NASA today (July 9) named the first four astronauts who will fly on the first U.S. commercial spaceflights in private crew transportation vehicles being built by Boeing and SpaceX – marking a major milestone towards restoring American human launches to U.S. soil as soon as mid-2017, if all goes well.
The four astronauts chosen are all veterans of flights on NASA’s Space Shuttles and to the International Space Station (ISS); Robert Behnken, Eric Boe, Douglas Hurley and Sunita Williams. They now form the core of NASA’s commercial crew astronaut corps eligible for the maiden test flights on board the Boeing CST-100 and Crew Dragon astronaut capsules.
Behnken, Boe and Hurley have each launched on two shuttle missions and Williams is a veteran of two long-duration flights aboard the ISS after launching on both the shuttle and Soyuz. All four served as military test pilots prior to being selected as NASA astronauts.
The experienced quartet of space flyers will work closely with Boeing and SpaceX as they begin training and prepare to launch aboard the first ever commercial ‘space taxi’ ferry flight missions to the ISS and back – that will also end our sole source reliance on the Russian Soyuz capsule for crewed missions to low-Earth orbit and further serve to open up space exploration and transportation services to the private sector.
Boeing and SpaceX were awarded contracts by NASA Administrator Charles Bolden in September 2014 worth $6.8 Billion to complete the development and manufacture of the privately developed CST-100 and Crew Dragon astronaut transporters under the agency’s Commercial Crew Transportation Capability (CCtCap) program and NASA’s Launch America initiative.
“I am pleased to announce four American space pioneers have been selected to be the first astronauts to train to fly to space on commercial crew vehicles, all part of our ambitious plan to return space launches to U.S. soil, create good-paying American jobs and advance our goal of sending humans farther into the solar system than ever before,” said NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, in a statement.
“These distinguished, veteran astronauts are blazing a new trail — a trail that will one day land them in the history books and Americans on the surface of Mars.”

The selection of astronauts for rides with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP) comes almost exactly four years to the day since the last American manned space launch of Space Shuttle Atlantis on the STS-135 mission to the space station on July 8, 2011 from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
Hurley was a member of the STS-135 crew and served as shuttle pilot under NASA’s last shuttle commander, Chris Ferguson, who is now Director of Boeing’s CST-100 commercial crew program. Read my earlier exclusive interviews with Ferguson about the CST-100 – here and here.
Since the retirement of the shuttle orbiters, all American and ISS partner astronauts have been forced to hitch a ride on the Soyuz for flights to the ISS and back, at a current cost of over $70 million per seat.
“Our plans to return launches to American soil make fiscal sense,” Bolden elaborated. “It currently costs $76 million per astronaut to fly on a Russian spacecraft. On an American-owned spacecraft, the average cost will be $58 million per astronaut.
Behnken, Boe, Hurley and Williams are all eager to work with the Boeing and SpaceX teams to “understand their designs and operations as they finalize their Boeing CST-100 and SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and operational strategies in support of their crewed flight tests and certification activities as part of their contracts with NASA.”
Until June 2015, Williams held the record for longest time in space by a woman, accumulating 322 days in orbit. Behnken is currently the chief of the astronaut core and conducted six space walks at the station. Boe has spent over 28 days in space and flew on the final mission of Space Shuttle Discovery in Feb. 2011 on STS-133.
The first commercial crew flights under the CCtCAP contract could take place in 2017 with at least one member of the two person crews being a NASA astronaut – who will be “on board to verify the fully-integrated rocket and spacecraft system can launch, maneuver in orbit, and dock to the space station, as well as validate all systems perform as expected, and land safely,” according to a NASA statement.
The second crew member could be a company test pilot as the details remain to be worked out.

The actual launch date depends on the NASA budget allocation for the Commercial Crew Program approved by the US Congress.
Congress has never approved NASA’s full funding request for the CCP program and has again cut the program significantly in initial votes this year. So the outlook for a 2017 launch is very uncertain.
Were it not for the drastic CCP cuts we would be launching astronauts this year on the space taxis.
“Every dollar we invest in commercial crew is a dollar we invest in ourselves, rather than in the Russian economy,” Bolden emphasizes about the multifaceted benefits of the commercial crew initiative.
