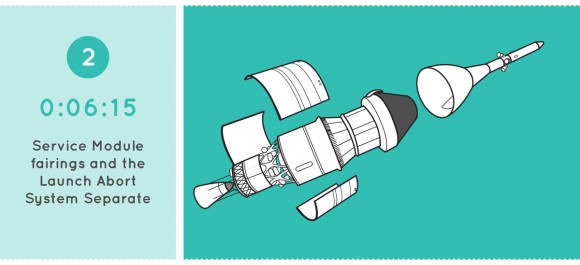
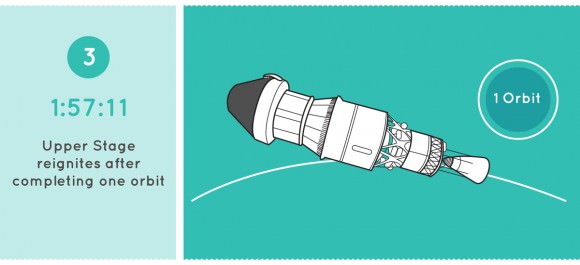
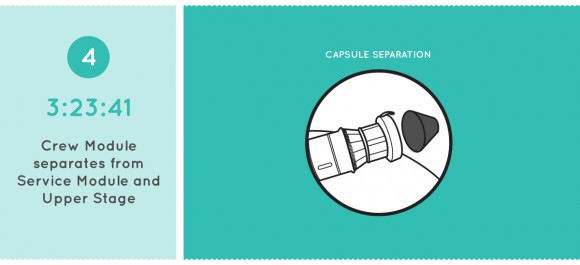
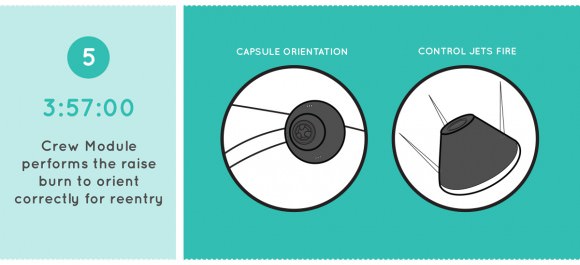
Video Caption: Animation details NASA’s Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) mission launching on Dec. 4. 2014. Credit: NASA
It’s not Science Fiction! It’s Not Star Trek!
No. It’s a really, really big NASA Mission! It’s Orion!
In fact, it’s the biggest and most important development in US Human Spaceflight since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011.
Orion is launching soon on its first flight, the pathfinding Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) mission and sets NASA on the path to send humans to Mars in the 2030s.
Watch this cool NASA animation beautifully detailing every key step of Orion’s First Launch!
Orion is designed to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before. Even farther into deep space than NASA’s Apollo moon landing which ended more than four decades ago!
We are T-MINUS 4 Days and Counting to the inaugural blastoff of Orion as of today, Sunday, November 30, 2014.
To learn even more about the 8 major events and goals happening during Orion’s EFT-1 mission be sure to check out my recent story with NASA’s fabulous new set of infographics – here.
