The mystery of the world famous “Jelly Doughnut” rock on Mars has at last been solved by diligent mission scientists toiling away in dank research labs on Earth.
The “Jelly Doughnut” rock achieved worldwide fame, or better yet infamy, when it suddenly appeared out of nowhere in pictures taken by NASA’s renowned Red Planet rover Opportunity in January.
And the answer is – well it’s not heretofore undetected Martian beings or even rocks falling from the sky.
Rather its ‘Alien Space Invaders’ – in some sense at least.
And that ‘Alien Space Invader’ is from – Earth! And her name is – Opportunity!
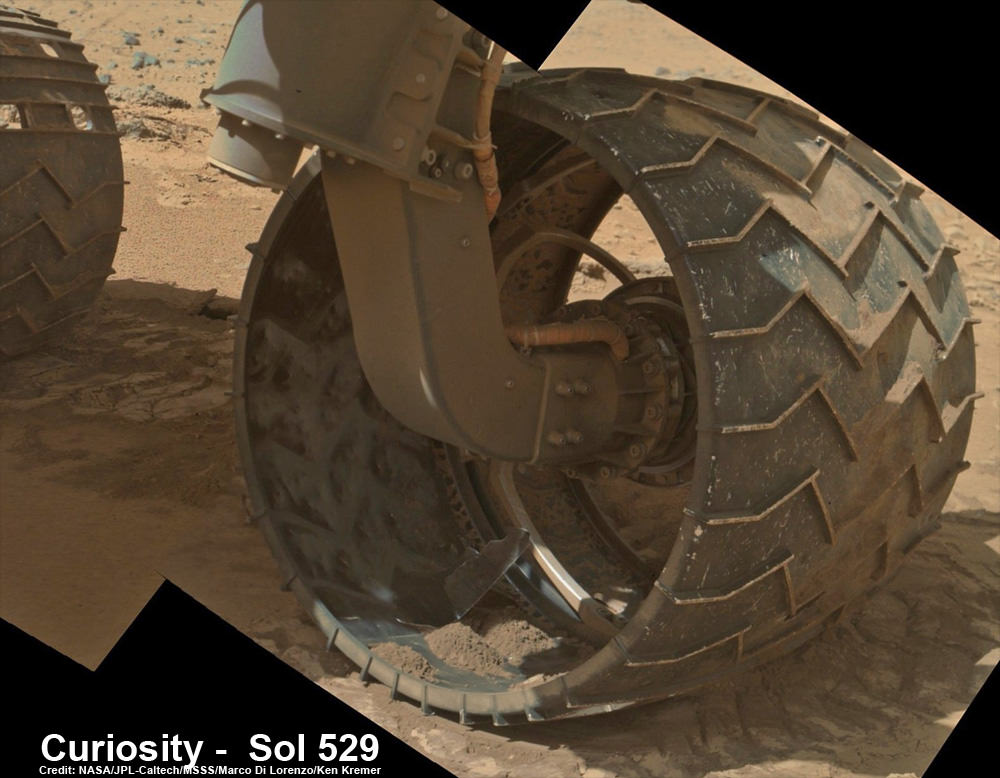
Indeed sister rover Curiosity may have unwittingly pointed to the culprit and helped resolve the riddle when she snapped a brand new photo of Earth – home planet to Opportunity and Curiosity and all their makers! See the evidence for yourselves – lurking here!
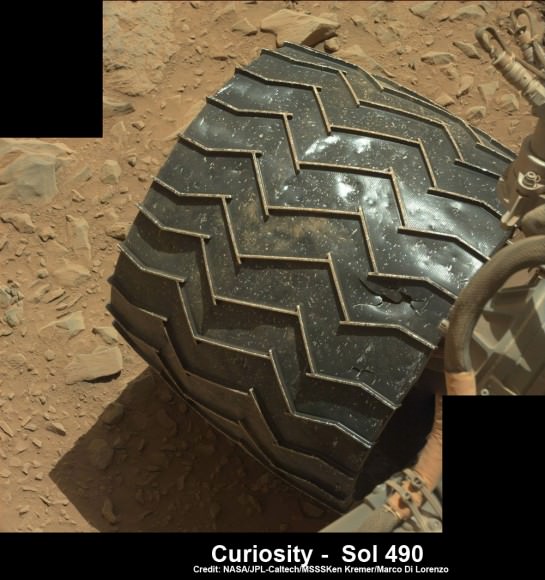
It turns out that the six wheeled Opportunity unknowingly ‘created’ the mystery herself when she drove over a larger rock, crushing it with the force from the wheels and her 400 pound (185 kg) mass.