Under the CCtCAP contract, NASA recently ordered the agency’s first commercial crew mission from Boeing – as outlined in my story here. SpaceX will receive a similar CCtCAP mission order later this year.
At a later date, NASA will decide whether Boeing or SpaceX will launch the actual first commercial crew test flight mission to low Earth orbit.

“This is a new and exciting era in the history of U.S. human spaceflight,” said Brian Kelly, director of Flight Operations at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, in a statement.
“These four individuals, like so many at NASA and the Flight Operations Directorate, have dedicated their careers to becoming experts in the field of aeronautics and furthering human space exploration. The selection of these experienced astronauts who are eligible to fly aboard the test flights for the next generation of U.S. spacecraft to the ISS and low-Earth orbit ensures that the crews will be well-prepared and thoroughly trained for their missions.”
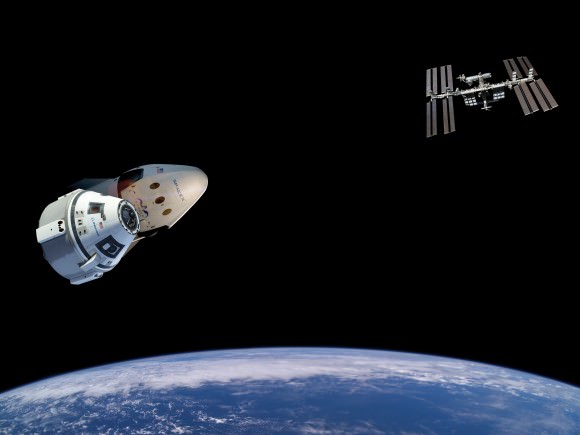
Both the CST-100 and Crew Dragon will typically carry a crew of four NASA or NASA-sponsored crew members, along with some 220 pounds of pressurized cargo. Each will also be capable of carrying up to seven crew members depending on how the capsule is configured.
The spacecraft will be capable to remaining docked at the station for up to 210 days and serve as an emergency lifeboat during that time.
The NASA CCtCAP contracts call for a minimum of two and a maximum potential of six missions from each provider.
The station crew will also be enlarged to seven people that will enable a doubling of research time.
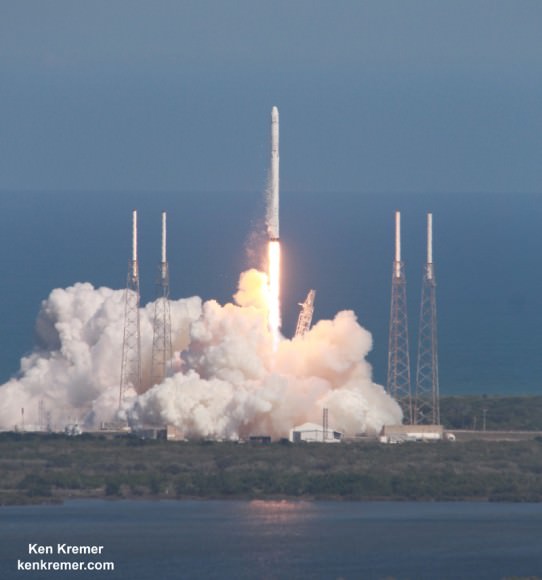
The CST-100 will be carried to low Earth orbit atop a man-rated United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket launching from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida. It enjoys a 100% success rate.
Boeing will first conduct a pair of unmanned and manned orbital CST-100 test flights earlier in 2017 in April and July, prior to the operational commercial crew rotation mission to confirm that their capsule is ready and able and met all certification milestone requirements set by NASA.
