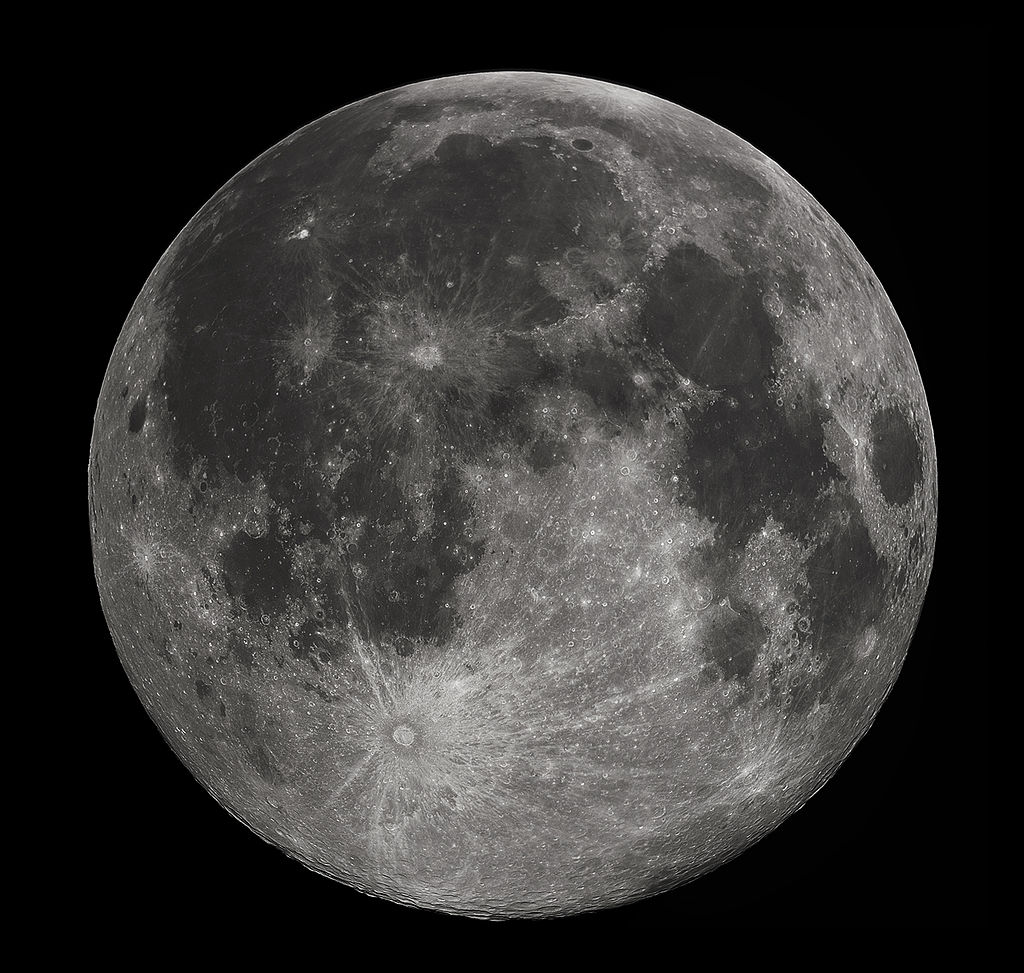
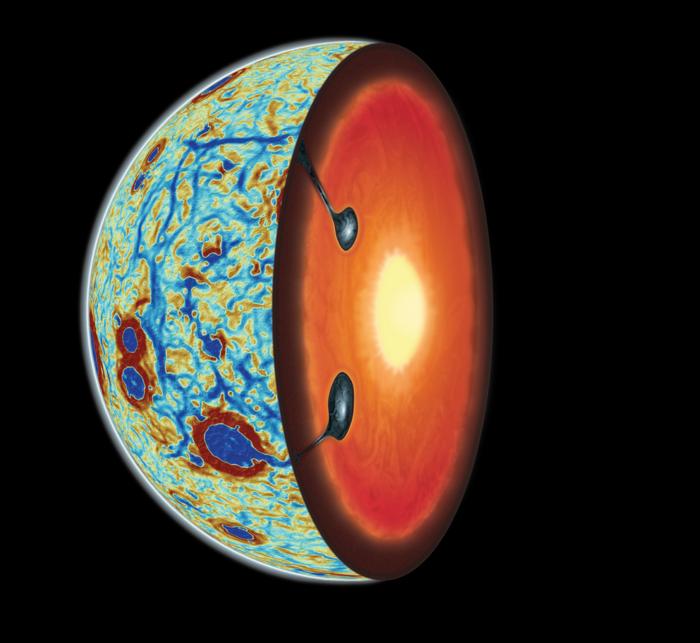
Pink Floyd was wrong, there is no dark side to the Moon. There is however, a far side. The tidal effects between the Earth and Moon have caused this captured or synchronous rotation. The two sides display very different geographical features; the near side with mare and ancient volcanic flows while the far side displaying craters within craters. New research suggests the Moon has turned itself inside out with heavy elements like titanium returning to the surface. It’s now thought that a giant impact on the far side pushed titanium to the surface, creating a thinner more active near side.
Continue reading “Finally, an Explanation for the Moon’s Radically Different Hemispheres”Finally, an Explanation for the Moon’s Radically Different Hemispheres