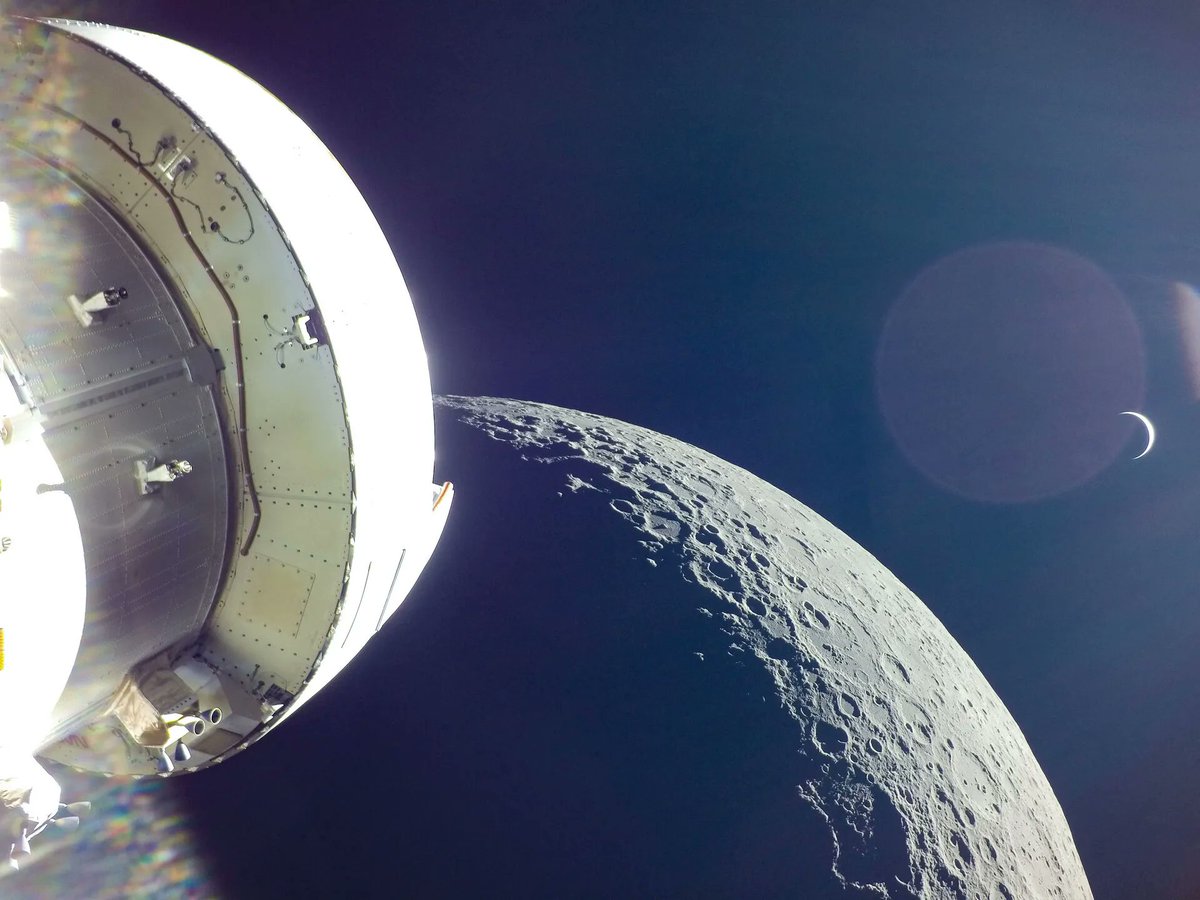
There’s an argument to be made that some astronomical pictures are better inspirational tools than all of the science that the missions that took them might have collected during their lifetimes. This author personally had his interest in space exploration sparked when he first saw the Ultra Deep Field and then had it permanently ingrained in his brain with the Pale Blue Dot and the associated book. The fact that they have individual names (Earth Rise, The Blue Marble, etc.) shows their importance to our collective understanding of our planet and our place in the Universe. Now, we might have a new one, as we’ve received a spectacular view of our Moon and a crescent Earth from the Artemis 1 mission.
