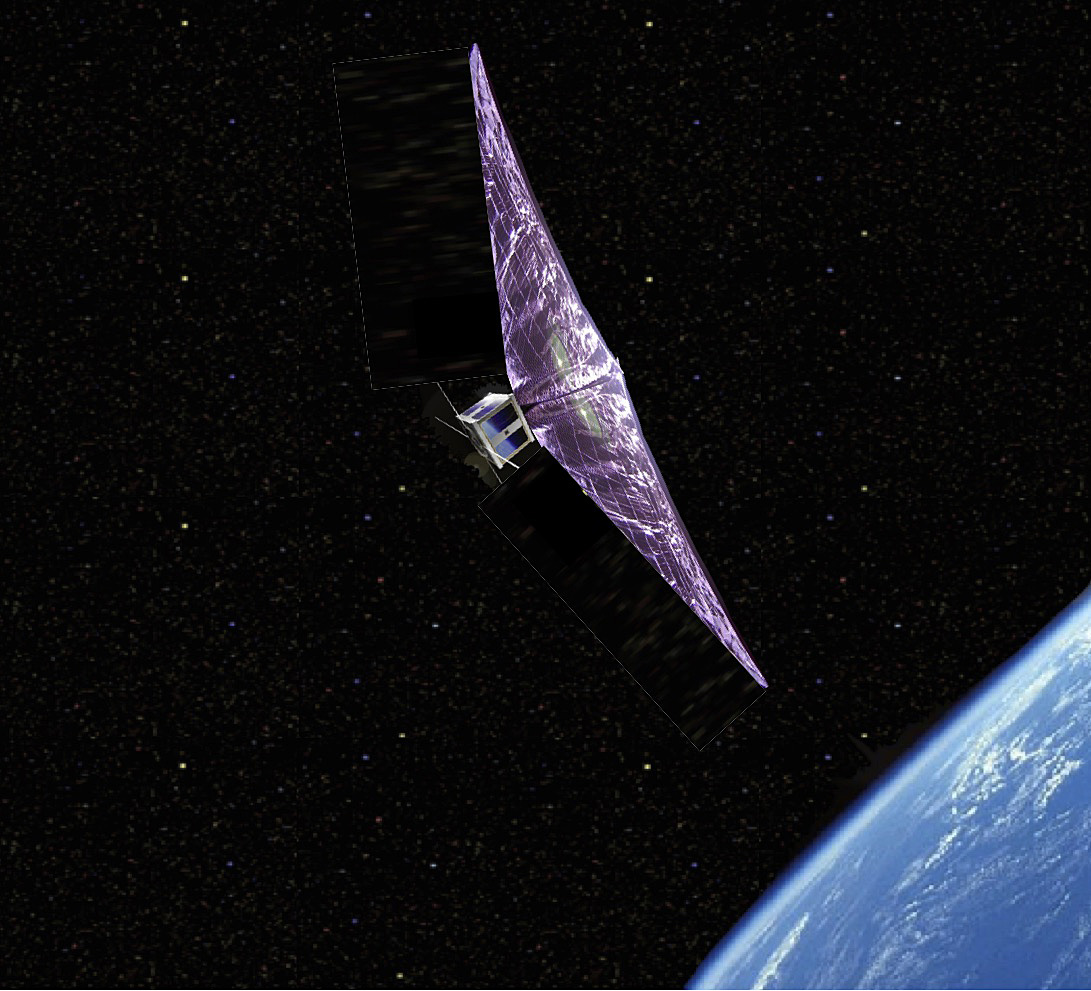
Space debris is a major problem for space exploration. There are millions of pieces up there in orbit from flecks of paint to defunct satellites. It is a known challenge to space exploration creating a shell of uncontrolled debris which could cause damage to orbiting craft or astronauts. A team at Astroscale have a spacecraft in orbit whose singular purpose has been to rendezvous with a defunct Japanese upper-stage rocket module. On arrival it is to survey the debris to test approach and survey techniques to ultimately inform how we can remove them from orbit.
