The gravitational wave background was first detected in 2016. It was announced following the release of the first data set from the European Pulsar Timing Array. A second set of data has just been released and, joined by the Indian Pulsar Timing Array, both studies confirm the existence of the background. The latest theory seems to suggest that we’re seeing the combined signal of supermassive black hole mergers.
Continue reading “More Evidence for the Gravitational Wave Background of the Universe”When Uranus and Neptune Migrated, Three Icy Objects Were Crashing Into Them Every Hour!
The giant outer planets haven’t always been in their current position. Uranus and Neptune for example are thought to have wandered through the outer Solar System to their current orbital position. On the way, they accumulated icy, comet-like objects. A new piece of research suggests as many as three kilomerer-sized objects crashed into them every hour increasing their mass. Not only would it increase the mass but it would enrich their atmospheres.
Continue reading “When Uranus and Neptune Migrated, Three Icy Objects Were Crashing Into Them Every Hour!”Astronomers Discover the Second-Lightest “Cotton Candy” Exoplanet to Date.
The hunt for extrasolar planets has revealed some truly interesting candidates, not the least of which are planets known as “Hot Jupiters.” This refers to a particular class of gas giants comparable in size to Jupiter but which orbit very closely to their suns. Strangely, there are some gas giants out there that have very low densities, raising questions about their formation and evolution. This is certainly true of the Kepler 51 system, which contains no less than three “super puff” planets similar in size to Jupiter but is about one hundred times less dense.
These planets also go by the moniker “cotton candy” giants because their density is comparable to this staple confection. In a recent study, an international team of astronomers spotted another massive planet, WASP-193b, a fluffy gas giant orbiting a Sun-like star 1,232 light-years away. While this planet is roughly one and a half times the size of Jupiter, it is only about 14% as massive. This makes WASP-193b the second-lightest exoplanet observed to date. Studying this and other “cotton candy” exoplanets could provide valuable insight into how these mysterious giants form.
Continue reading “Astronomers Discover the Second-Lightest “Cotton Candy” Exoplanet to Date.”Did Earth’s Multicellular Life Depend on Plate Tectonics?

How did complex life emerge and evolve on the Earth and what does this mean for finding life beyond Earth? This is what a recent study published in Nature hopes to address as a pair of researchers investigated how plate tectonics, oceans, and continents are responsible for the emergence and evolution of complex life across our planet and how this could address the Fermi Paradox while attempting to improve the Drake Equation regarding why we haven’t found life in the universe and the parameters for finding life, respectively. This study holds the potential to help researchers better understand the criterion for finding life beyond Earth, specifically pertaining to the geological processes exhibited on Earth.
Continue reading “Did Earth’s Multicellular Life Depend on Plate Tectonics?”Hubble Sees a Brand New Triple Star System

In a world that seems to be switching focus from the Hubble Space Telescope to the James Webb Space Telescope, Hubble still reminds us it’s there. Another amazing image has been released that shows the triple star system HP Tau, HP Tau G2, and HP Tau G3. The stars in this wonderful system are young, HP Tau for example is so young that it hasn’t started to fuse hydrogen yet and is only 10 million years old!
Continue reading “Hubble Sees a Brand New Triple Star System”The Venerable Hubble Space Telescope Keeps Delivering