Continue reading “Will This be the Iconic Picture From Artemis I?”Perseverance’s Latest Sample is Just Crumbled Regolith. When Scientists get Their Hands on it, we’ll Learn so Much About how to Live on Mars
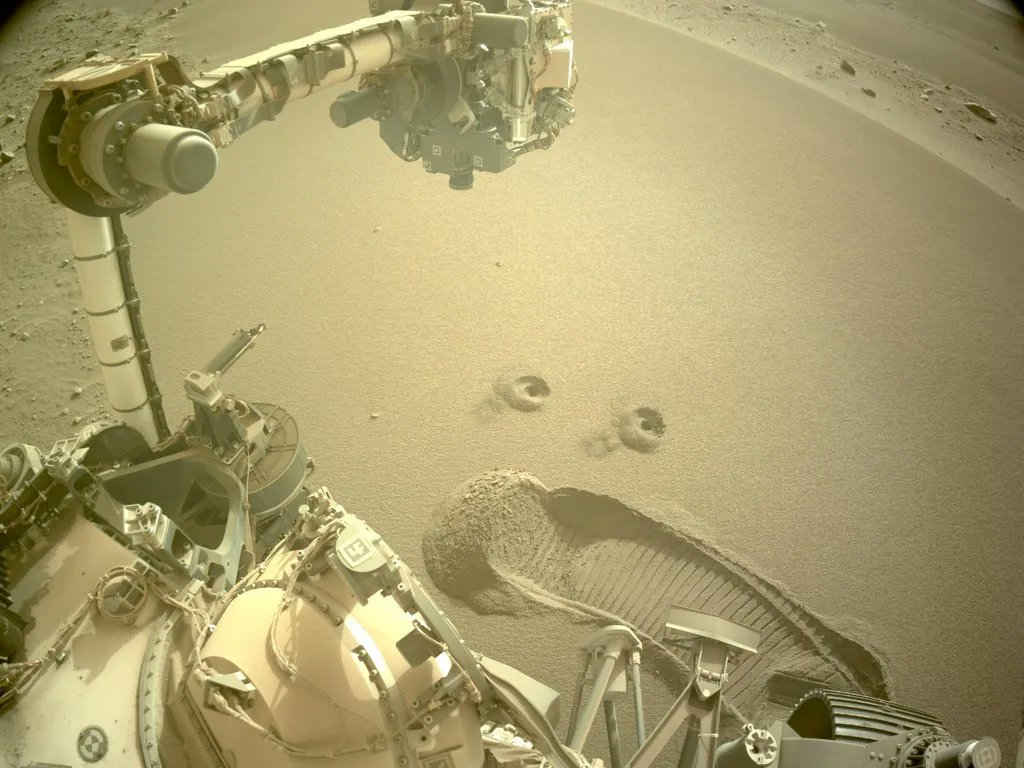
The Mars Sample Return (MSR) part of Perseverance’s mission is picking up – literally. For the past few months, the rover has concentrated on picking up samples that will eventually be returned to Earth as part of the future Mars Sample Return mission. Back on Earth, plenty of advanced technologies can poke and prod the samples in ways that would never be feasible to launch with a spacecraft. However, if scientists decide to poke or prod Perseverance’s latest collections, they might have a hard time because they are made of regular regolith.