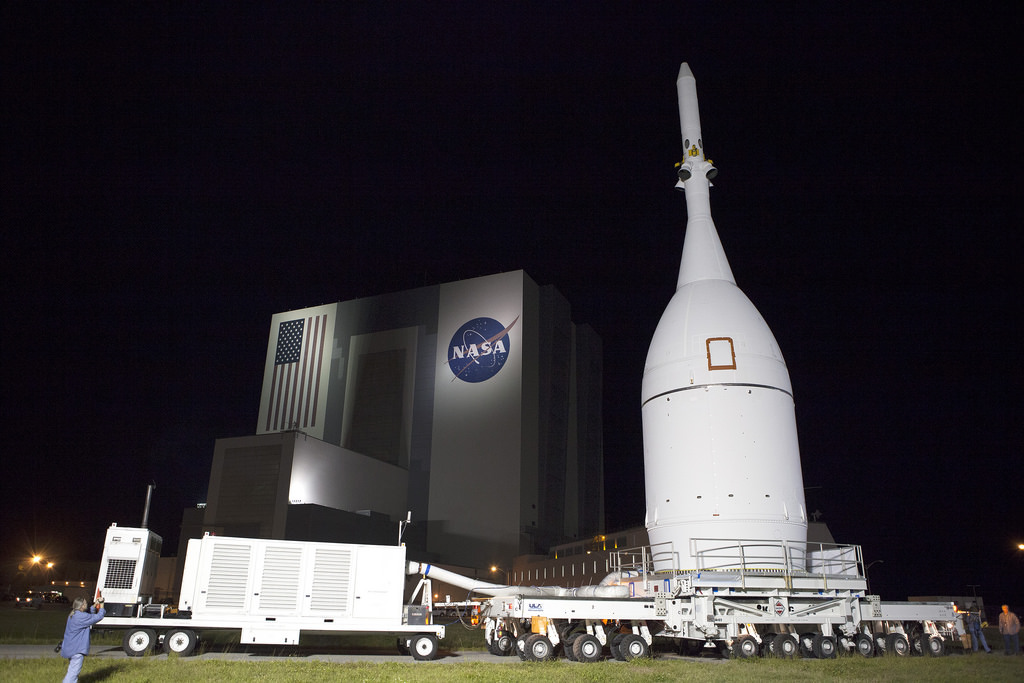
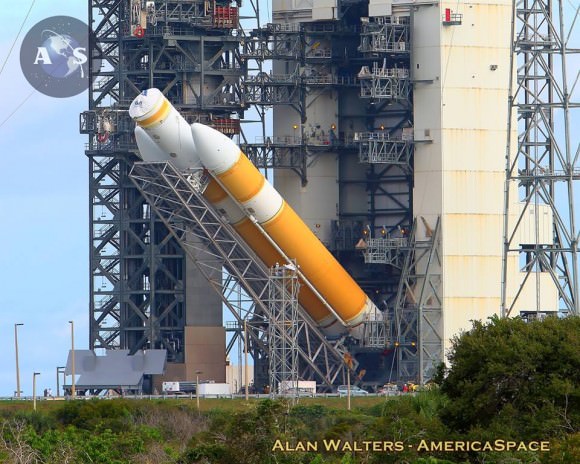
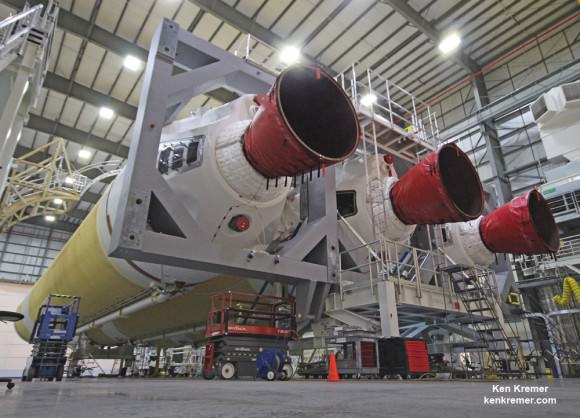
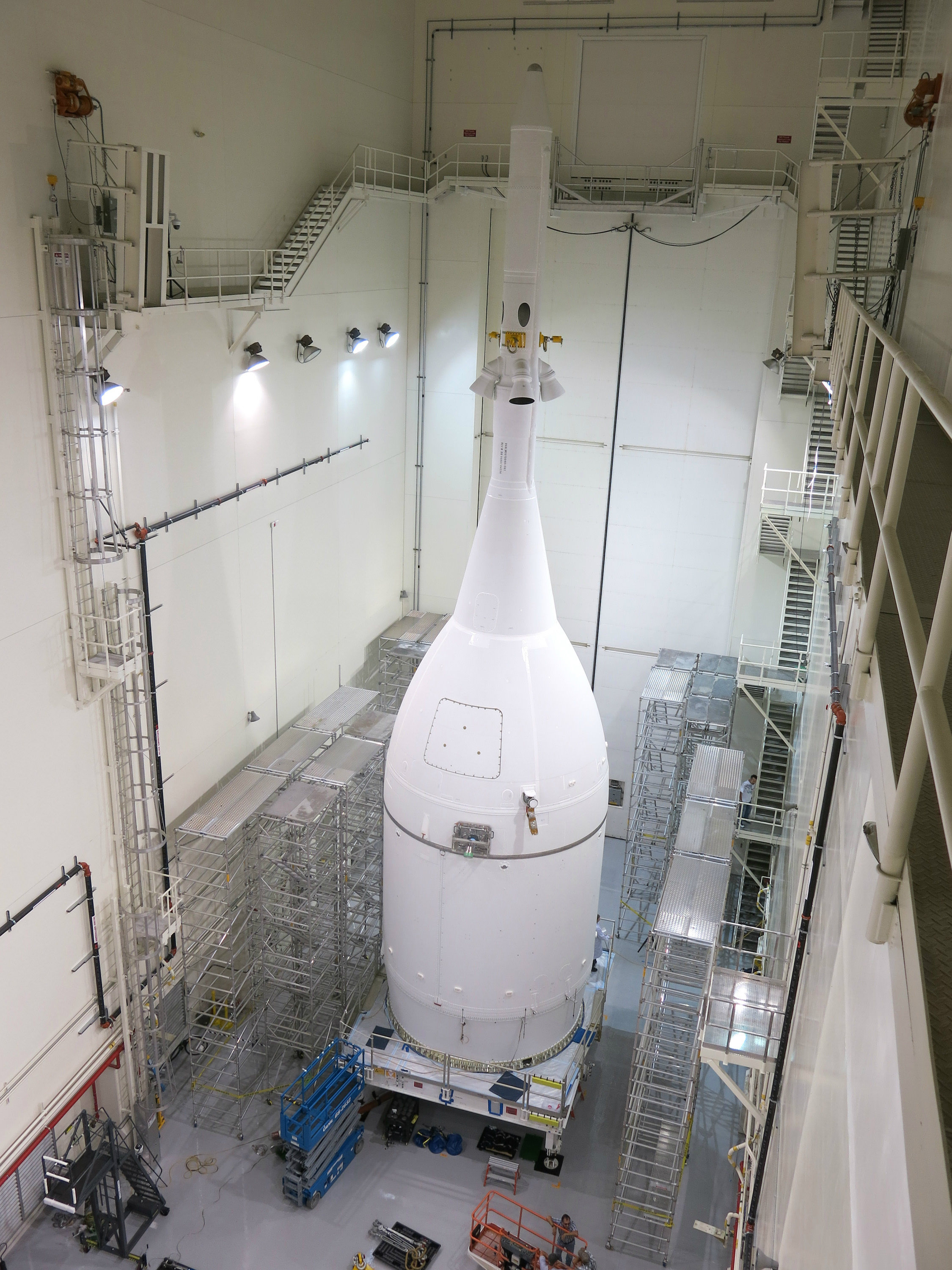
