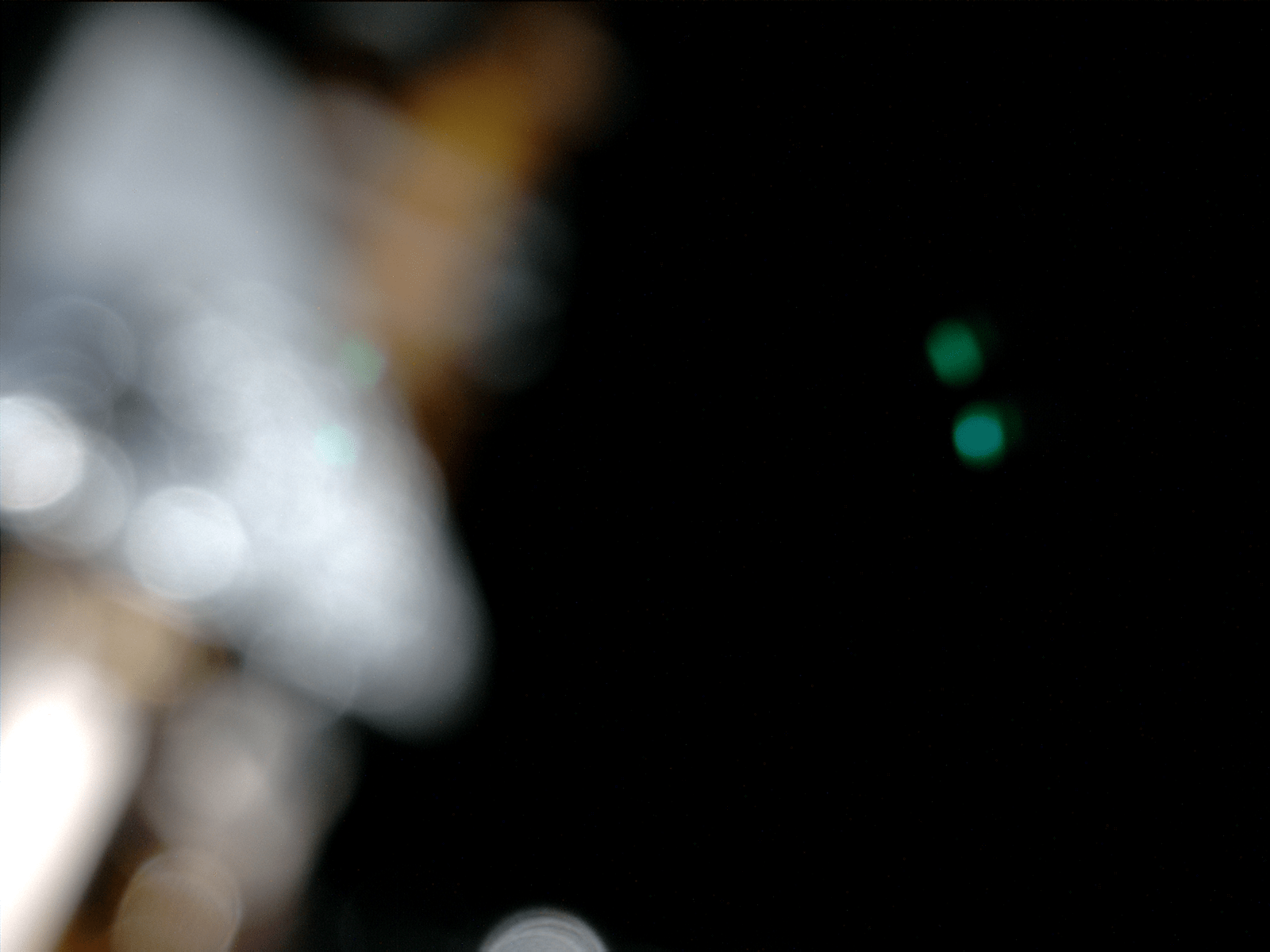[/caption]
Take a look around Curiosity’s cozy cabin! Ok, there’s really not much to see (she didn’t get a window seat) but when the image above was taken by the rover’s Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) camera on April 20, the spacecraft she’s tucked into was just over 120 million km (74 million miles) from Earth, en route to Mars. In other words, just past those blurry components and outside that dark shell is real outer space… that’s cool!
This color image was planned by the MSL team, used to confirm that MAHLI is operating as it should. The two green dots are reflections of the camera’s LED lights, and the rusty-orange out-of-focus parts are cables. The silver thing is a bracket holding said cables.
So why is this fancy camera taking blurry pictures (and the folks at NASA are happy about it?) Since MAHLI is designed to take both close-up images of rocks on Mars as well as landscape shots, it has a focusing motor. But when it’s not in use — such as during its current 11-month-long cruise to Mars — the motor puts the focusing lens into a safe position to protect it from damage during launch, entry and landing.
Positioned this way, MAHLI can only focus on objects 2 cm (less than an inch) away from its lens, and there simply aren’t any inside the capsule.
Of course, once Curiosity arrives at Mars and completes her exciting landing at Gale Crater, MAHLI will have plenty of things to take pictures of! Until then we’ll be patient, it can take a rest and we can rest assured that it’s working just fine.
Keep up with the latest news from the Mars Science Laboratory team here.
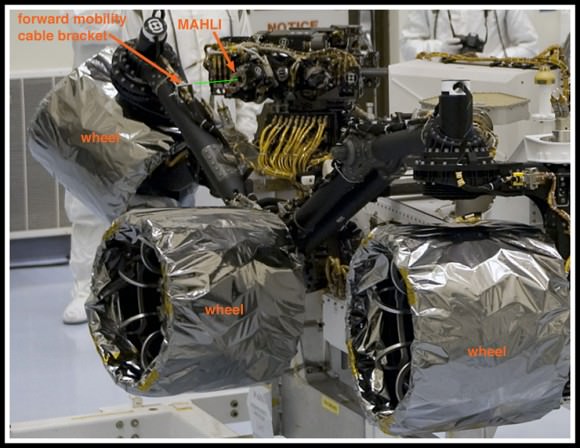
San Diego-based Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS) built and operates the Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) aboard the Curiosity Mars rover. MSSS also built and operates the rover’s Mastcams and Mars Descent Imager. Read more about their contributions to Curiosity’s exploration mission here.