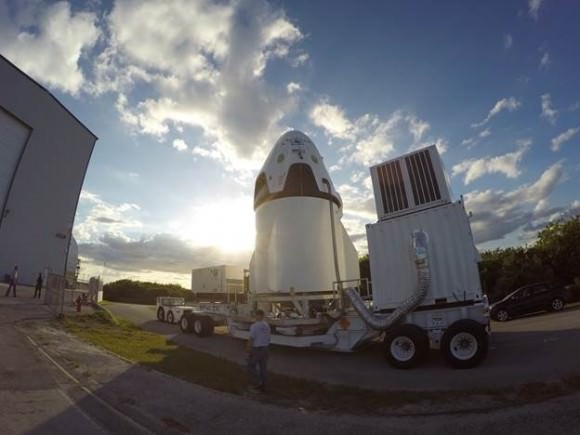
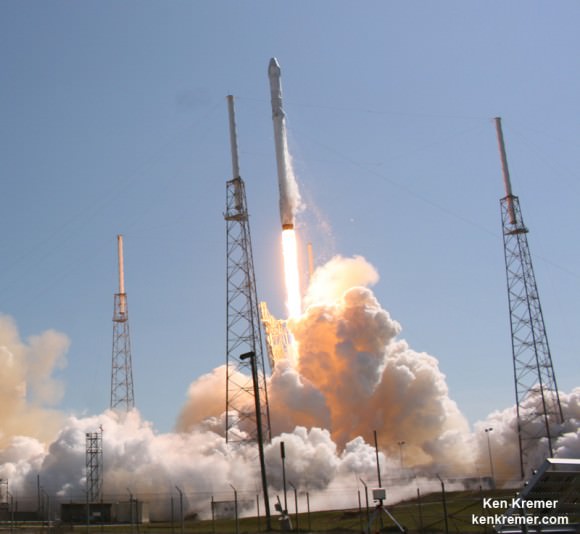
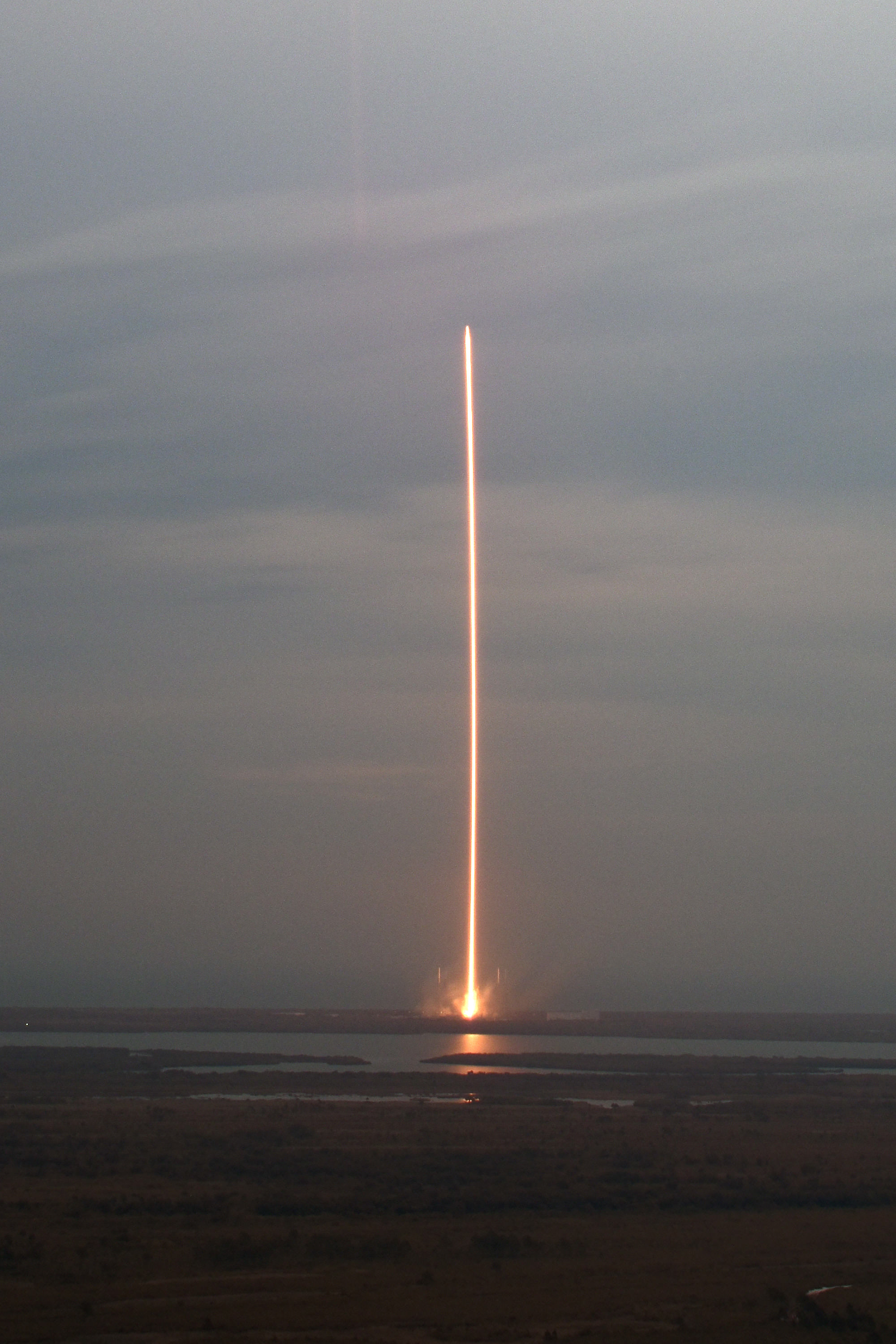
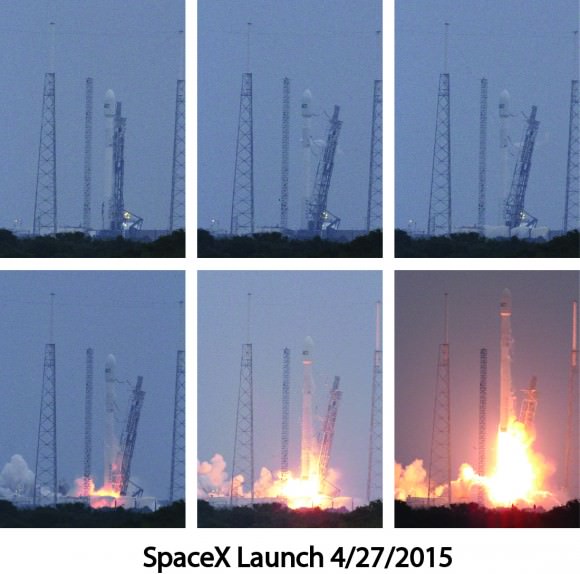
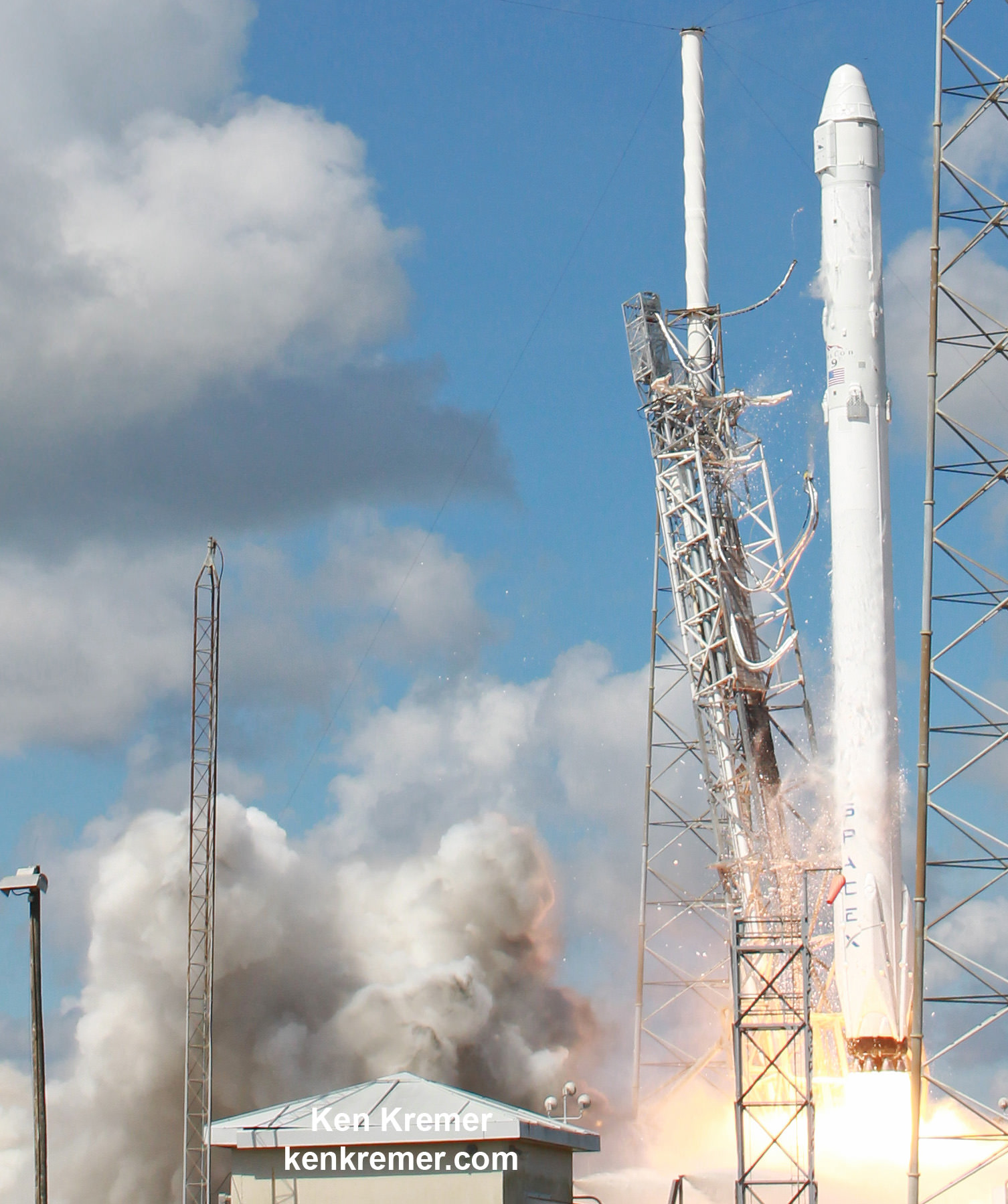
The Crew Dragon will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. It