Continue reading “Perseverance’s Latest Sample is Just Crumbled Regolith. When Scientists get Their Hands on it, we’ll Learn so Much About how to Live on Mars”We Could Simulate Living in Lunar Lava Tubes in Caves on Earth
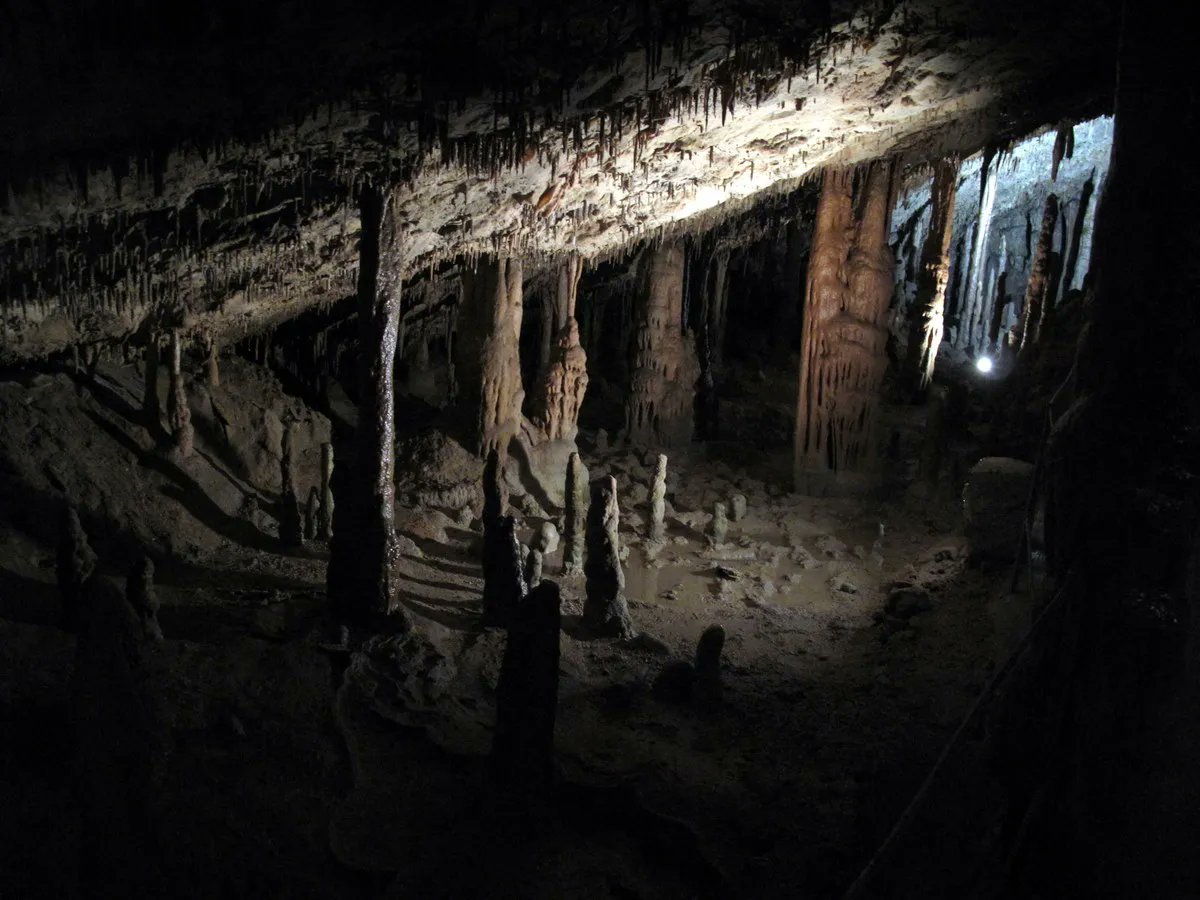
Simulation is key to space exploration. Scientists and engineers test as many scenarios as possible before subjecting their projects to the harshness of space. It should not be any different with the future living quarters of explorers on the Moon. One of the most commonly cited locations for a future permanent lunar base is in the relatively recently discovered lava tube caves scattered throughout the lunar mare. Simulating such an environment on Earth might be difficult, but a team from the Center for Space Exploration in China thinks they might have a solution – using karst caves to simulate lunar lava tubes.
Continue reading “We Could Simulate Living in Lunar Lava Tubes in Caves on Earth”If Dark Matter is Made of Axions, This Could be the Detector That Finds Them
As we’ve noted in plenty of other articles, science also moves forward by constraints. Understanding the limits of a physical phenomenon helps to develop better methods of looking for it, especially in its absence. Dark matter is an archetype of a missing phenomenon, but there are plenty of potential explanations for it. One of them is known as the axion, which was originally developed as a hypothetical particle that could plug a hole in the Standard Model of particle physics but could also solve the problem of dark energy. That is if they actually exist. Now a new experiment from researchers at CERN can help the scientific community better define where to look for those axions.
