More than two decades of Hubble observations have produced more than 25 terabytes of data. Thanks to the wealth of information stored in the Hubble data archive, astronomers can easily revisit old images in an effort to better understand new discoveries.
Now, astronomers have used the archive to find the progenitor of a mysterious type of supernova, dubbed Type 1ax, which is less energetic and much fainter than its Type Ia cousin.
A Type 1a supernova occurs when a white dwarf siphons material off a companion star, building an additional layer of hydrogen on its surface that will eventually trigger a runaway reaction that detonates the accumulated gas.
The most popular explanation for Type 1ax supernovae is that they’re created in the same way, except the explosion doesn’t completely tear the white dwarf into pieces. Instead, the white dwarf ejects roughly half of its mass. It becomes battered and bruised, leaving behind a hot core composed of carbon and oxygen.
So far, astronomers have identified more than 30 of these mini-explosions, which occur at one-fifth the rate of Type 1a supernovae.
“Astronomers have been searching for decades for the progenitors of Type Ia’s,” said Saurabh Jha from Rutgers University in a NASA press release. “Type Ia’s are important because they’re used to measure vast cosmic distances and the expansion of the universe. But we have very few constraints on how any white dwarf explodes. The similarities between Type Iax’s and normal Type Ia’s make understanding Type Iax progenitors important, especially because no Type Ia progenitor has been conclusively identified.”
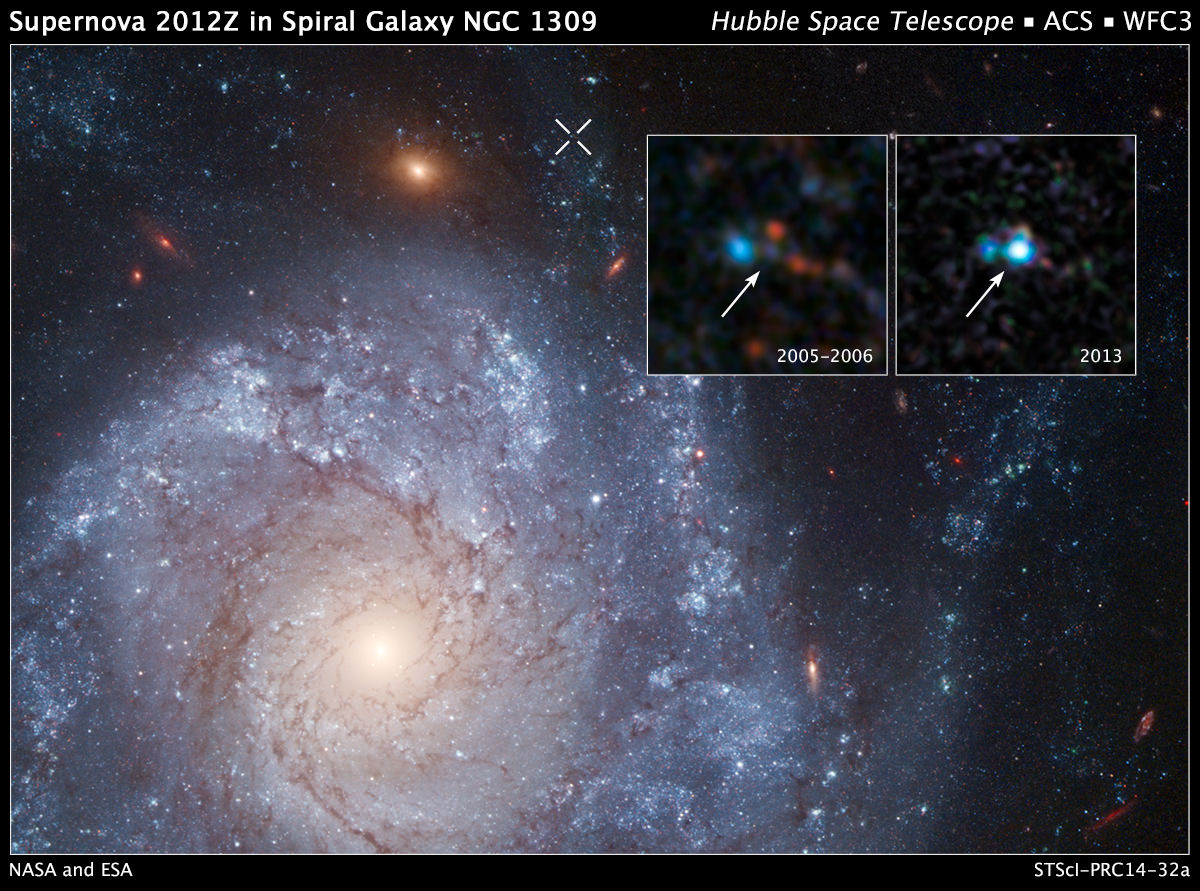
So after the team observed the weak supernova, dubbed SN 2012Z, in the Lick Observatory Supernova Search, they dug through Hubble’s archive. Fortuitously, Hubble had observed the supernova’s host galaxy, NGC 1309, in 2005, 2006, and 2010, before the supernova outburst.
Curtis McCully, a graduate student at Rutgers and lead author on the team’s paper, reprocessed the pre-explosion images to find an object at the supernova’s position.
“I was very surprised to see anything at the supernova’s location,” said McCully. “We expected that the progenitor system would be too faint to see, like in previous searches for normal Type Ia supernova progenitors. It is exciting when nature surprises us.”
The pre-supernova observations reveal a bright, blue source the team calls S1. McCully and colleagues concluded that they were most likely seeing a star that had lost its outer hydrogen envelope, revealing its helium core. But they don’t think it’s a type of star that was about to explode, rather it’s the companion that fed the white dwarf’s outburst.
The most likely explanation involves a binary star system where each star detonates mass to the other over time.
The team acknowledges that they can’t totally rule out other possibilities for the object’s identity, including that it was simply a single, massive star that exploded as a supernova. To settle any uncertainties the team plans to use Hubble again in 2015. Hopefully by then the supernova should fade enough to get a better look at what remains.
The team’s results will appear in the journal Nature tomorrow.