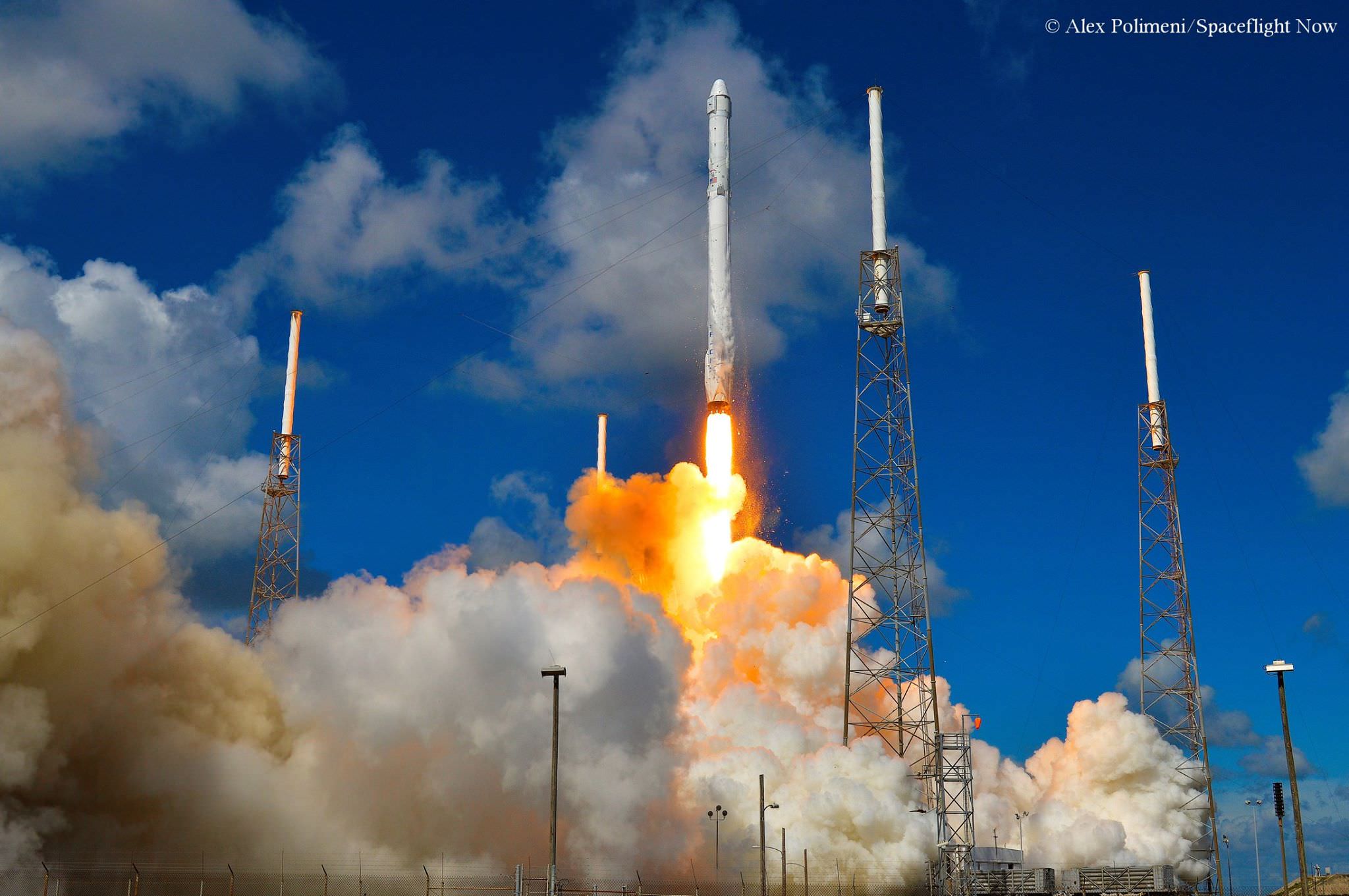
A commercial Cygnus cargo freighter has just arrived at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida to begin intensive processing for a critical mission to deliver some four tons of science experiments and supplies to the International Space Station (ISS) atop an Atlas V rocket in early December – as manufacturer Orbital ATK takes a big step in ramping up activities to fulfill its station resupply commitments and recover from the catastrophic launch failure of the firms Antares rocket last October.