Fragments were sent hurtling across the summit of the north facing Solander Point mountain top, where she is currently climbing up ‘Murray Ridge’ along the western rim of a vast crater named Endeavour that spans some 22 kilometers (14 miles) in diameter. See traverse map below.
One piece unwittingly rolled downhill.
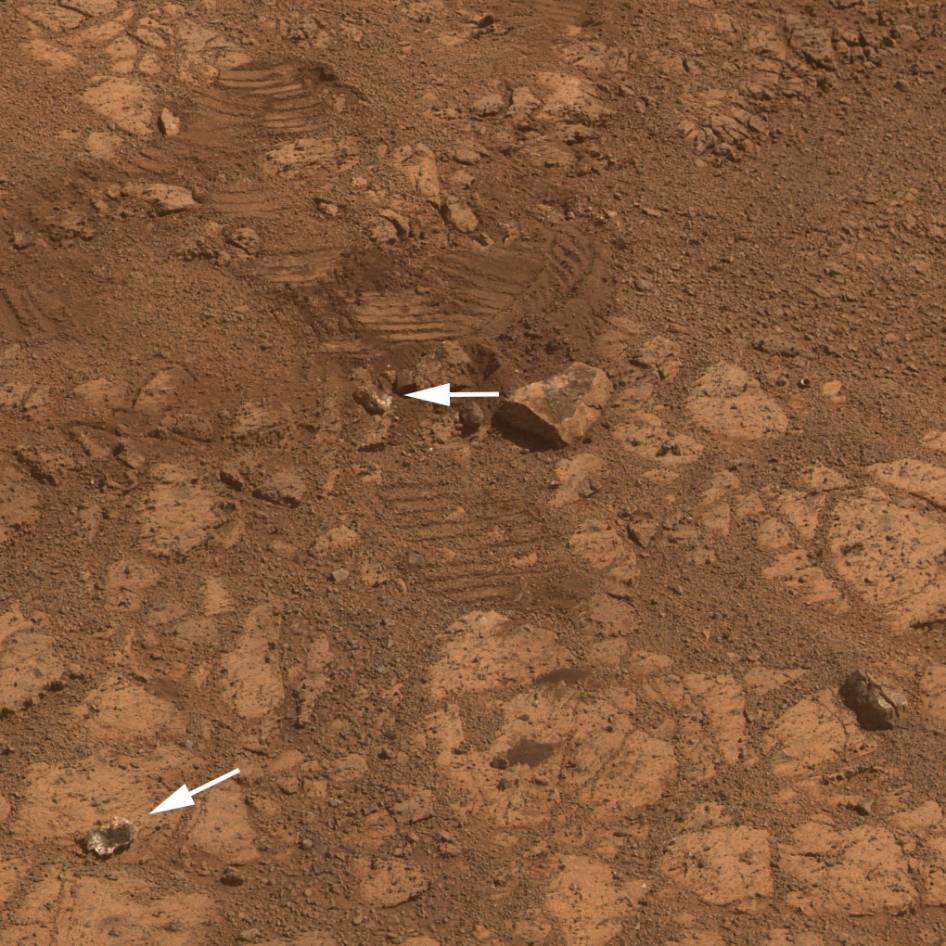
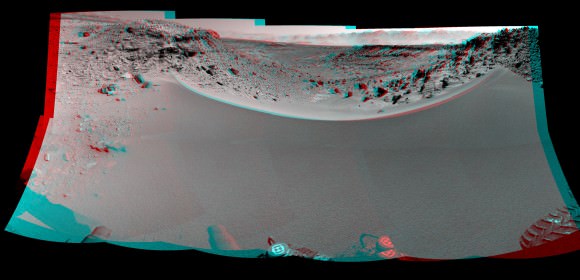
That rock fragment – now dubbed ‘Pinnacle Island’ – suddenly appeared in pictures taken by Opportunity’s cameras on Jan, 8, 2014 (Sol 3540).

