As Comet 2011 L4 PanSTARRS moves out of the inner solar system, we’ve got another comet coming into view this month for northern hemisphere observers.
Comet C/2012 F6 Lemmon is set to become a binocular object low to the southeast at dawn for low northern latitudes in the first week of April. And no, this isn’t an April Fools’ Day hoax, despite the comet’s name. Comet Lemmon (with two m’s) was discovered by the Mount Lemmon Sky Survey (MLSS) based outside of Tucson, Arizona on March 23, 2012. MLSS is part of the Catalina Sky Survey which searches for Near Earth Asteroids. We’ve got another comet coming into view this month for northern hemisphere observers as Comet 2011 L4 PanSTARRS moves out of the inner solar system.
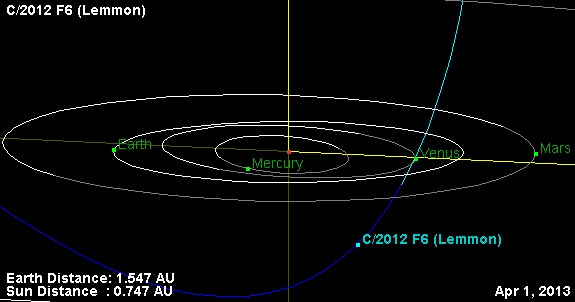
The comet is on an extremely long elliptical orbit, with a period of over 11,000 years. Comet Lemmon just passed perihelion at 0.74 astronomical units from the Sun on March 24th.

Southern hemisphere observers have been getting some great views of Comet Lemmon since the beginning of this year. It passed only three degrees from the south celestial pole on February 5th, and since that time has been racing up the “0 Hour” line in right ascension. If that location sounds familiar, that’s because another notable comet, 2011 L4 PanSTARRS has been doing the same. In fact, astrophotographers in the southern hemisphere were able to catch both comets in the same field of view last month.
Another celestial body occupies 0 Hour neighborhood this time of year. The Sun just passed the vernal equinox marking the start of Spring in the northern hemisphere and Fall in the southern on March 19th.
And like PanSTARRS, Comet Lemmon has a very steep orbit inclined 82.6° relative to the ecliptic.
Comet Lemmon broke naked-eye visibility reaching +6th magnitude in late February and has thus far closely matched expectations. Current reports place it at magnitude +4 to +5 as it crosses northward through the constellation Cetus. Predictions place the maximum post-perihelion brightness between magnitudes +3 and +5 in early April, and thus far, Comet Lemmon seems to be performing right down the middle of this range.
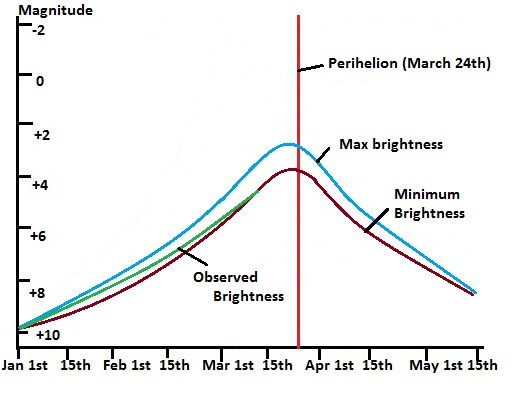
Southern observers have caught a diffuse greenish 30” in diameter nucleus on time exposures accompanied by a short, spikey tail. Keep in mind, the quoted brightness of a comet is extended over its entire surface area. Thus, while a +4th magnitude star may be easily visible in the dawn, a 3rd or even 2nd magnitude comet may be invisible to the unaided eye. Anyone who attempted to spot Comet PanSTARRS in the dusk last month knows how notoriously fickle it actually was. Binoculars are your friend in this endeavor. Begin slowly sweeping the southeast horizon about an hour before local sunrise looking for a fuzzy “star” that refuses to reach focus. Comet Lemmon will get progressively easier in the dawn sky for latitudes successively farther north as the month of April progresses.

Comet Lemmon will continue to gain elevation as it crosses from Cetus into the constellation Pisces on April 13th. An interesting grouping occurs as the planet Mercury passes only a few degrees from the comet from April 15th to April 17th. Having just past greatest elongation on March 31st, Mercury will shine at magnitude -0.1 and make a good guide to locate the comet in brightening dawn skies. The pair is joined by the waning crescent Moon on the mornings of April 7th and 8th which may also provide for the first sighting opportunities from low north latitudes around these dates.
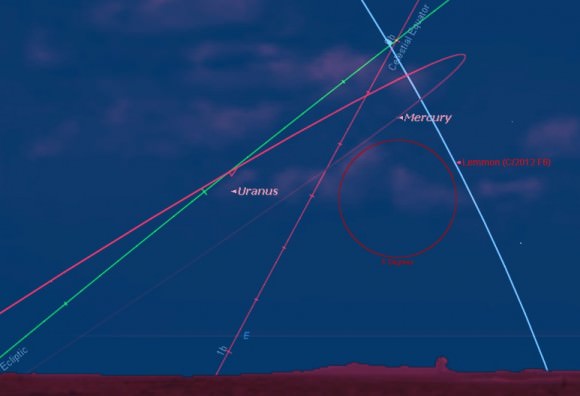
The Moon reaches New phase on Wednesday, April 10th at 5:35AM EDT/9:35 UT. It will be out of the morning sky for the next couple of weeks until it reaches Full on April 25th, at which point it will undergo the first eclipse of 2013, a very shallow partial. (More on that later this month!)
Comet Lemmon will then slide across the celestial equator on April 20th and cross the plane of the ecliptic on April 22nd as it heads up into the constellation Andromeda in mid-May. We’re expecting Comet Lemmon to be a fine binocular object for late April, but perhaps not as widely observed due to its morning position as PanSTARRS was in the dusk.
By mid-May, Comet Lemmon will have dipped back down below +6th magnitude and faded out of interest to all but a few deep sky enthusiasts. Comet Lemmon will pass within 10° of the north celestial pole on August 9th, headed back out into the icy depths of the solar system not to return for another 11,000-odd years.
It’s interesting to see how these two springtime comets will effect observers expectations for the passage of Comet C/2012 S1 ISON. Will this in fact be the touted “Comet of the Century?” Much hinges on whether ISON survives its November 28th perihelion only 1,166,000 kilometers from the center of our Sun (that’s 0.68 solar-radii or about 3 times the Earth-Moon distance from the surface of the Sun). If so, we could be in for a fine “Christmas Comet” rivaling the passage of Comet Lovejoy in late 2011. On the other hand, a disintegration of Comet ISON would be more akin to the fizzle of Comet Elenin earlier in 2011.
In the meantime, enjoy Comet Lemmon as an Act 2 in the 2013 Three Act “Year of the Comet!”

