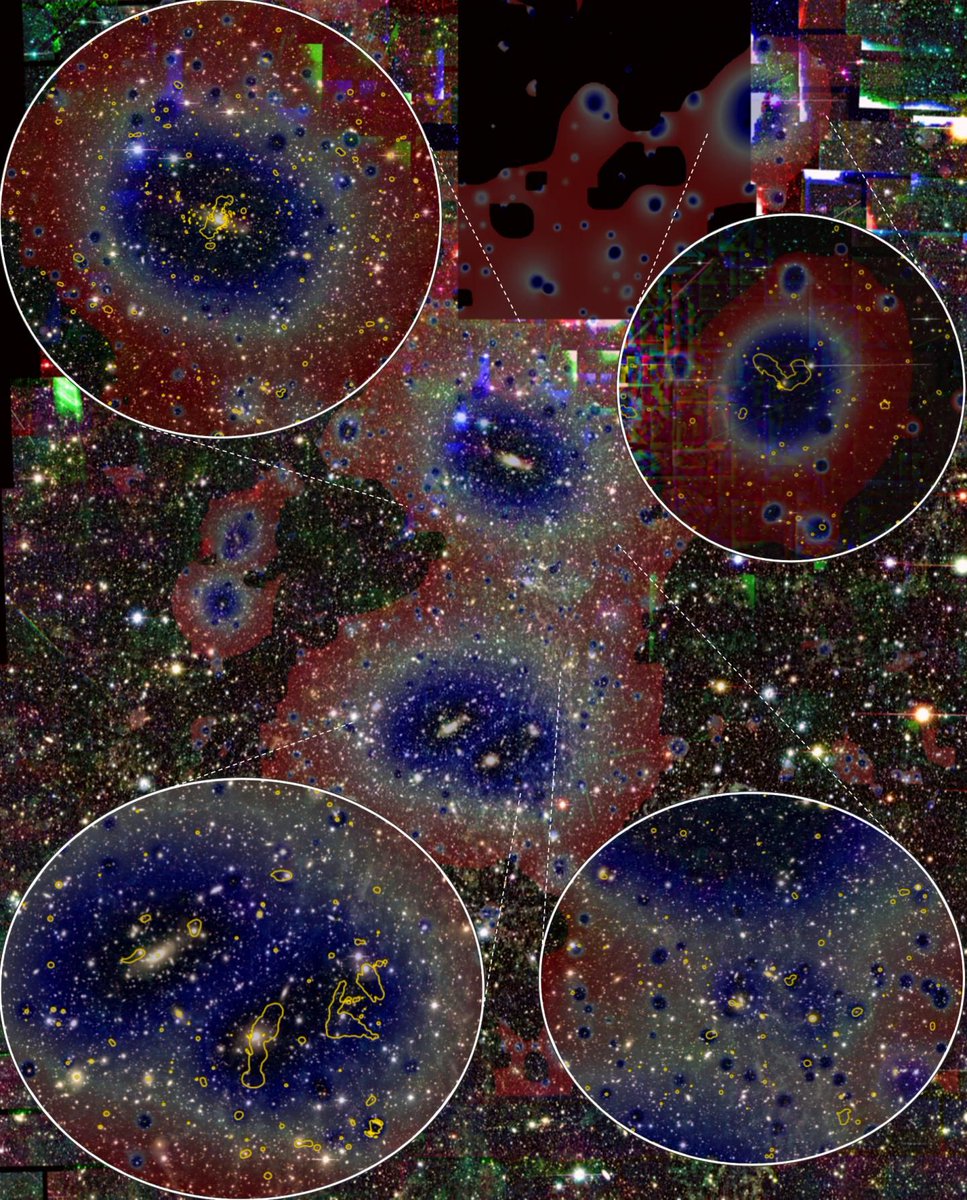
Minute vibrating strings found in string theory are not the only ones that are of interest to physicists. The Standard Model of particle physics provides for a theory regarding a different type of string – this one is a string of very sparse gas strung over very long distances. In fact, the standard model predicts that a large percentage of “baryonic matter” (i.e. the type that makes up everything we can see and interact with) would be contained in these filaments. And now for the first time, scientists led by a team at the University of Bonn in Germany have detected one of these super long strings of gas.
Continue reading “A Single Filament of Gas Has Been Discovered That Stretches 50 Million Light-Years”