Continue reading “If Dark Matter is Made of Axions, This Could be the Detector That Finds Them”The Geminids Will be Peaking on December 14th. They’re Usually the Most Active Meteor Shower Every Year
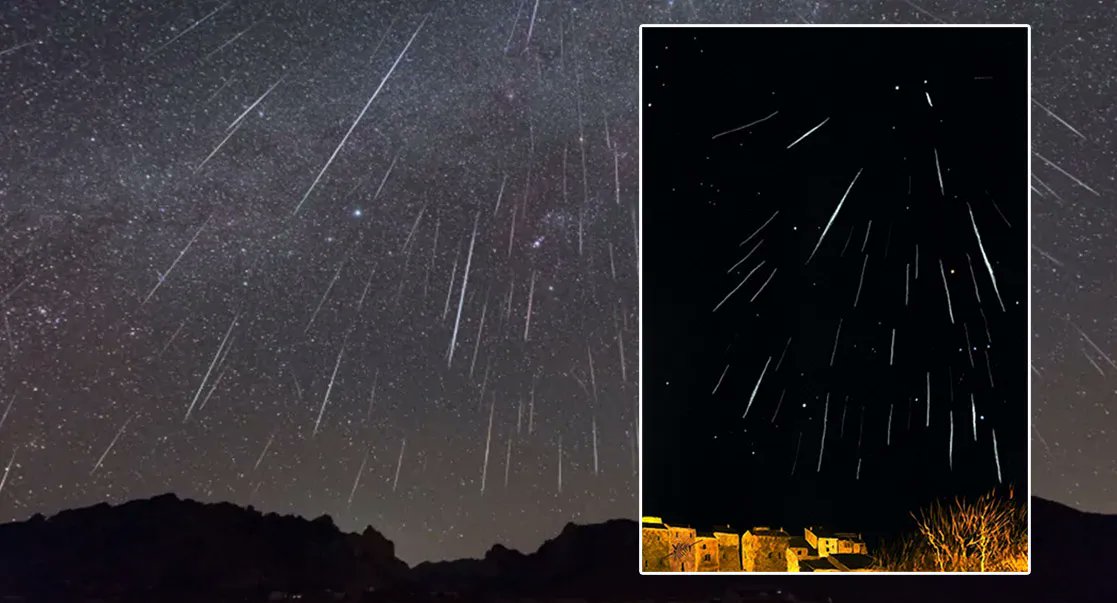
Meteor showers are a great way to share a love of astronomy with those who might not be as familiar with it. Almost everyone loves watching streaks of light flash across the sky, but usually, it’s so intermittent that it can be frustrating to watch. That’s not the case for the next few weeks, though, as the annual Geminid meteor shower is underway until December 24th.
Continue reading “The Geminids Will be Peaking on December 14th. They’re Usually the Most Active Meteor Shower Every Year”Not Just Stars. Gaia Mapped a Diverse and Shifting Universe of Variable Objects
We’ve reported on Gaia’s incredible data-collection abilities in the past. Recently, it released DR3, its latest data set, with over 1.8 billion objects in it. That’s a lot of data to sift through, and one of the most effective ways to do so is through machine learning. A group of researchers did just that by using a supervised learning algorithm to classify a particular type of object found in the data set. The result is one of the world’s most comprehensive catalogs of the type of astronomical object known as variables.
Continue reading “Not Just Stars. Gaia Mapped a Diverse and Shifting Universe of Variable Objects”Maybe we don’t see Aliens Because They’re Waiting to Hear a Signal From us First
We’ve had a long-running series here at UT on potential solutions Fermi Paradox – why aren’t we able to detect any alien life out there in the Universe? But more possible solutions are being developed all the time. Now, another paper adds some additional theory to one of the more popular solutions – that aliens are just too busy to care about us.