Continue reading “Astroscale Closes Within 50 Meters of its Space Junk Target”Watch a Satellite Reaction Wheel Melt in a Simulated Orbital Re-Entry
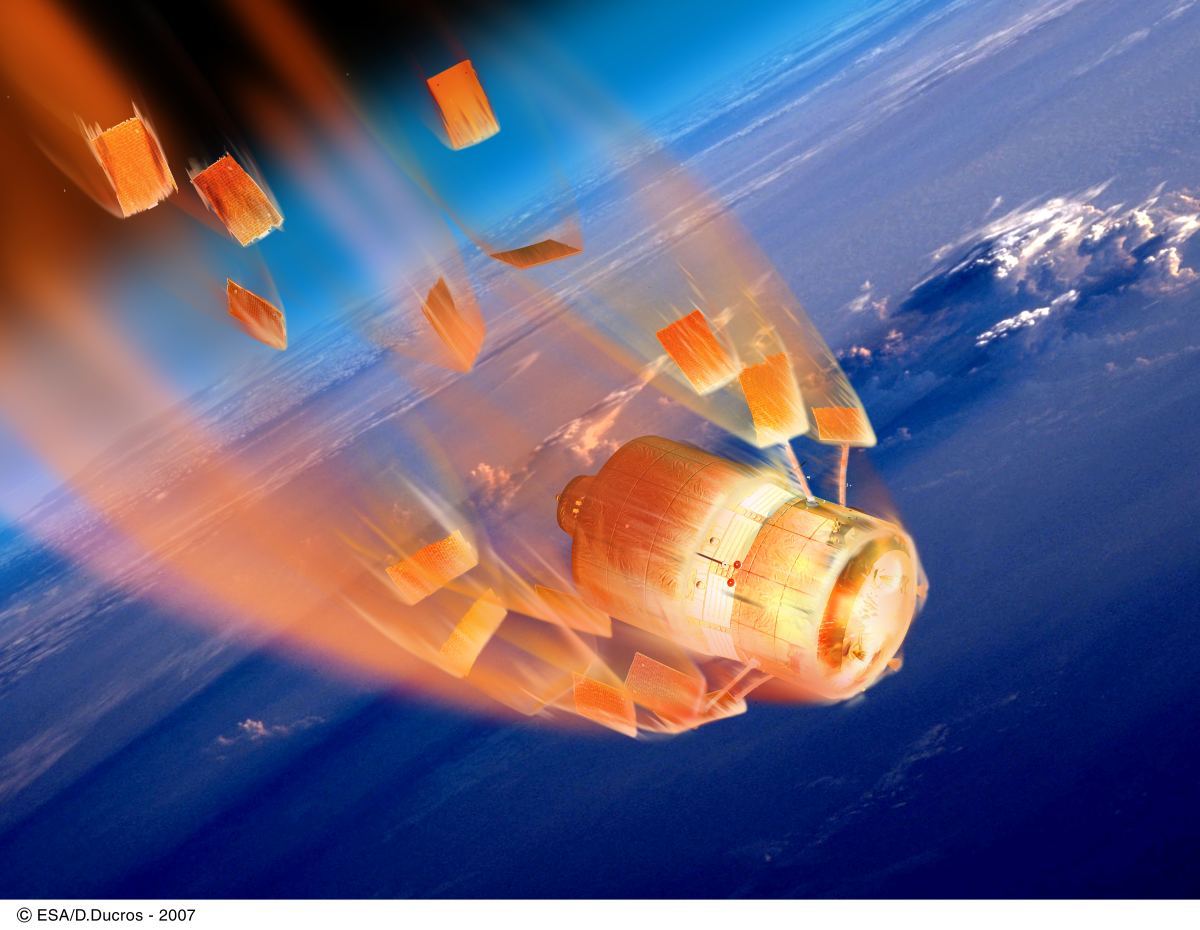

Most satellites share the same fate at the end of their lives. Their orbits decay, and eventually, they plunge through the atmosphere toward Earth. Most satellites are destroyed during their rapid descent, but not always
Heavy pieces of the satellite, like reaction wheels, can survive and strike the Earth. Engineers are trying to change that.
Continue reading “Watch a Satellite Reaction Wheel Melt in a Simulated Orbital Re-Entry”First Laser Space Debris Detection Made… in Daylight
A new technique may prove to be a powerful tool in the battle to mitigate space debris.
As the Space Age continues into its seventh decade, space debris is now growing at an exponential rate. Most of this debris is in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), and ranges from bus-sized discarded rocket boosters and defunct satellites, to tiny millimeter-sized fragments.
Continue reading “First Laser Space Debris Detection Made… in Daylight”Can We Use Special Sails To Bring Old Satellites Back Down To Earth?
