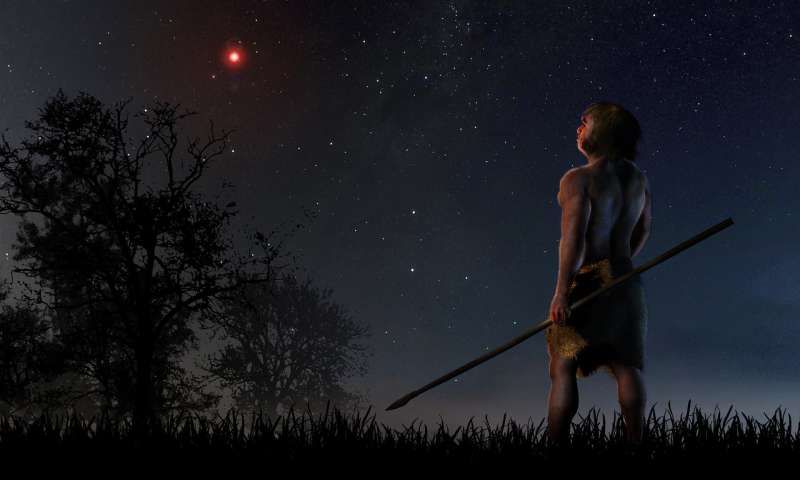
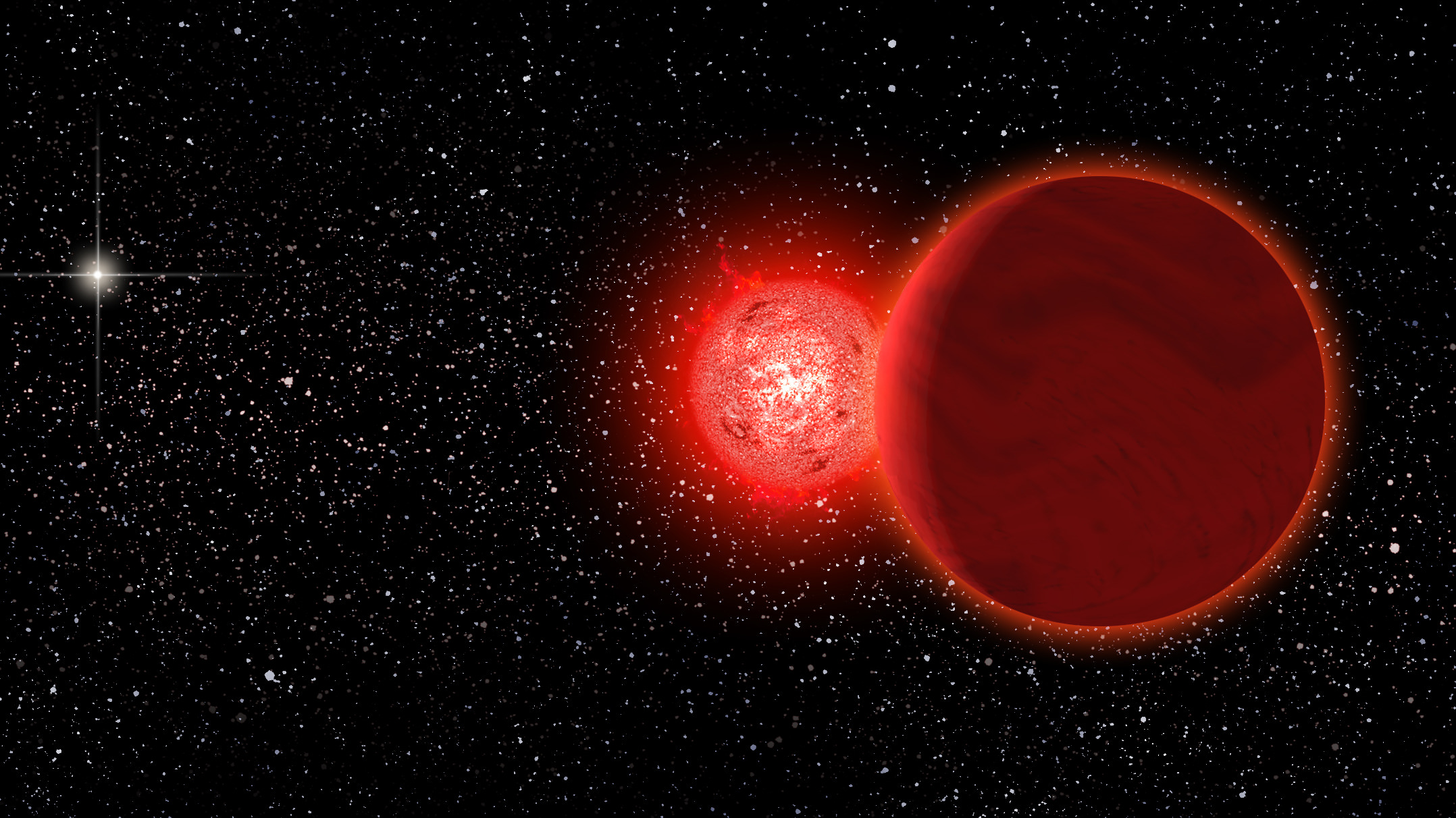
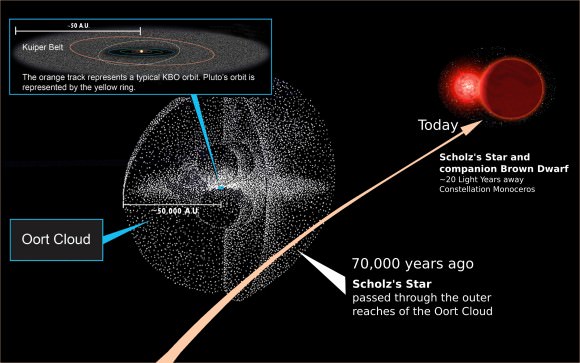
70,000 years ago, our keen-eyed ancestors may have noticed something in the sky: a red dwarf star that came as close as 1 light year to our Sun. They would’ve missed the red dwarf’s small, dim companion—a brown dwarf—and in any case they would’ve quickly returned to their hunting and gathering. But that star’s visit to our Solar System had an impact astronomers can still see today.