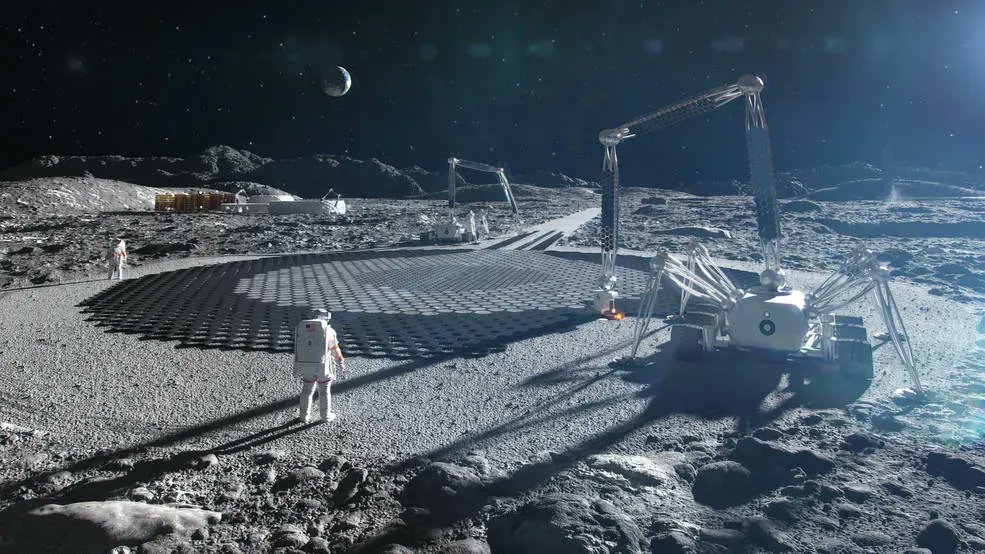
Continue reading “Maybe we don’t see Aliens Because They’re Waiting to Hear a Signal From us First”NASA Wants to Build Landing Pads on the Moon
NASA has started engaging with commercial partners are some out-there projects. One of the most recent is a six year, $57.2 million deal with ICON, a company based in Austin, Texas that specializes in in-situ resource utilization 3D printing technologies.
Continue reading “NASA Wants to Build Landing Pads on the Moon”Sometimes Astronomy isn’t About What you see, but What you don’t see
Constraints are critical in any scientific enterprise. If a hypothesis predicts that there should be an observable phenomenon, and there isn’t any trace of it, that’s a pretty clear indication that the hypothesis is wrong. And even false hypotheses still move science forward. So it is with astronomy and, in particular, explorations of the early universe. A paper authored by researchers at Cambridge and colleagues now puts a particularly useful constraint on the development of early galaxies, which has been a hot topic in astronomy as of late.
Continue reading “Sometimes Astronomy isn’t About What you see, but What you don’t see”Quasars Produce Giant Jets That Focus Like Lasers. Why They Focus is Still a Mystery, but it’s not Coming From the Galaxy Itself
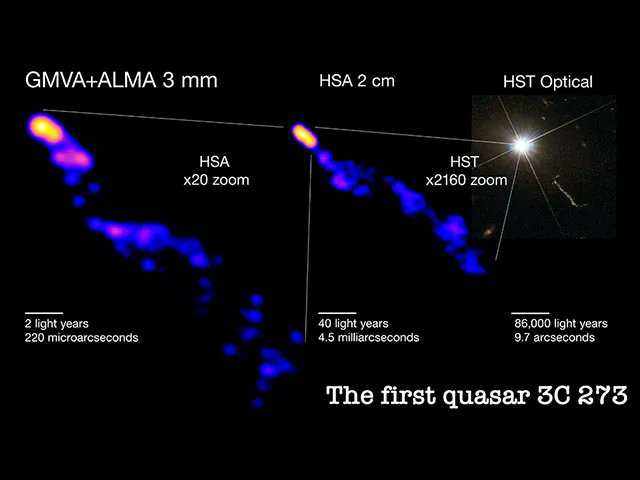
New technologies bring new astronomical insights, which is especially satisfying when they help answer debates that have been ongoing for decades. One of those debates is why exactly the plasma emitted from pulsars “collimates” or is brought together in a narrow beam. While it doesn’t provide a definitive answer to that question, a new paper from an international group of scientists points to a potential solution, but it will require even more advanced technologies.
Continue reading “Quasars Produce Giant Jets That Focus Like Lasers. Why They Focus is Still a Mystery, but it’s not Coming From the Galaxy Itself”