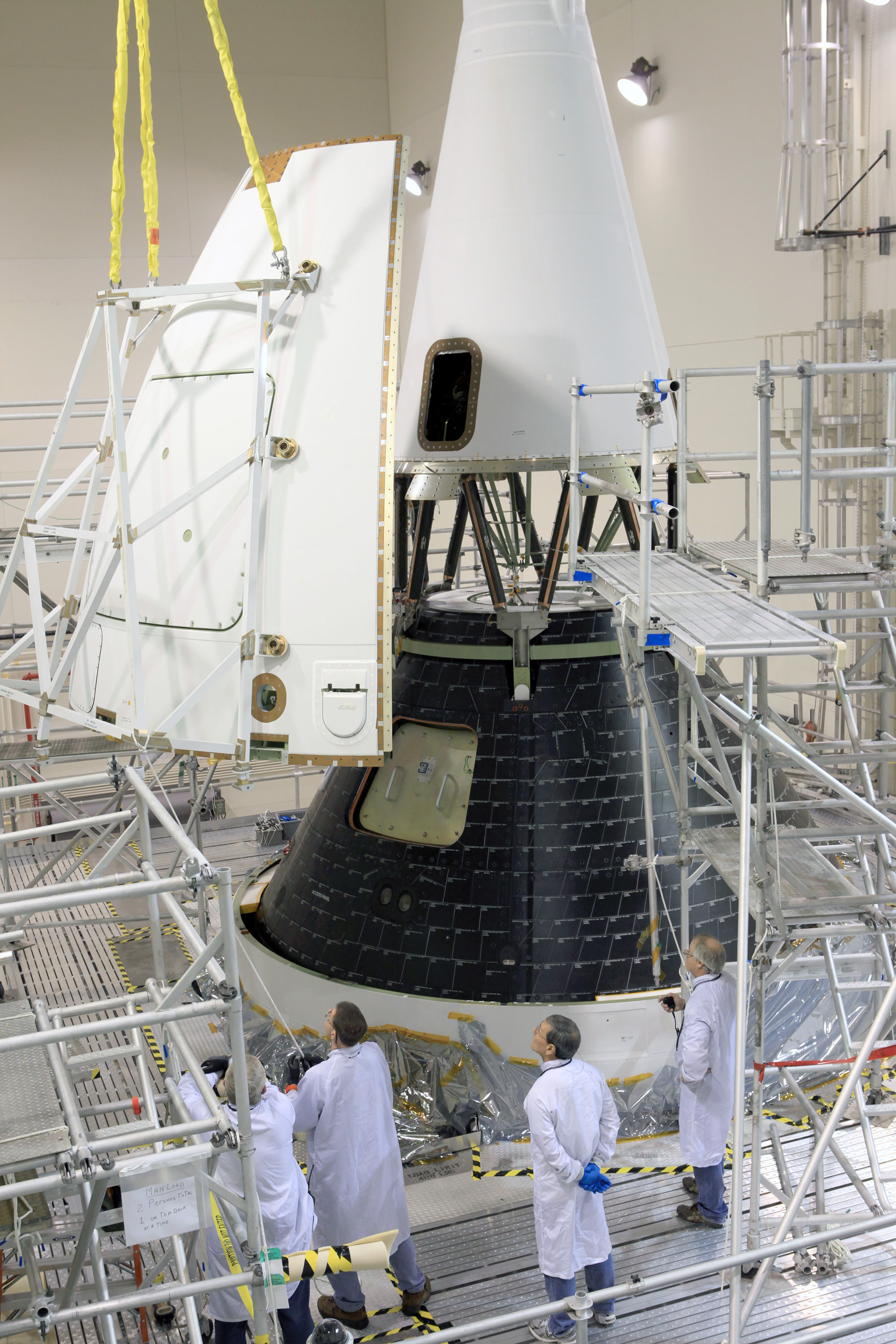
Every aspect of the final processing steps now in progress by engineers and technicians from NASA, rocket provider United Launch Alliance, and Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin is proceeding smoothly and marching towards launch.