Taking advantage of the built in flexibility to launch Cygnus on a variety of rockets, Orbital ATK quickly contracted rocket maker United Launch Alliance (ULA) to propel the cargo ship as soon as practical on the venerable Atlas V – as Orbital simultaneously endeavors to reengineer the Antares and bring that vehicle back to full flight status in 2016.
Since the fastest and most robust path back to on orbital cargo delivery runs through Florida via an Atlas V, Orbital ATK teamed up with ULA to launch a minimum of one Cygnus with an option for more.
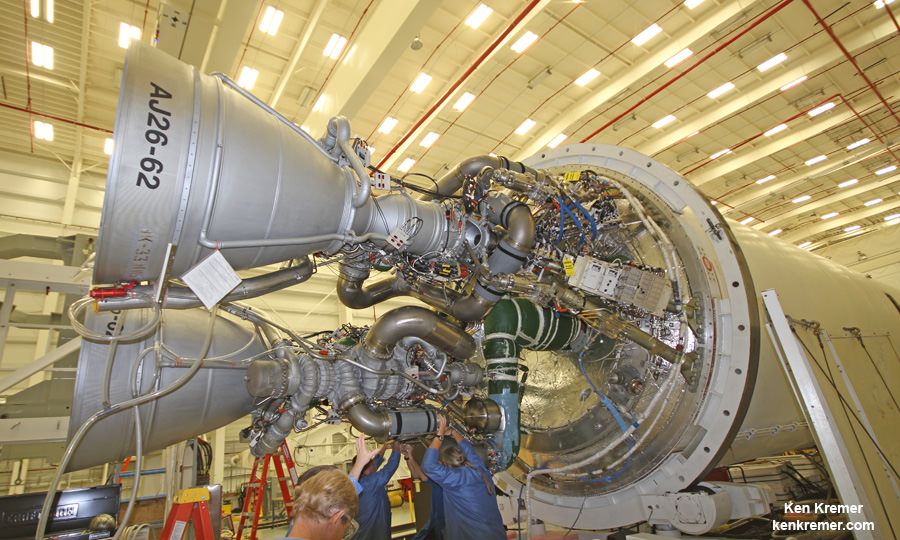