enjoyed a 100% success rate until last weeks launch on its 19th flight which ended with an explosion two minutes after liftoff from Cape Canaveral on June 28, 2015.

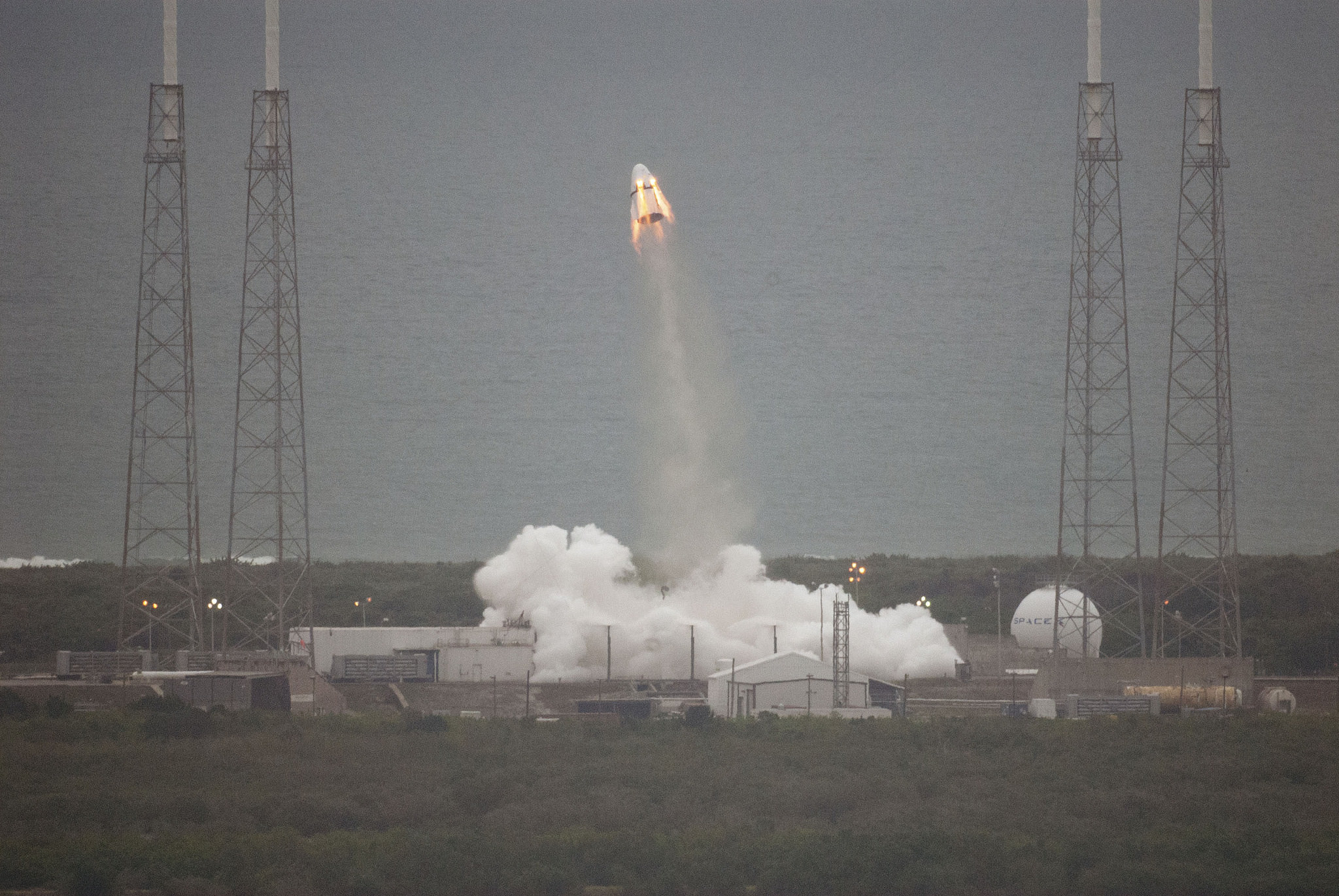
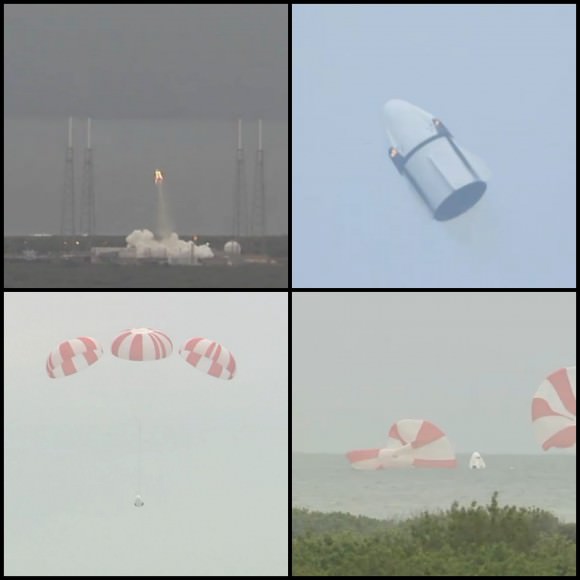
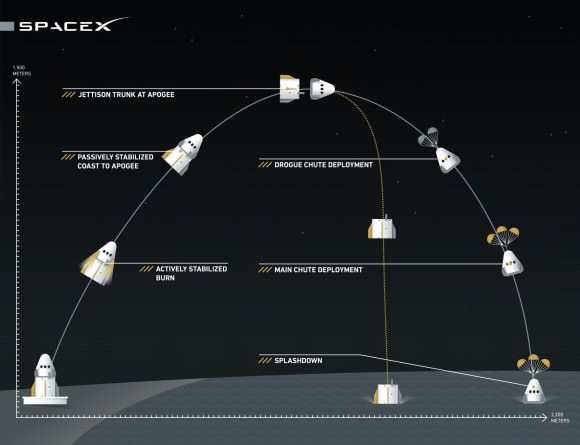
SpaceX conducted a successful Pad Abort Test of the Crew Dragon on May 6, as I reported here. The goal was to test the spacecrafts abort systems that will save astronauts lives in a split second in the case of a launch emergency such as occurred during the June 28 rocket failure in flight that was bound for the ISS with the initial cargo version of the SpaceX Dragon.
SpaceX plans an unmanned orbital test flight of Crew Dragon perhaps by the end of 2016. The crewed orbital test flight would follow sometime in 2017.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.