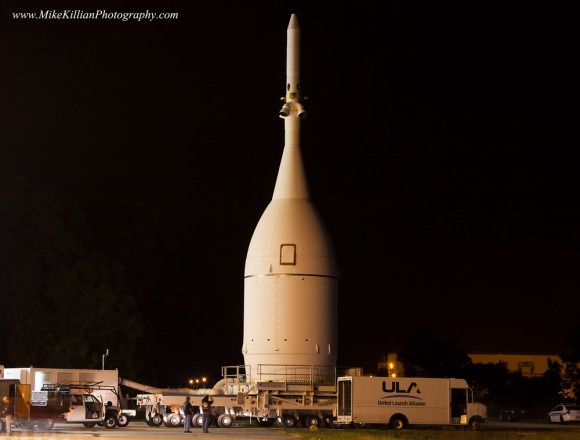

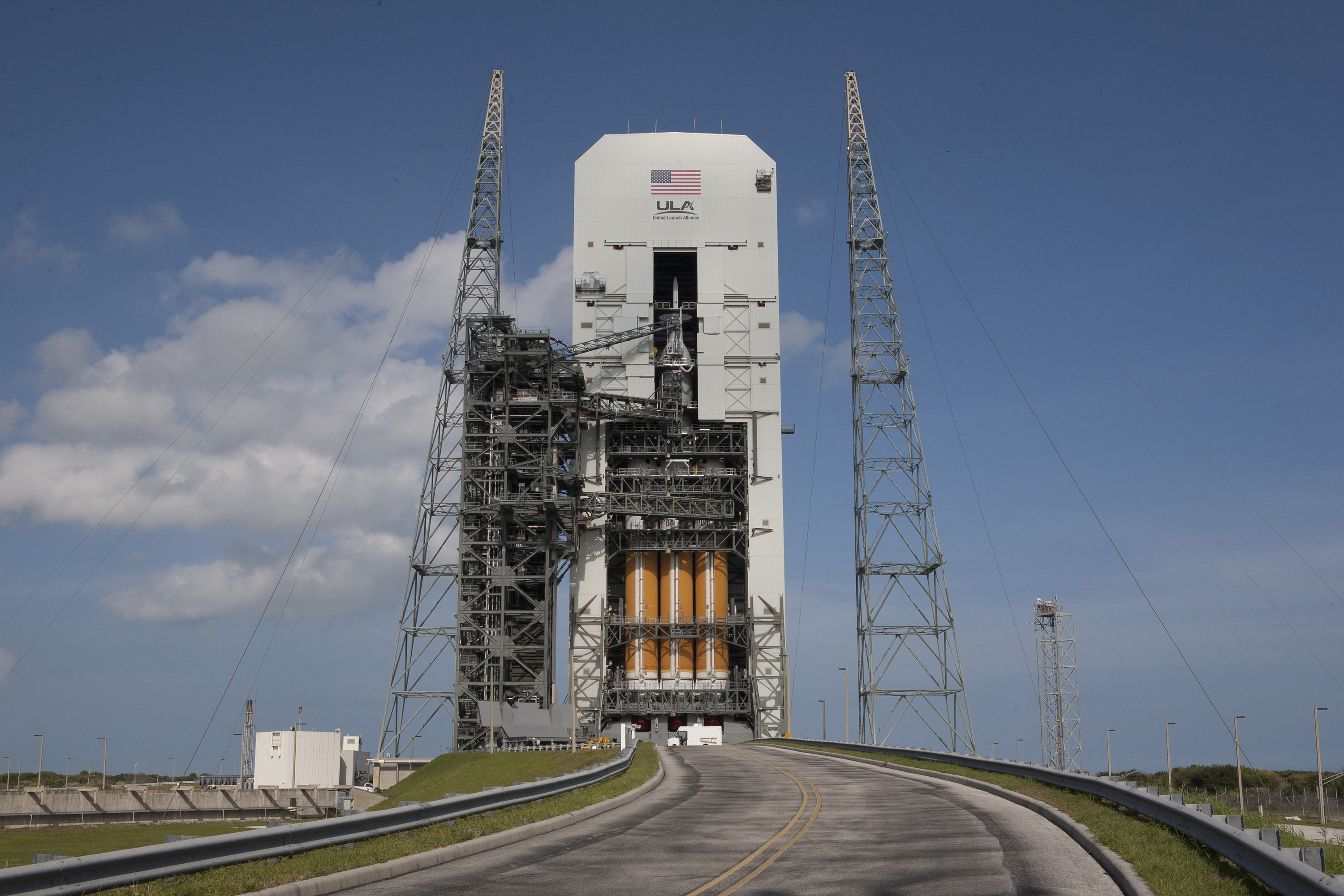
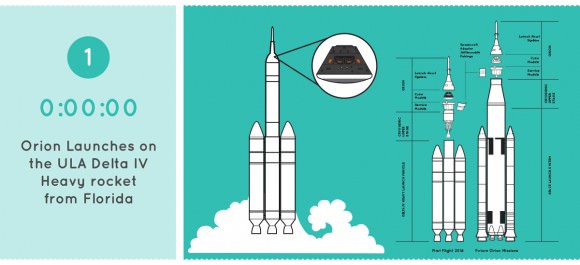
Orion will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket on its inaugural test flight to space on the uncrewed Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) mission at 7:05 a.m. EST on December 4, 2014, from Space Launch Complex 37 (SLC-37) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
The two-orbit, four and a half hour Orion EFT-1 flight around Earth will lift the Orion spacecraft and its attached second stage to an orbital altitude of 3,600 miles, about 15 times higher than the International Space Station (ISS) – and farther than any human spacecraft has journeyed in 40 years.
