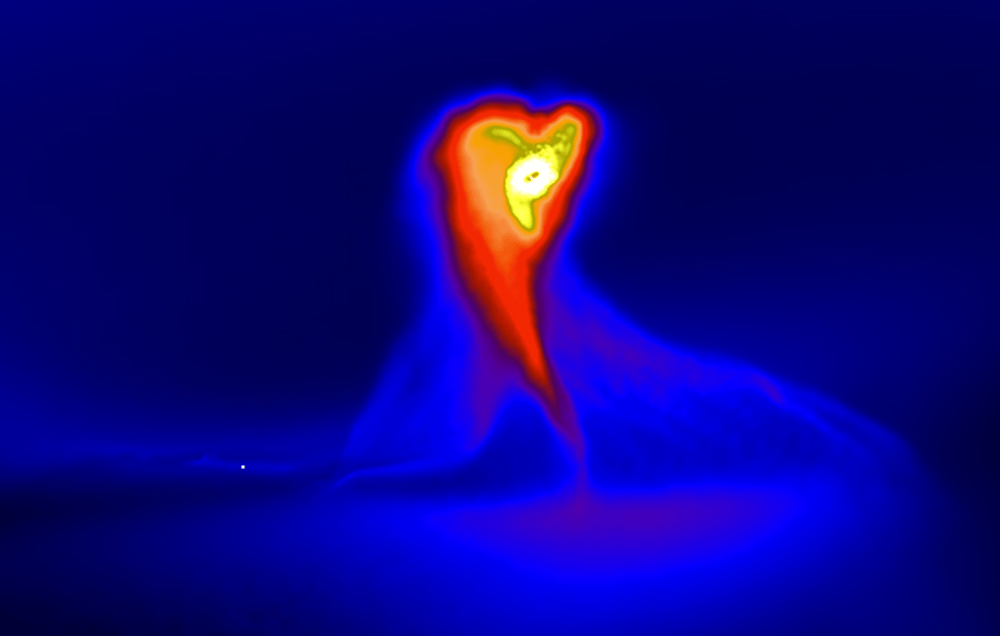
In 1936 astronomers watched as FU Orionis, a dim star in the Orion constellation, brightened dramatically. The star’s brightness increased by a factor of 100 in a matter of months. When it peaked, it was 100 times more luminous than our Sun.
Astronomers had never observed a young star brightening like this.
Continue reading “The Hubble and FU Orionis: a New Look at an Old Mystery”

![Artist’s impression of one of the two stars in the FU Orionis binary system, surrounded by an accreting disk of material. What has caused this star — and others like it — to dramatically brighten? [NASA/JPL-Caltech]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/PIA20689_fig1.jpg)