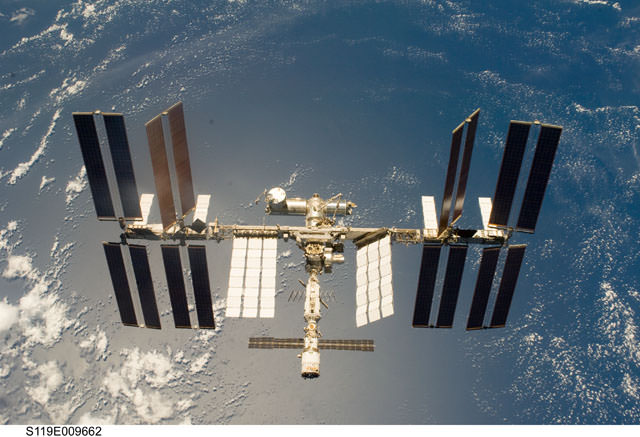
It’s away… and the hunt is on. The Japanese Space Agency’s H-II Transfer Vehicle Kounotori automated cargo spacecraft rocketed out of the Tanegashima Space Center today, headed for the ISS.
Loaded with over 6,000 kilograms of experiments and supplies, HTV-5 is on a five day odyssey that you can follow from your backyard, starting tonight. Kounotori stands for ‘white stork,’ or the purveyor of joyful things in Japanese, and in this instance, the name is appropriate, as the HTV-5 is delivering much needed supplies to the International Space Station.

Launch occurred this morning at 11:50 UT/7:50 AM EDT, hitting an instantaneous window to chase after the International Space Station for grapple and berthing on Monday.
Unlike the Progress and Soyuz spacecraft, which have the capability to rendezvous and dock with the ISS, the HTV-5 and Dragon spacecraft are grappled with the Canadian Space Agency’s Canadarm 2, and stowed or ‘berthed’ in place.
Grapple with berthing to the nadir node of the Harmony module is set for Monday, August 24th, at 11:54 UT/7:54 AM EDT.
Unlike other vehicles that periodically visit the International Space Station, the HTV does not incorporate deployable solar panels, but instead, has panels wrapped around its body. This can also lend itself to some pretty bright flares as it passes overhead.

The H-IIB is a two stage rocket, and ground observers should keep an eye out for the second stage booster during ISS passes as well. Debris was also jettisoned during last weeks’ spacewalk, and there’s no word as of yet if this has reentered as well, though ground-spotters have yet to report any sightings. This is a typical EVA maneuver, and cosmonauts conducted the release in such a fashion as to pose no danger to the ISS or HTV. Debris jettisoned from the ISS typically reenters the Earth’s atmosphere after about a week or so.
Prospects for Seeing HTV-5 this Weekend
Grapple of the HTV-5 will occur Monday over central Asia. Keep in mind, the HTV-5 will have to perform several burns to reach the elevation of the ISS: this means its orbit will evolve daily. Heavens-Above and NASA’s Spot the Station tracker typically publish sighting predictions for cargo vehicles such as the HTV-5 along with ISS sighting opportunities online.
And we’ll be posting daily updates and maps as @Astroguyz on Twitter. We see the best prospects for spotting the ISS and HTV5 over the next few days leading up to Monday’s berthing are for latitudes 25-45 north (dusk) and latitudes 30-50 south (dawn). That covers a wide range of observers in Europe, North America, South Africa and Australia/New Zealand.
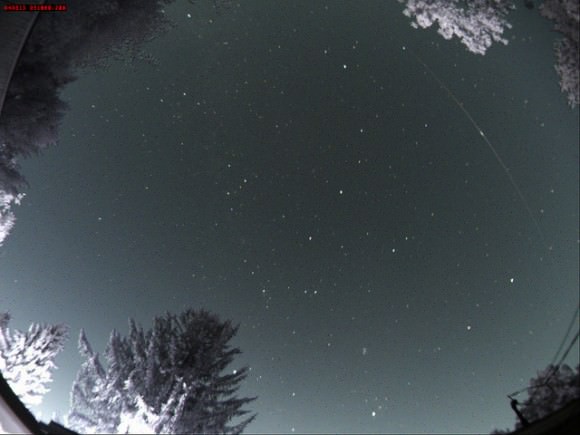

We’ve caught sight of JAXA’s HTV on previous missions, and contest to it being a conspicuous object.
Pro-tip: the trick to a successful sighting is to start watching early. The HTV-5 will be fainter than the brilliant ISS, but still visible to the naked eye at about magnitude +1 to +2 or so when directly overhead. The HTV-5 will follow the same orbital trace as the station. Spot the ISS and still don’t see HTV-5? Linger for a bit and keep watching after the ISS has passed, as the HTV might follow shortly. And the darker the skies you can find to carry out your HTV-5 vigil under, the better!
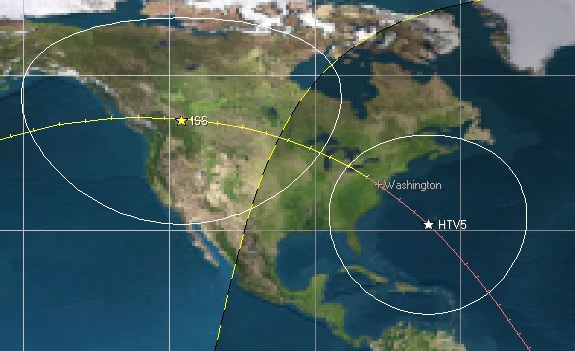
Here’s a sampling of ISS passes for Washington D.C. for the next few days:
Wednesday, August 19th: 8:46 PM EDT (Elevation 65 degrees NE)
Thursday, August 20th: 9:29 PM EDT (Elevation 23 degrees SW)
Friday, August 21st: 8:35 PM EDT (Elevation 48 degrees SW)
Clouded out? You can still watch the grapple and berthing action online courtesy of NASA TV.
Want more? Other orbital alumni that have placed a port of call at humanity’s orbital outpost include: SpaceX’s Dragon, the U.S. Space Shuttle fleet (excepting the Columbia orbiter), Progress, ATV, HTV, Soyuz, and Orbital Science’s Cygnus spacecraft. And while the shuttle and the European Space Agency’s ATV fleet are retired, you can follow the next launch of a crewed Soyuz (TMA-18M) on September 2nd from the Baikonur Cosmodrome on a four-orbit fast-track docking.
JAXA plans to launch one HTV a year, out to HTV-9 in 2019.
Good luck, and good sat-spotting… next time we park the Jeep Liberty in the garage, we’re going to refer to it as a ‘grapple and berthing…’ it just sounds cool.
Got a picture of the International Space Station and friends? Be sure to send ‘em in to Universe Today.