EFT-1 will test the rocket, second stage, jettison mechanisms as well as avionics, attitude control, computers and electronic systems inside the Orion spacecraft.
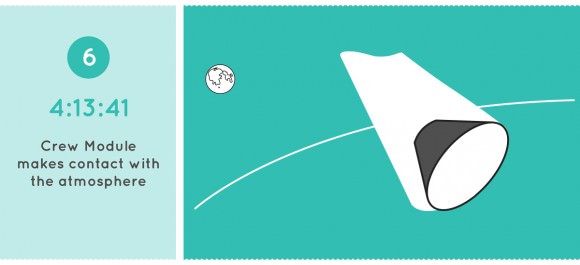
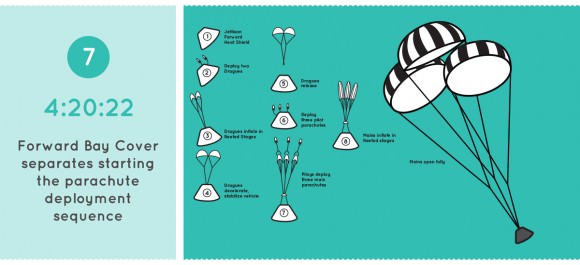
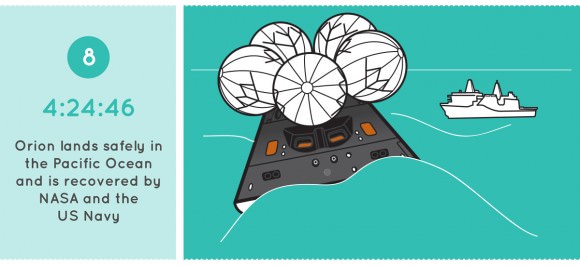
Then the spacecraft will carry out a high speed re-entry through the atmosphere at speeds approaching 20,000 mph and scorching temperatures near 4,000 degrees Fahrenheit to test the heat shield, before splashing down for a parachute assisted landing in the Pacific Ocean.
Orion is NASA’s next generation human rated vehicle that will carry America’s astronauts beyond Earth on voyages venturing farther into deep space than ever before – beyond the Moon to Asteroids, Mars, and other destinations in our Solar System.