The world was much different in 1990 when NASA astronauts removed the Hubble Space Telescope from Space Shuttle Discovery’s cargo bay and placed it into orbit. The Cold War was ending, there were only 5.3 billion humans, and the World Wide Web had just come online.
Continue reading “The Venerable Hubble Space Telescope Keeps Delivering”The BepiColombo Mission To Mercury is Losing Power
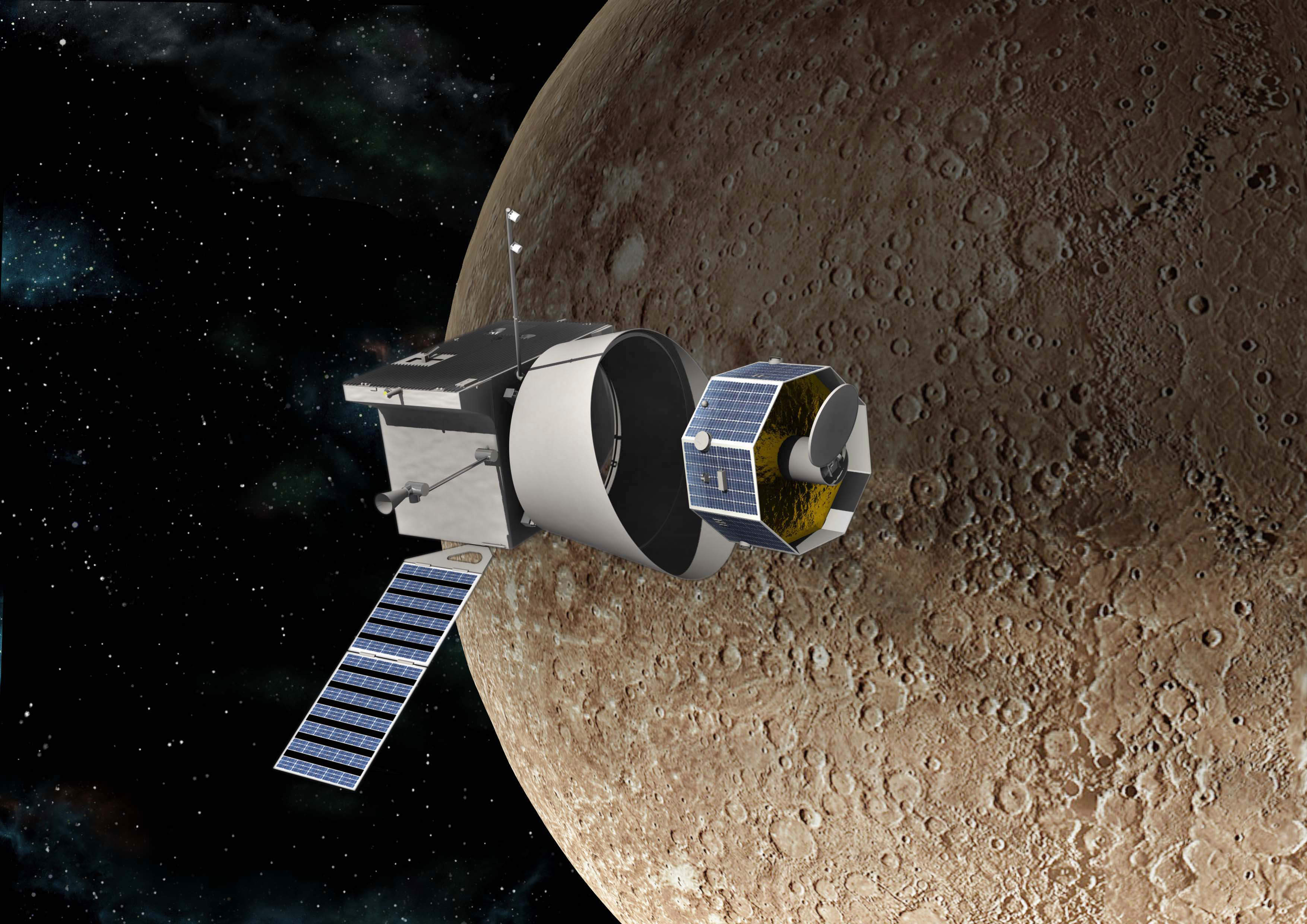
BepiColombo is a joint ESA/JAXA mission to Mercury. It was launched in 2018 on a complex trajectory to the Solar System’s innermost planet. The ESA reports that the spacecraft’s thrusters have lost some power.
Continue reading “The BepiColombo Mission To Mercury is Losing Power”Astronauts Could Deploy Extra Arms to Stay Stable on the Moon
Walking along on the surface of the Moon, as aptly demonstrated by the Apollo astronauts, is no easy feat. The gravity at the Moon’s surface is 1/6th of Earth’s and there are plenty of videos of astronauts stumbling, falling and then trying to get up! Engineers have come up with a solution; a robotic arm system that can be attached to an astronauts back pack to give them a