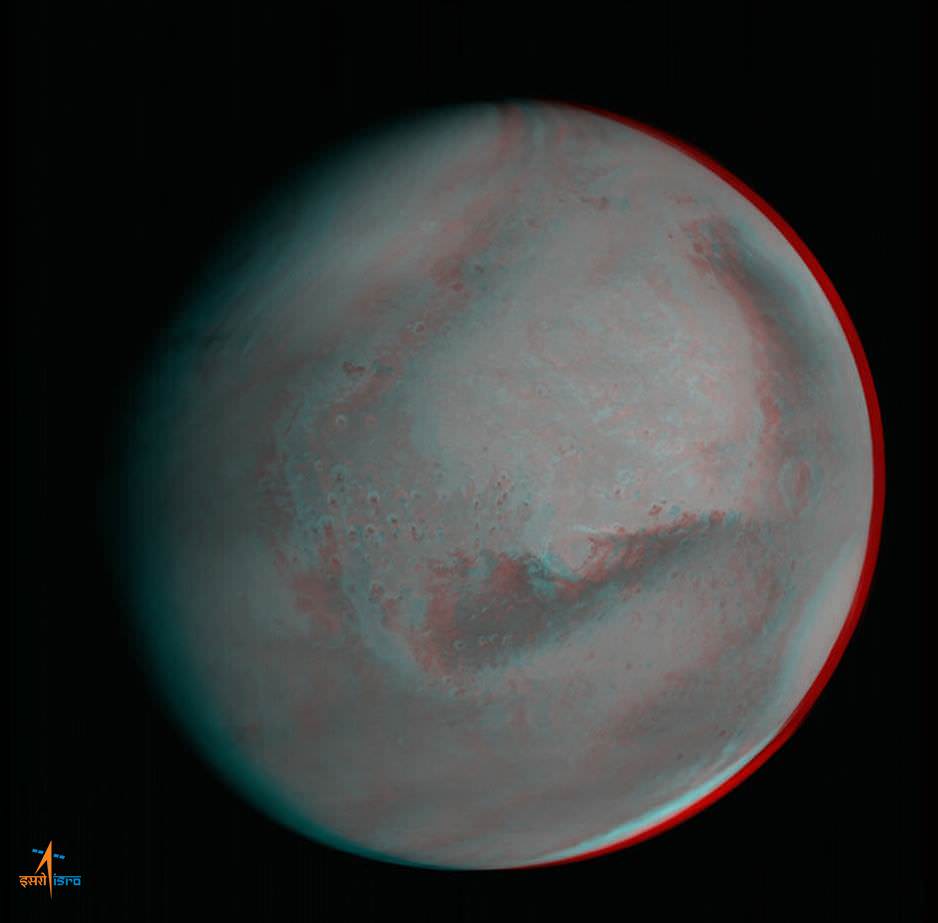
Here’s another breathtakingly glorious view from India’s Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) – her first global 3-D portrait of her new home careening around the Red Planet.
MOM is India’s first deep space voyager to explore beyond the confines of her home planet’s influence and just successfully arrived at the Red Planet after the “history creating” orbital insertion maneuver on Sept. 23/24 following a ten month journey.
This newly released 3-D view from MOM expands upon the initial 2-D global color view of Mars released by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), India’s space agency. See below and detailed in my earlier story – here.
The 3-D image was generated from multiple pictures acquired by MOM’s on-board Mars Color Camera on Sept 28, 2014, from the very high altitude of approximately 74,500 kilometers as the spacecraft orbits Mars.
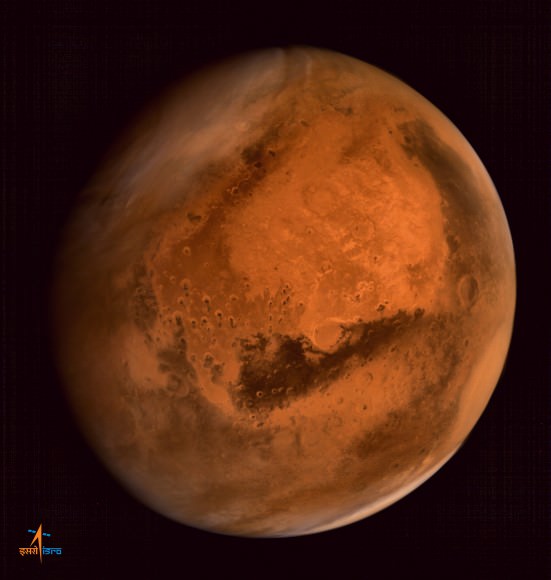