NASA TV will provide several hours of live coverage
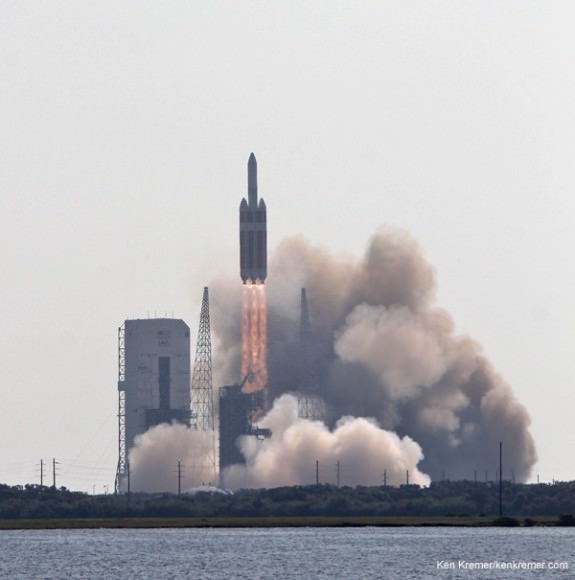

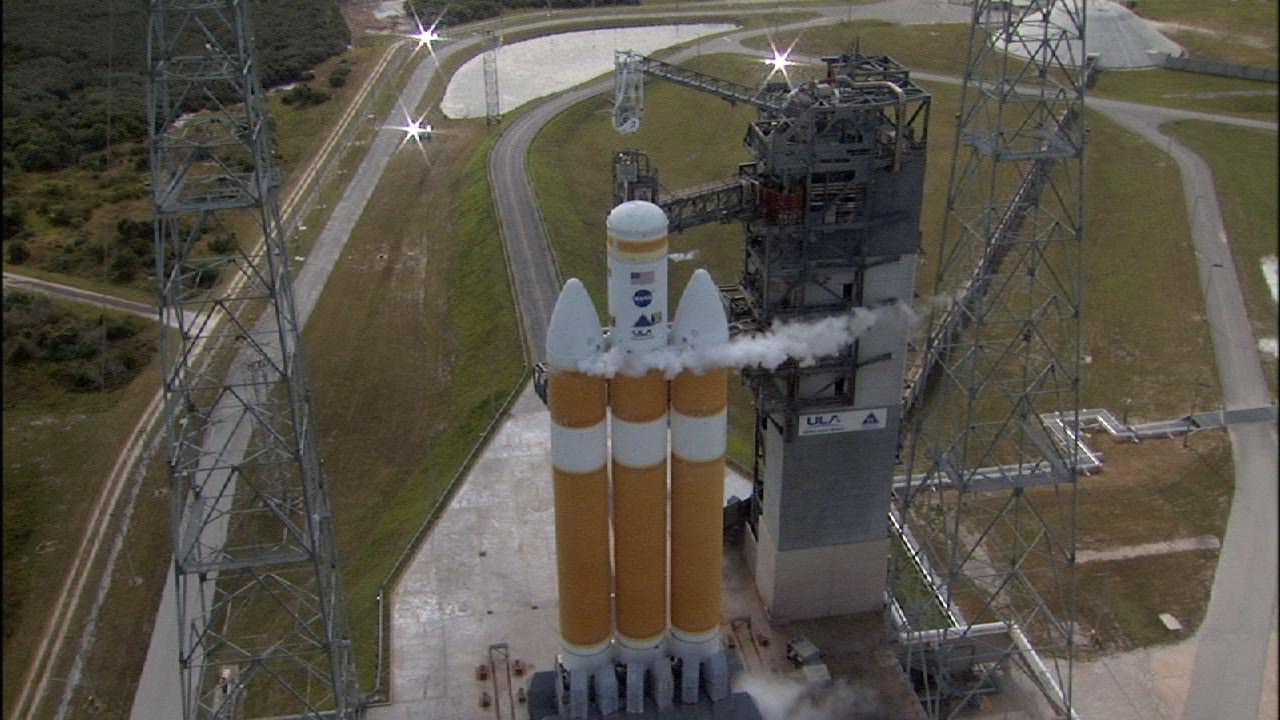
Delta 4 Heavy rocket and super secret US spy satellite roars off Pad 37 on June 29, 2012, from Cape Canaveral, Florida. NASA’s Orion EFT-1 capsule will blastoff atop a similar Delta 4 Heavy Booster in December 2014. Credit: Ken Kremer- kenkremer.com
Watch for Ken’s ongoing Orion coverage and he’ll be onsite at KSC in the days leading up to the historic launch on Dec. 4.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Orion and Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
………….
Learn more about Orion, SpaceX, Antares, NASA missions and more at Ken’s upcoming outreach events:
Dec 1-5: “Orion EFT-1, SpaceX CRS-5, Antares Orb-3 launch, Curiosity Explores Mars,” Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL, evenings