helping hand if they fall. The “SuperLimbs” as they have been called will not only aid them as they walk around the surface but also give them extra stability while carrying out tasks.
Continue reading “Astronauts Could Deploy Extra Arms to Stay Stable on the Moon”Not All Black Holes are Ravenous Gluttons
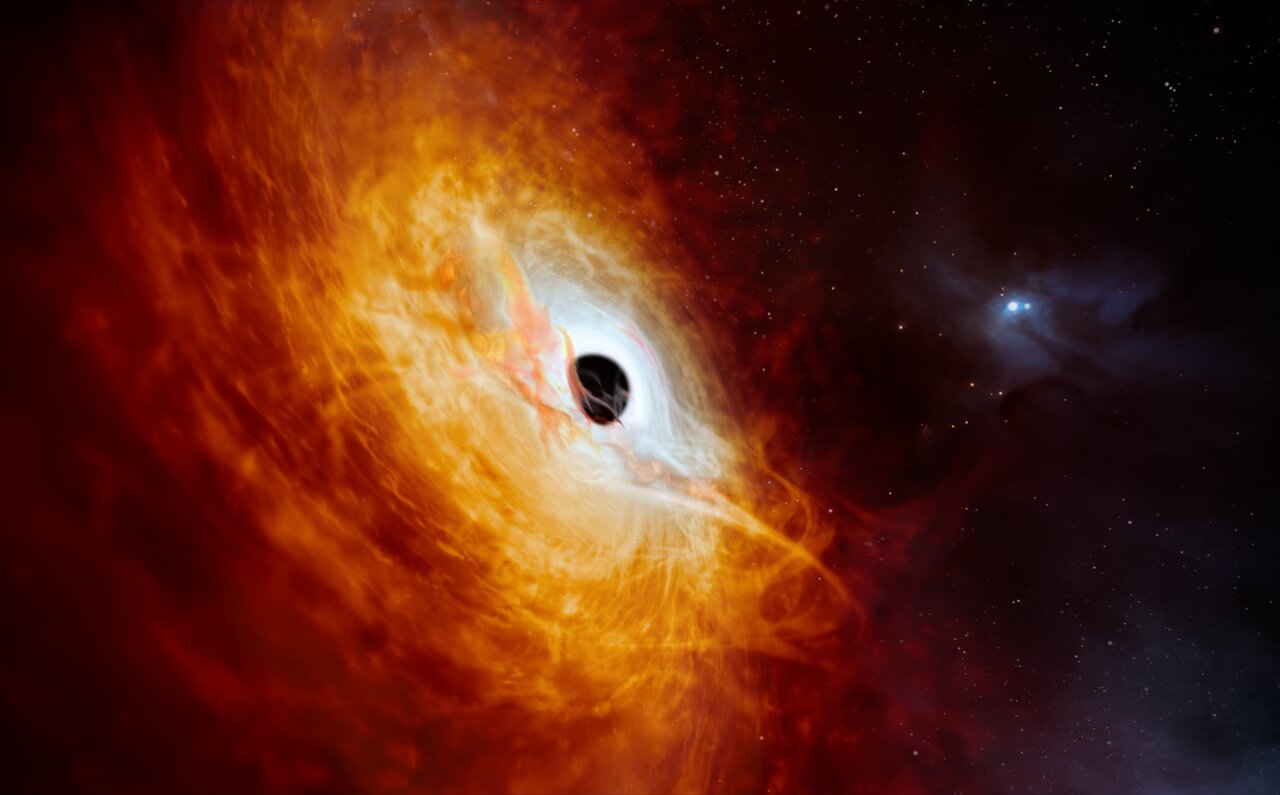

Some Supermassive Black Holes (SMBHs) consume vast quantities of gas and dust, triggering brilliant light shows that can outshine an entire galaxy. But others are much more sedate, emitting faint but steady light from their home in the heart of their galaxy.
Observations from the now-retired Spitzer Space Telescope help show why that is.
Continue reading “Not All Black Holes are Ravenous Gluttons”Webb Sees Black Holes Merging Near the Beginning of Time

A long time ago, in two galaxies far, far away, two massive black holes merged. This happened when the Universe was only 740 million years old. A team of astronomers used JWST to study this event, the most distant (and earliest) detection of a black hole merger ever.
Continue reading “Webb Sees Black Holes Merging Near the Beginning of Time”