And that exact same spot had been vacant of debris in photos taken barely 4 days earlier – during which time the rover didn’t move a single millimeter.
Pinnacle Island measures only about 1.5 inches wide (4 centimeters) with a noticeable white rim and red center – hence its jelly doughnut nickname.
The Martian riddle was finally resolved when Opportunity roved a tiny stretch and took some look back photographs to document the ‘mysterious scene’ for further scrutiny.
“Once we moved Opportunity a short distance, after inspecting Pinnacle Island, we could see directly uphill an overturned rock that has the same unusual appearance,” said Opportunity Deputy Principal Investigator Ray Arvidson of Washington University in St. Louis, in a NASA statement.
“We drove over it. We can see the track. That’s where Pinnacle Island came from.”
New pictures showed another fragment of the rock – dubbed ‘Stuart Island’ – eerily similar in appearance to the ‘Pinnacle Island’ doughnut.

To gather some up-close clues before driving away, the rover deployed its robotic arm to investigate ‘Pinnacle Island’ with her microscopic imager and APXS mineral mapping spectrometer.
The results revealed high levels of the elements manganese and sulfur “suggesting these water-soluble ingredients were concentrated in the rock by the action of water,” says NASA.
“This may have happened just beneath the surface relatively recently,” Arvidson noted, “or it may have happened deeper below ground longer ago and then, by serendipity, erosion stripped away material above it and made it accessible to our wheels.”

The Solander Point mountaintop is riven with outcrops of minerals, including clay minerals, that likely formed in flowing liquid neutral water conducive to life – potentially a scientific goldmine.
Opportunity is NASA’s 1st ever ‘Decade Old’ living Mars rover.
