Hurricane Danny, the first Atlantic Ocean hurricane of the 2015 season has been caught on camera by NASA astronaut Scott Kelly, in a beautiful image taken on Thursday, August 20 at 6 a.m. EDT from his glorious perch aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
Poking majestically down at the sprawling hurricane is the space stations Canadian-built robotic arm that will be used by Kelly in a few days to grapple Kounotori, the Japanese cargo ship launched earlier this week and berth it at a docking port.
Kelly is nearly five months into his year-long stay aboard the ISS and is a prolific photographer of the natural wonders of our home planet.
“Hurricane Danny. Keeping an eye on you from the International Space Station. Looks like you’re 1st in the Atlantic this year. Stay safe below! #YearInSpace,” wrote Kelly on his Facebook and twitter pages.
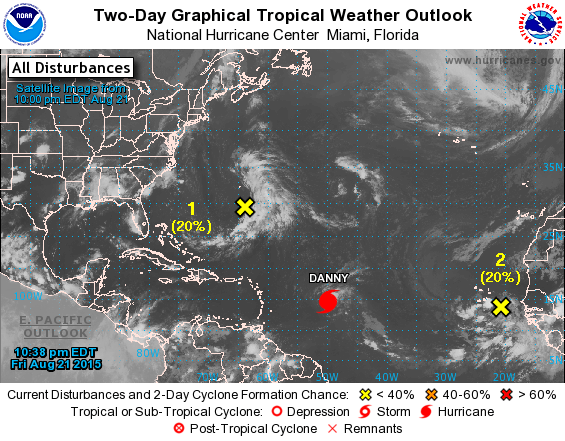
Danny had risen to a Category 3 hurricane by Friday afternoon, August 21, with winds over 115 mph and was moving westward in the Central Atlantic Ocean towards the Leeward Islands in the Caribbean.
By 11 a.m. EDT (1500 UTC) on Friday, August 21, the eye of Hurricane Danny was located near latitude 14.0 North, longitude 48.2 West, according to NASA. The center of Danny was about 930 miles (1,195 km) east of the Leeward Islands. With maximum sustained winds of near 105 mph (165 kph), Danny was a Category 2 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale.
By 8:00 p.m. Friday evening, Friday, the National Hurricane Center said Danny was located over the central tropical Atlantic Ocean about 800 miles east of the Leeward Islands.
Late this evening at 11 p.m., the National Hurricane Center said it had weakened slightly back to a Category 2 storm with maximum winds of 110 mph and was located at 14.8°N and 49.8°W while moving west northwest at 10 mph.
The NASA GOES-East animation below combines visible and infrared imagery showing Hurricane Danny’s movement in the eastern and central Atlantic Ocean from Aug. 18 to 21, 2015.
Video caption: Hurricane Danny Seen By GOES-East. This animation of visible and infrared imagery of Hurricane Danny in the Central Atlantic Ocean was taken from NOAA’s GOES-East satellite from Aug. 18 to 21. Credits: NASA/NOAA GOES Project
Forecasters with the National Hurricane Center think it may weaken over the next few days as it heads towards the Caribbean islands.
“Vertical shear is expected to increase further during the next couple of days, which should allow drier air in the surrounding environment to penetrate into Danny’s circulation. Therefore,there is no change in the thinking that Danny should weaken as it approaches and moves across the Leeward Islands and the Greater Antilles during the forecast period.”
Danny could reach Puerto Rico by Monday in a weakened state.
Although it’s still far away from the US, it’s not expected to impact the East Coast but that could change.
If Danny were to take aim at the US, it could impact plans to launch the Air Force MUOS-4 satellite on Aug. 31 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station by United Launch Alliance (ULA).
Here’s a map showing the current location:
On Aug. 19, NASA’s Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission core satellite passed over Danny and analyzed the structure of its rainfall, as seen in this image.