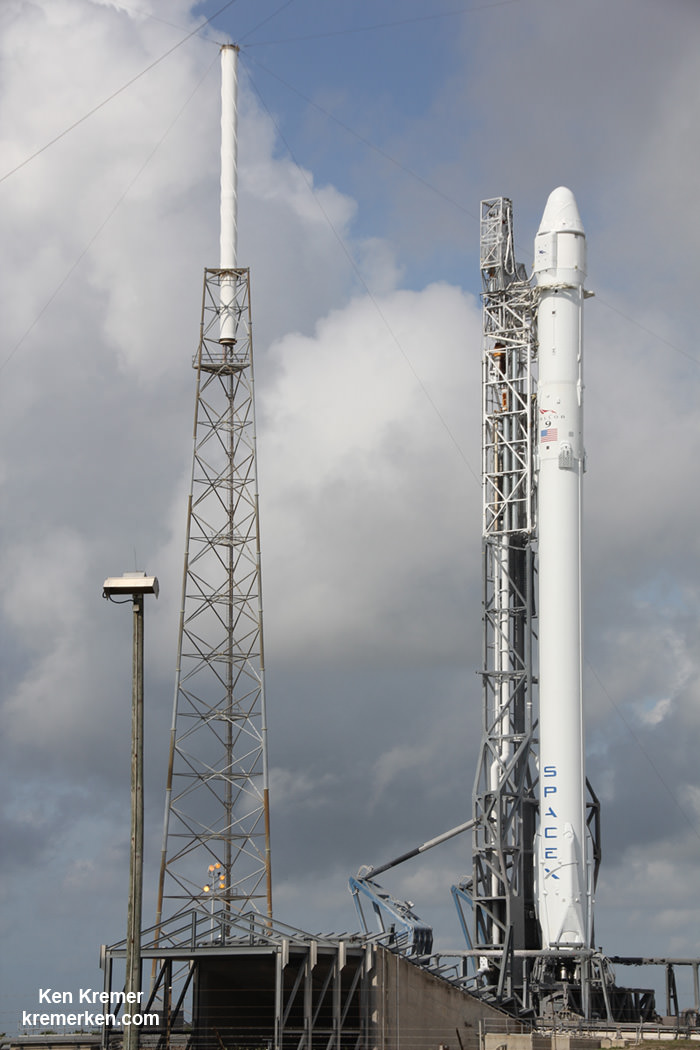
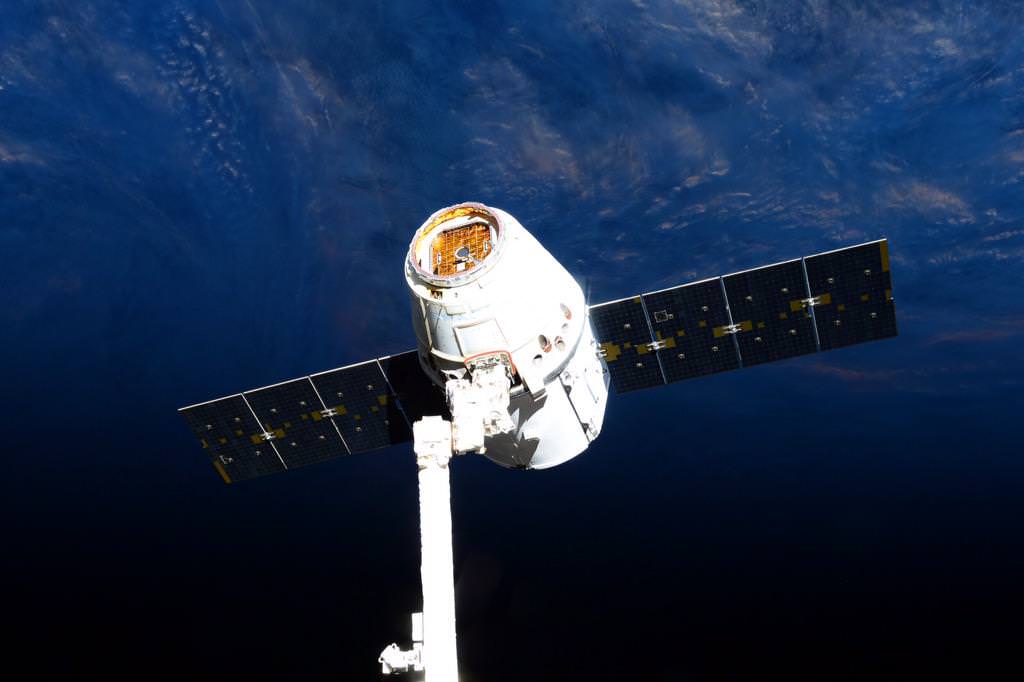
Cygnus is comprised of a pressurized cargo module (PCM) manufactured by Thales Alenia Space’s production facility in Turin, Italy and a service module (SM) manufactured at Orbital ATK’s Dulles, Virginia satellite manufacturing facility.
The PCM arrived on Monday, Aug. 11 and is now being processed for the flight dubbed OA-4 at KSC inside the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF). After the SM arrives in October it will be mated to the PCM inside the SSPF.

