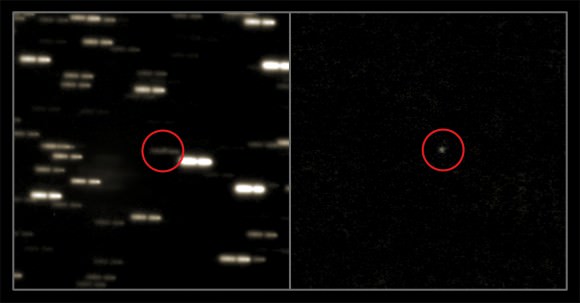
After four months behind the sun from Earth’s perspective, comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko is back in view — and brighter than ever! New pictures of the comet reveal it is 50 percent brighter than the last images available from October 2013. You can see the result below the jump.
“The new image suggests that 67P is beginning to emit gas and dust at a relatively large distance from the Sun,” stated Colin Snodgrass, a post-doctoral researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research in Germany. Snodgrass added that this confirms previous work he and his colleagues did showing that in March 2014, the comet’s activity could be seen from Earth.
Pictures were taken with the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope from 740 million kilometers (460 million miles) away. As you can see in the image below, several exposures were taken to obtain the fainter comet. And we know that scientists are eager to take a closer look with Rosetta.
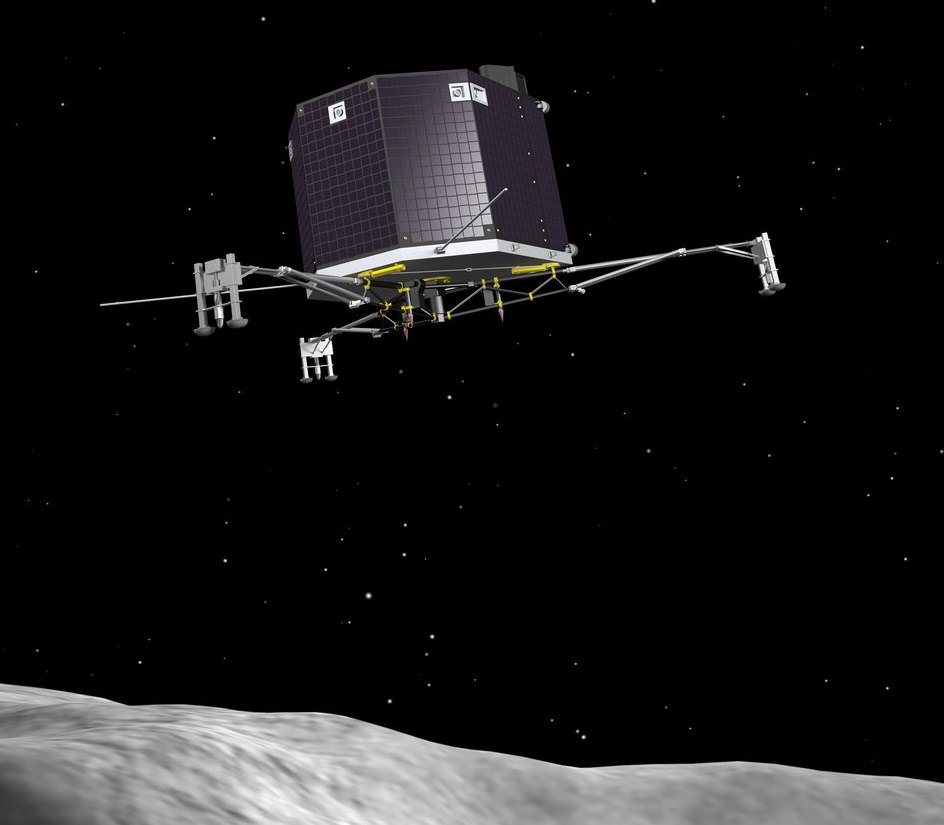
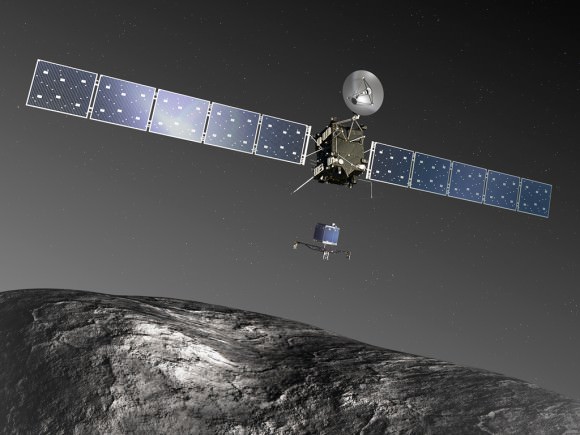
In January, the Rosetta spacecraft woke up after 31 months of hibernation (a little later than expected, but still healthy as ever.) It’s en route to meet up with the comet in August and will stay alongside it at least until 2015’s end. The next major step is to wake up its lander, Philae, which will happen later this month.
Should all go to plan, Philae will make a daring landing on the comet in November to get an up-close view of the activity as the comet flies close to the sun. You can read more details in this past Universe Today story.