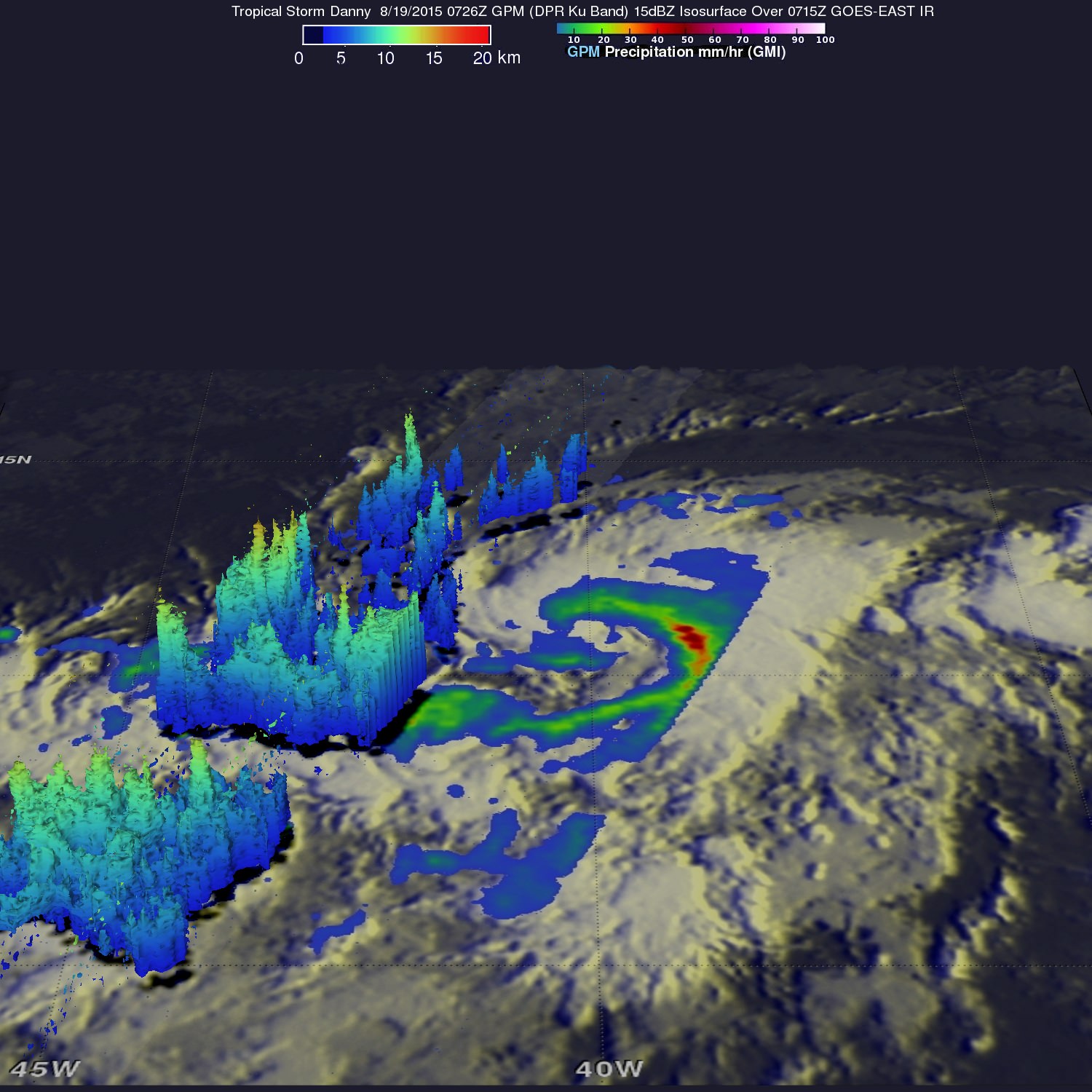
A research team at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, created a 3-D rendering of Danny using data from the GPM DPR (Dual-frequency Precipitation Radar) instrument.
“GPM showed that Danny was still in the process of becoming organized. The rain structure was still very asymmetric as noted by a large rain band being located mainly on the eastern side of the storm. Within this rain band, GPM detected rain rates of up to 73.9 mm/hour. At the time of this image, Danny was still a minimal tropical storm with sustained winds estimated at 50 mph by the National Hurricane Center (NHC),” said officials.
And dont forget that you can watch Commander Scott Kelly and his five international crew mates on a regular basis as they soar overhead. Just click on NASA’s Spot the Station link and plug in your location.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.