She has been uncovering and solving Mars’ billion years old secrets for over 10 years now since landing back on January 24, 2004 on Meridiani Planum – although she was only expected to function a mere 90 days!
Today, Feb 15, marks Opportunity’s 3578th Sol or Martian Day roving Mars.
So far she has snapped over 188,700 amazing images on the first overland expedition across the Red Planet.
Her total odometry stands at over 24.07 miles (38.73 kilometers) since touchdown on Jan. 24, 2004 at Meridiani Planum.
Read more about sister Spirit – here and here.
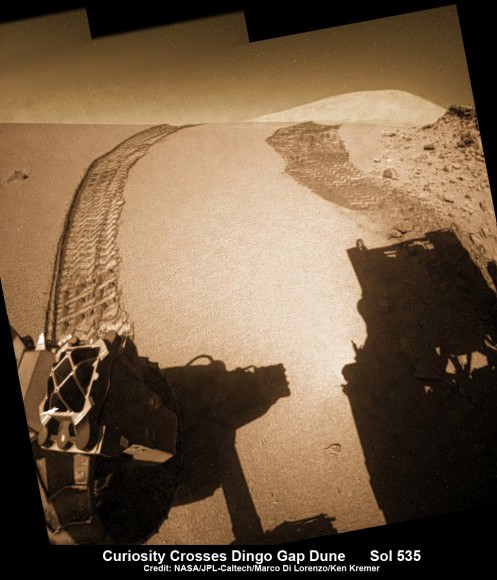
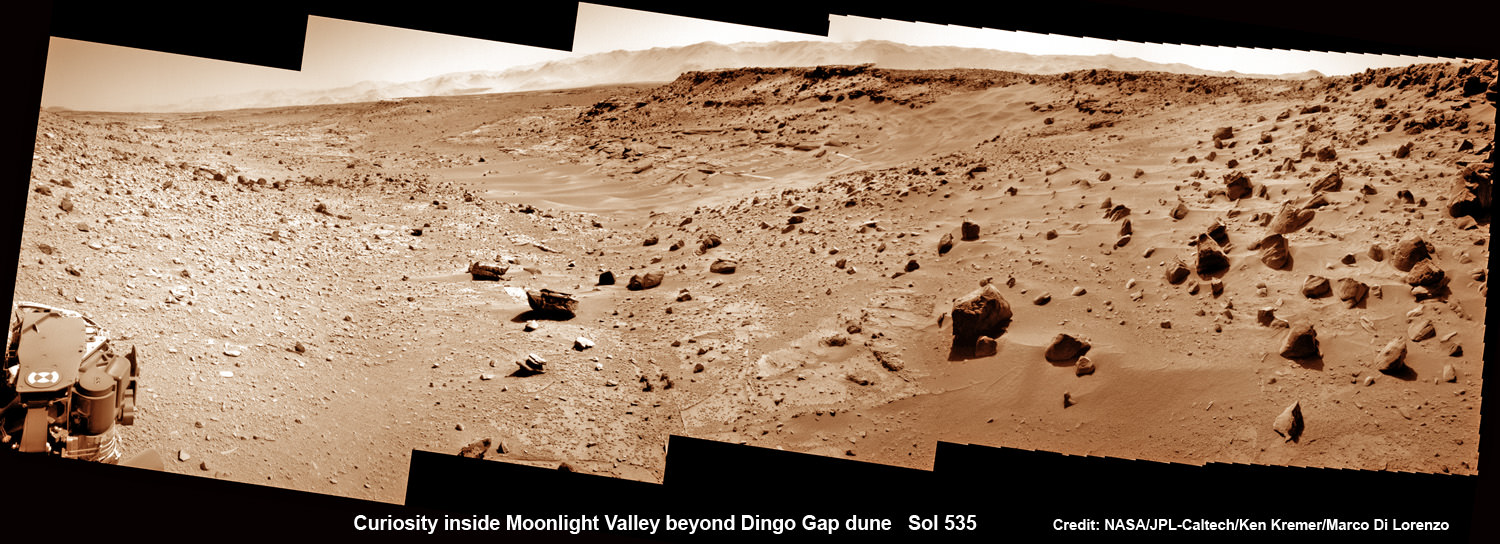
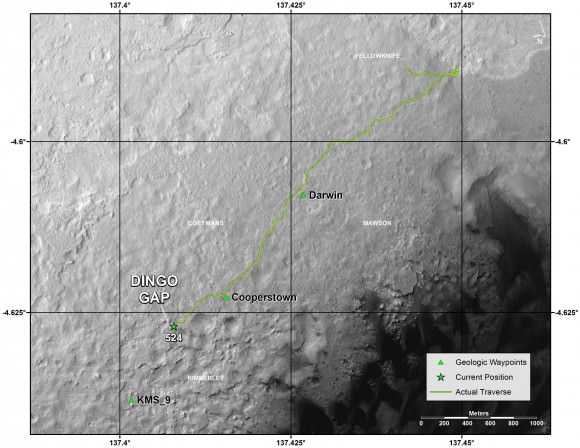
Meanwhile on the opposite side of Mars, Opportunity’s younger sister rover Curiosity is trekking towards gigantic Mount Sharp and just crested over the Dingo Gap sand dune. She celebrated 500 Sols on Mars on New Years Day 2014.
And a pair of new orbiters are streaking to the Red Planet to fortify Earth’s invasion fleet- NASA’s MAVEN and India’s MOM.
Finally, China’s Yutu rover has awoken for her 3rd workday on the Moon.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Opportunity, Curiosity, Chang’e-3, LADEE, MAVEN, Mars rover, MOM and continuing planetary and human spaceflight news.
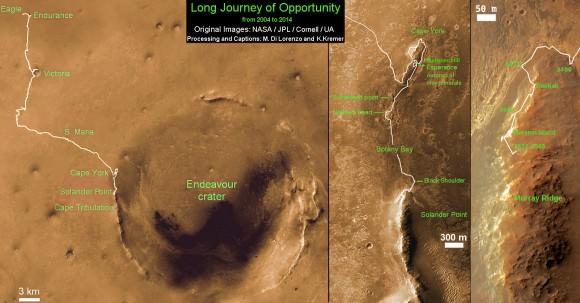
This map shows the entire path the rover has driven during a decade on Mars and over 3560 Sols, or Martian days, since landing inside Eagle Crater on Jan 24, 2004 to current location by Solander Point summit at the western rim of Endeavour Crater. Rover will spend 6th winter here atop Solander. Opportunity discovered clay minerals at Esperance – indicative of a habitable zone. Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/ASU/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer – kenkremer.com