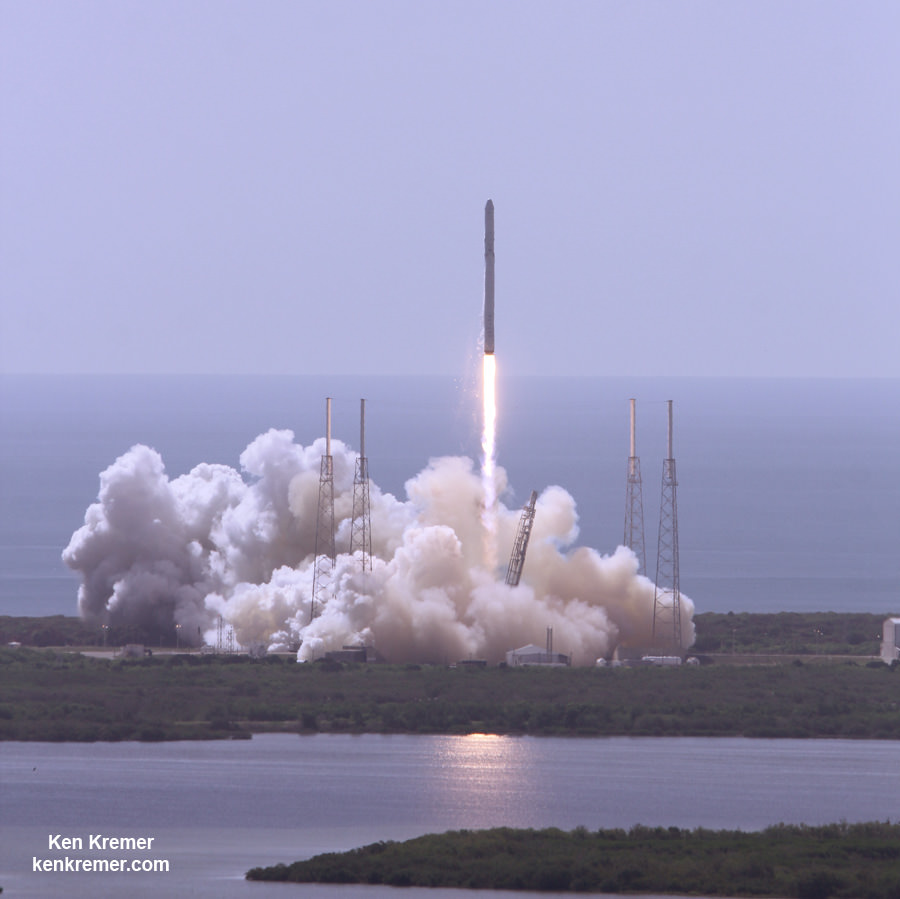
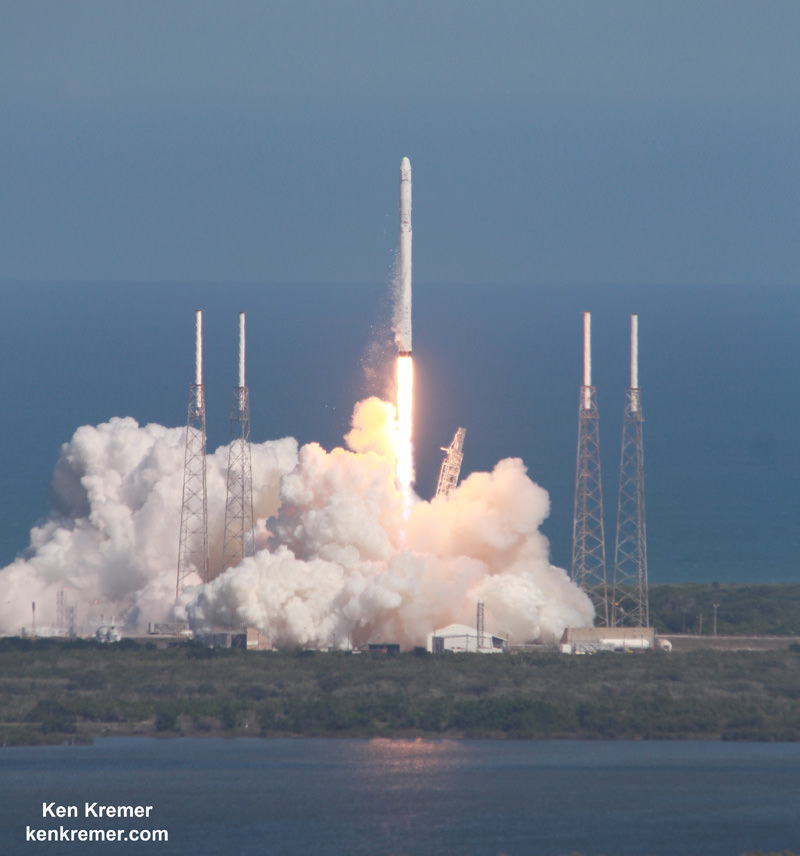
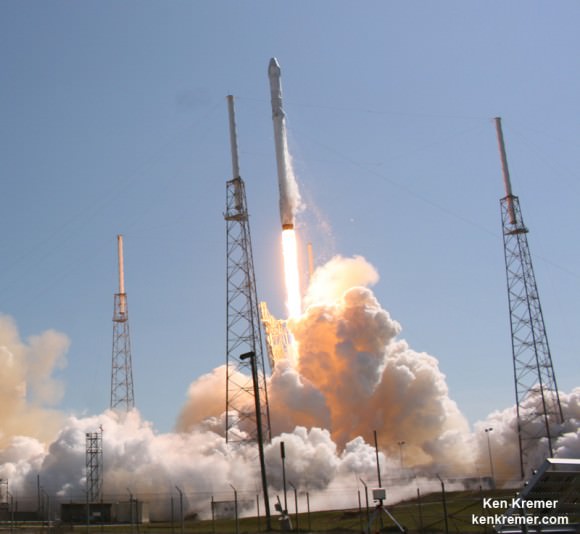
The first Cygnus cargo mission should liftoff sometime late in the fourth quarter of 2015, perhaps as soon as Dec. 3, aboard an Atlas V 401 vehicle from Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
Since ULA’s Atlas V manifest was already fully booked, ULA managers told me that they worked diligently to find a way to manufacture and insert an additional Atlas V into the tight launch sequence flow at the Cape.
And since the station and its six person crews can’t survive and conduct their scientific research work without a steady train of cargo delivery missions from the station’s partner nations, Orbital ATK is “devoting maximum efforts” to get their Antares/Cygnus ISS resupply architecture back on track as fast as possible.
Orbital ATK holds a Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract from NASA worth $1.9 Billion to deliver 20,000 kilograms of research experiments, crew provisions, spare parts and hardware for eight Cygnus cargo delivery flights to the ISS.