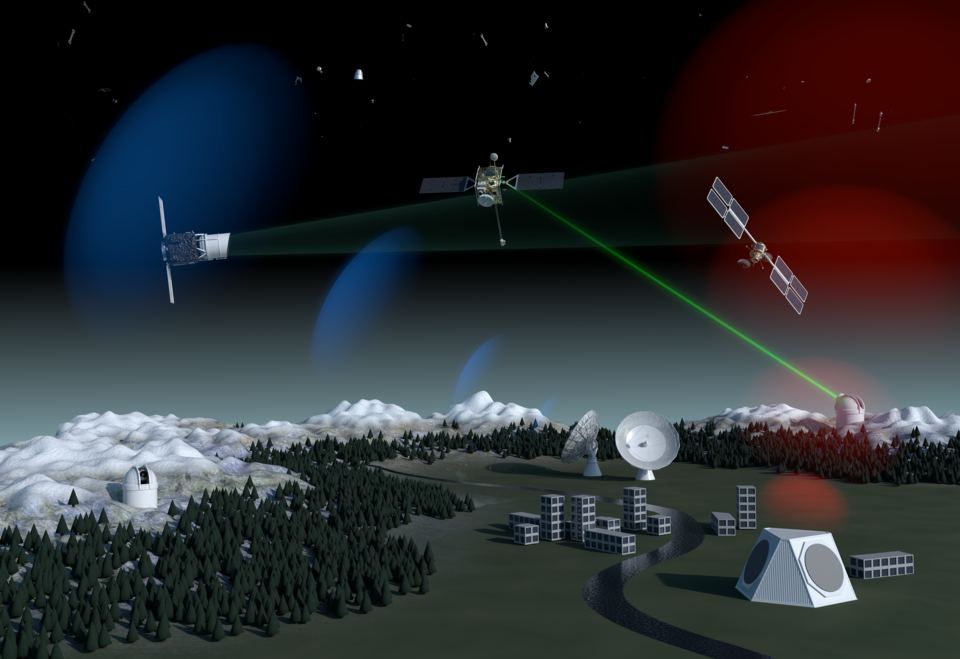
The growing problem of space debris in LEO (Low-Earth Orbit) is garnering more and more attention. With thousands of satellites in orbit, and thousands more on the way, our appetite for satellites seems boundless. But every satellite has a shelf-life. What do we do with them when they’ve outlived their usefulness and devolve into simple, troublesome space debris?
Continue reading “Can We Use Special Sails To Bring Old Satellites Back Down To Earth?”A New Solution to the Space Junk Problem. Spacecraft with Plasma Beams to Force Space Junk to Burn Up
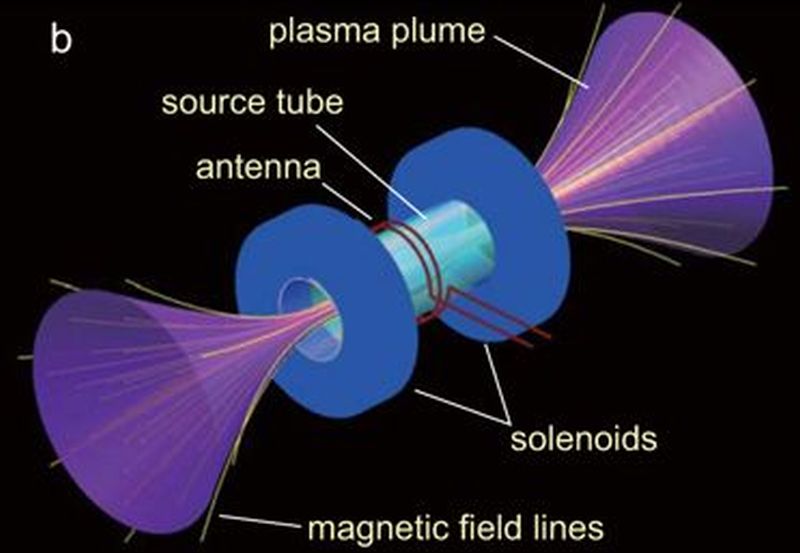
Space junk is a growing problem. For decades we have been sending satellites into orbit around Earth. Some of them de-orbit and burn up in Earth’s atmosphere, or crash into the surface. But most of the stuff we send into orbit is still up there.
This is becoming an acute problem as years go by and we launch more and more hardware into orbit. Since the very first satellite—Sputnik 1—was launched into orbit in 1957, over 8000 satellites have ben placed in orbit. As of 2018, an estimated 4900 are still in orbit. About 3000 of those are not operational. They’re space junk. The risk of collision is growing, and scientists are working on solutions. The problem will compound itself over time, as collisions between objects create more pieces of debris that have to be dealt with.