The star in question is called Scholz’s star, after astronomer Ralf-Dieter Scholz, the man who discovered it in 2013. A new study published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society by astronomers at the Complutense University of Madrid, and at the University of Cambridge, shows the impact Scholz’s star had. Though the star is now almost 20 light years away, its close approach to our Sun changed the orbits of some comets and asteroids in our Solar System.
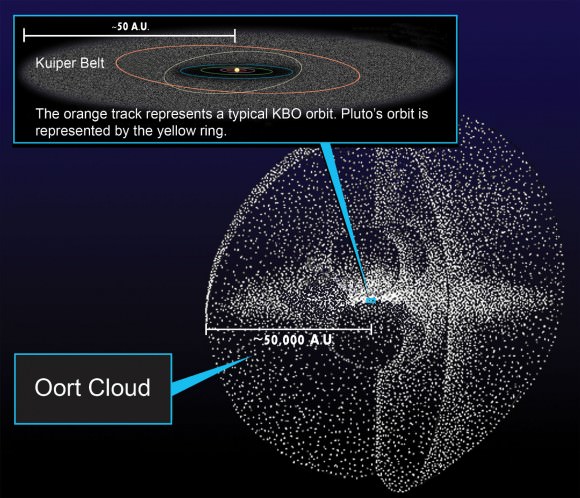
When it came to our Solar System 70,000 years ago, Scholz’s star entered the Oort Cloud. The Oort Cloud is a reservoir of mostly-icy objects that spans the range from about 0.8 to 3.2 light years from the Sun. Its visit to the Oort Cloud was first explained in a paper in 2015. This new paper follows up on that work, and shows what impact the visit had.
“Using numerical simulations, we have calculated the radiants or positions in the sky from which all these hyperbolic objects seem to come.” – Carlos de la Fuente Marcos, Complutense University of Madrid.
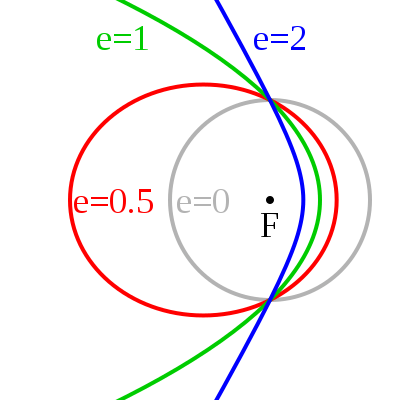
In this new paper, the astronomers studied almost 340 objects in our Solar System with hyperbolic orbits, which are V-shaped rather than elliptical. Their conclusion is that a significant number of these objects had their trajectories shaped by the visit from Scholz’s star. “Using numerical simulations, we have calculated the radiants or positions in the sky from which all these hyperbolic objects seem to come,” explains Carlos de la Fuente Marcos, a co-author of the study now published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. They found that there’s a cluster of these objects in the direction of the Gemini Constellation.
“In principle,” he adds, “one would expect those positions to be evenly distributed in the sky, particularly if these objects come from the Oort cloud. However, what we find is very different—a statistically significant accumulation of radiants. The pronounced over-density appears projected in the direction of the constellation of Gemini, which fits the close encounter with Scholz’s star.”
There are four ways that objects like those in the study can gain hyperbolic orbits. They might be interstellar, like the asteroid Oumuamua, meaning they gained those orbits from some cause outside our Solar System. Or, they could be natives of our Solar System, originally bound to an elliptical orbit, but cast into a hyperbolic orbit by a close encounter with one of the planets, or the Sun. For objects originally from the Oort Cloud, they could start on a hyperbolic orbit because of interactions with the galactic disc. Finally, again for objects from the Oort Cloud, they could be cast into a hyperbolic orbit by interactions with a passing star. In this study, the passing star is Scholz’s star.
The one potentially weak area of this study is pointed out by the authors themselves. As they say in their summary, “…due to their unique nature, the orbital solutions of hyperbolic minor bodies are based on relatively brief arcs of observation and this fact has an impact on their reliability. Out of 339 objects in the sample, 232 have reported uncertainties and 212 have eccentricity with statistical significance.” Translated, it means that some of the computed orbits of individual objects may have errors. But the team expects the overall conclusions of their study to be correct.
The study of minor objects with hyperbolic orbits has heated up since the interstellar asteroid Oumuamua made its visit. This new study successfully connects one population of hyperbolic objects with a pre-historic visit to our Solar System by another star. The team behind the study expects that follow up studies will confirm their results.