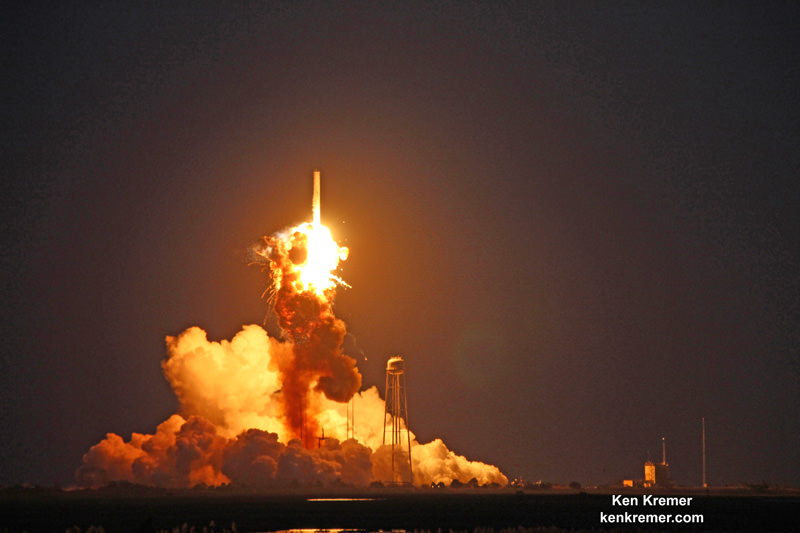
However, the Cygnus missions were put on hold when the third operational Antares/Cygnus flight was destroyed in a raging inferno about 15 seconds after liftoff on the Orb-3 mission from launch pad 0A at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility on Virginia’s eastern shore.

“We committed to NASA that we would resume CRS cargo delivery missions as soon as possible under a comprehensive ‘go-forward’ plan after the Antares launch failure last October,” said David W. Thompson, President and Chief Executive Officer of Orbital ATK.
“Since that time our team has been sharply focused on fulfilling that commitment. With a Cygnus mission slated for later this year and at least three missions to the Space Station planned in 2016, we are on track to meet our CRS cargo requirements for NASA.”
Orbital says they will deliver the full quantity of cargo specified in the CRS contract with NASA.