The images were taken by the tri-color camera as MOM swooped around the Red Planet in a highly elliptical orbit whose nearest point to Mars (periapsis) is at 421.7 km and farthest point (apoapsis) at 76,993.6 km, according to ISRO.
Therefore, the 3-D Red Planet portrait was captured nearly at apoapsis. And being three dimensional, it gives a stereo sense of the huge dust storm swirling over a large swath of the planet’s Northern Hemisphere set against the blackness of space.
Below right is the southern polar ice cap. To see the 3-D effect, whip out your handy pair of left-eye red, right-eye blue color anaglyph glasses.
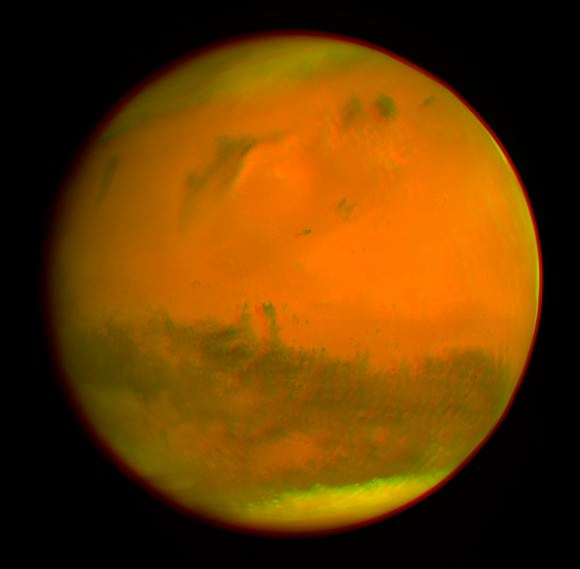
And while we’re on the subject of spacely 3-D, it’s worth noting that another of humanity’s ground breaking probes currently making news – ESA’s comet hunting Rosetta probe – likewise snapped a glorious 3-D view of Mars way back in 2007, during the brief, but critical, gravity assist slingshot maneuver that flung Rosetta along her vast 10 year path through interplanetary space.
So by way of comparison let’s take a trip down memory lane and be sure to look back at Rosetta’s global 3-D Martian views (below) taken by the high resolution OSIRIS camera on 24 February 2007 at 19:28 CET from a distance of about 240,000 kilometers.
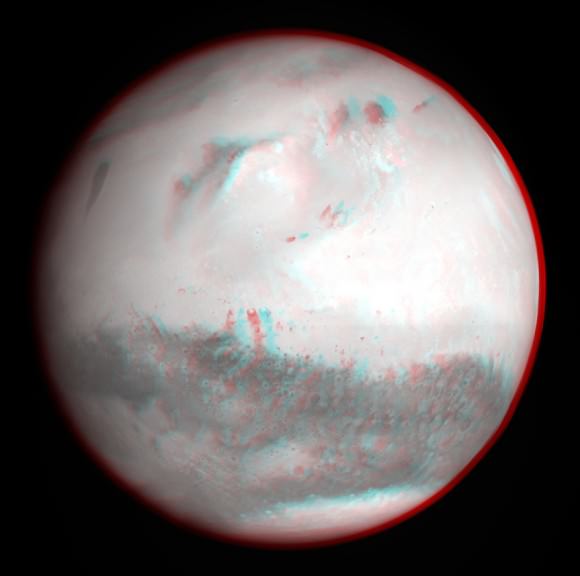
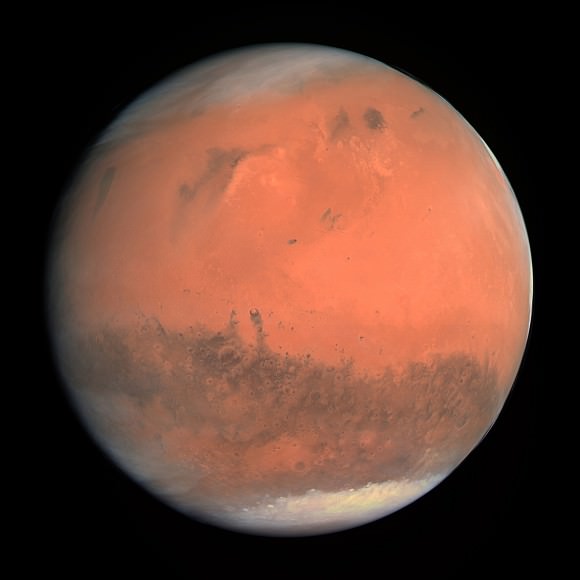
The Rosetta team created both color and black & white 3-D views of Mars.

And be sure to check out Rosetta’s 2-D true color view showing a different swatch of the Red Planet compared to MOM, along with a more expansive view of the southern polar ice cap.

The $73 million MOM mission is expected to last at least six months.
MOM’s success follows closely on the heels of NASA’s MAVEN orbiter which also successfully achieved orbit barely two days earlier on Sept. 21 and could last 10 years or more.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.


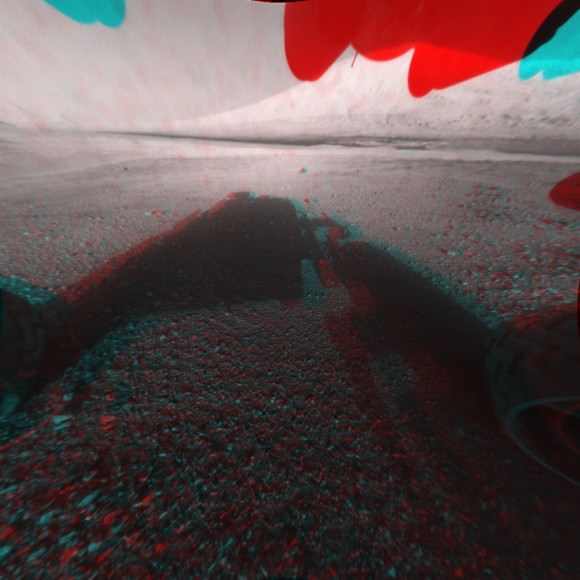
![673969main_PIA15993-43_full[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/673969main_PIA15993-43_full1-580x435.jpg)