“Our team and our partners are devoting maximum efforts to ensuring the success of NASA’s ISS commercial cargo program.”
“We are committed to meeting all CRS mission requirements, and we are prepared to continue to supply the Space Station.”
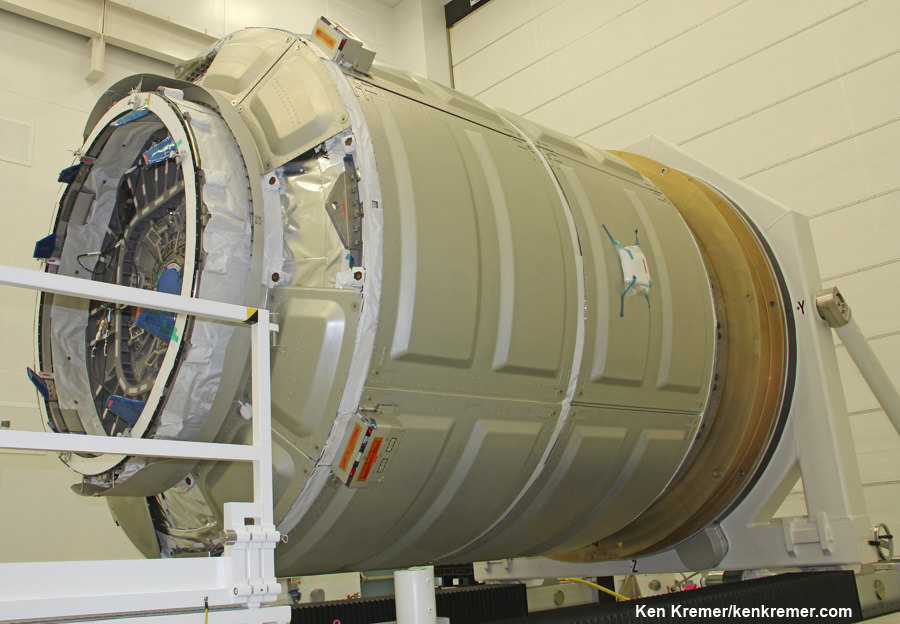

For the OA-4 cargo mission, Cygnus will be loaded with its heaviest cargo to date on nearly four tons.
The weightier cargo is possible because a longer version of Cygnus will be employed.
This mission will fly with the extended Cygnus Pressurized Cargo Module (PCM) which will carry approximately 3,500 kg or 7,700 pounds of supplies to station.
“This is a very exciting time for the Cygnus team at Orbital ATK,” said Frank DeMauro, vice president of Human Space Systems and program director of the Commercial Resupply Services program at Orbital ATK.
“Not only are we launching from Kennedy on an Atlas V for the first time, but this will also be the first flight of the Enhanced Cygnus, which includes a larger cargo module and a more mass-efficient service module.”
Use of the enhanced Cygnus in combination with the added thrust ULA V is a game changer enabling the Cygnus to carry its maximum possible cargo load for NASA.
“During our first three missions, we delivered 3,629 kilograms to the space station, about the weight of two F-150 pickup trucks,” said Frank DeMauro.
The OA-4 Cygnus alone will deliver some 3,500 kilograms.
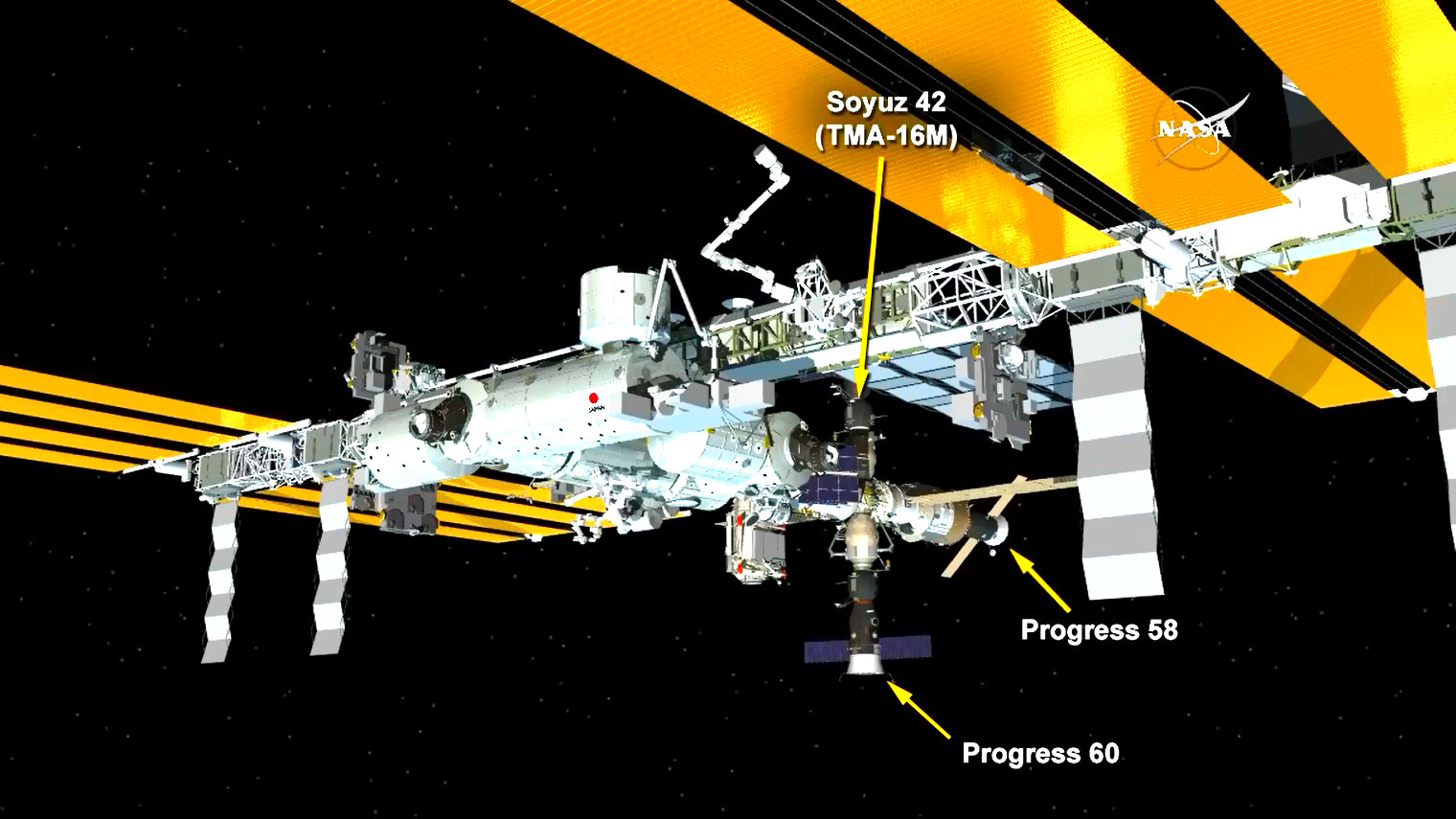
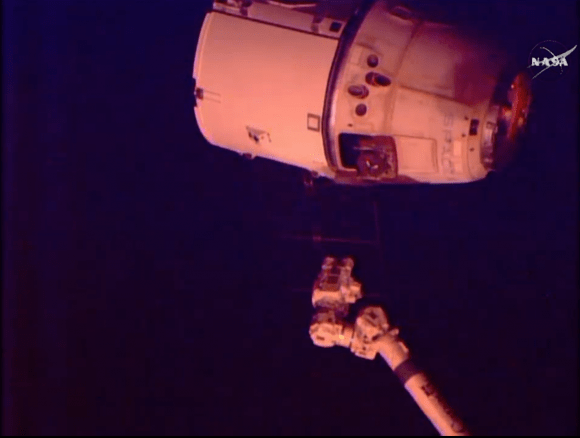
Once in orbit, Cygnus fires its onboard thrusters to precisely guide itself close to the space station so that the astronauts can grapple it with the robotic arm and berth it to a port on the station.
Be sure to read Ken’s earlier eyewitness reports about last October’s Antares failure at NASA Wallops and ongoing reporting about Orbital ATK’s recovery efforts – all here at Universe Today.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.