The march towards first launch of NASA’s next generation Orion crew vehicle is accelerating rapidly.
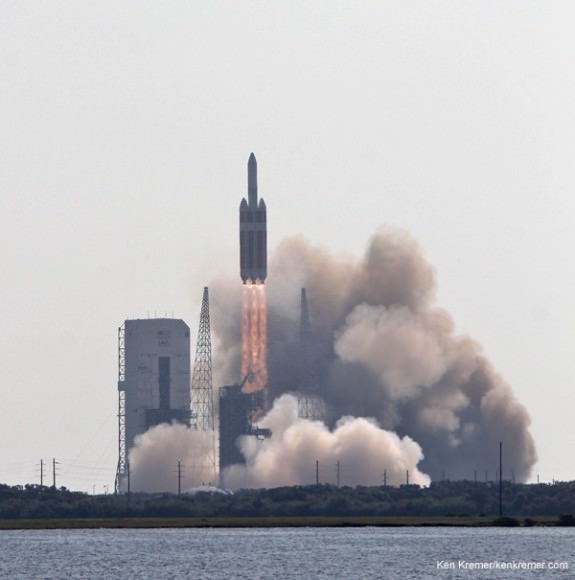
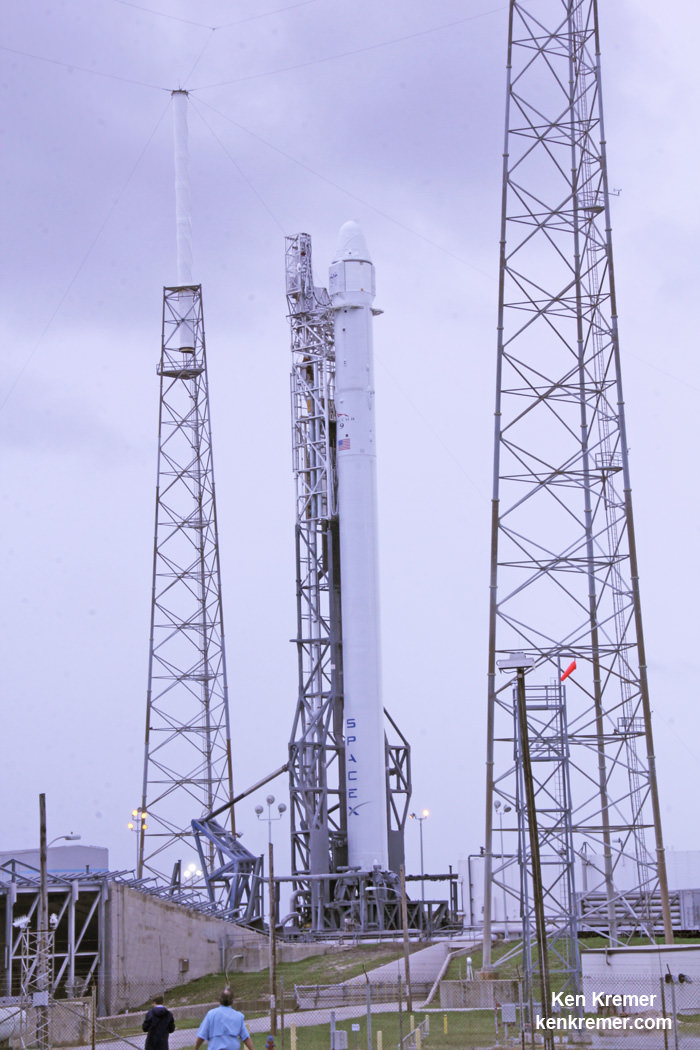
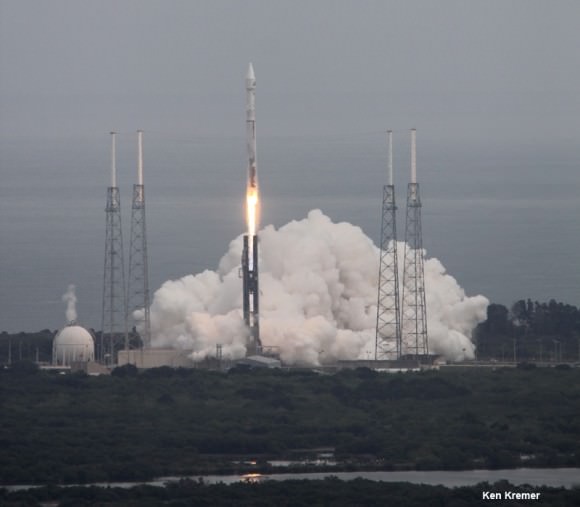
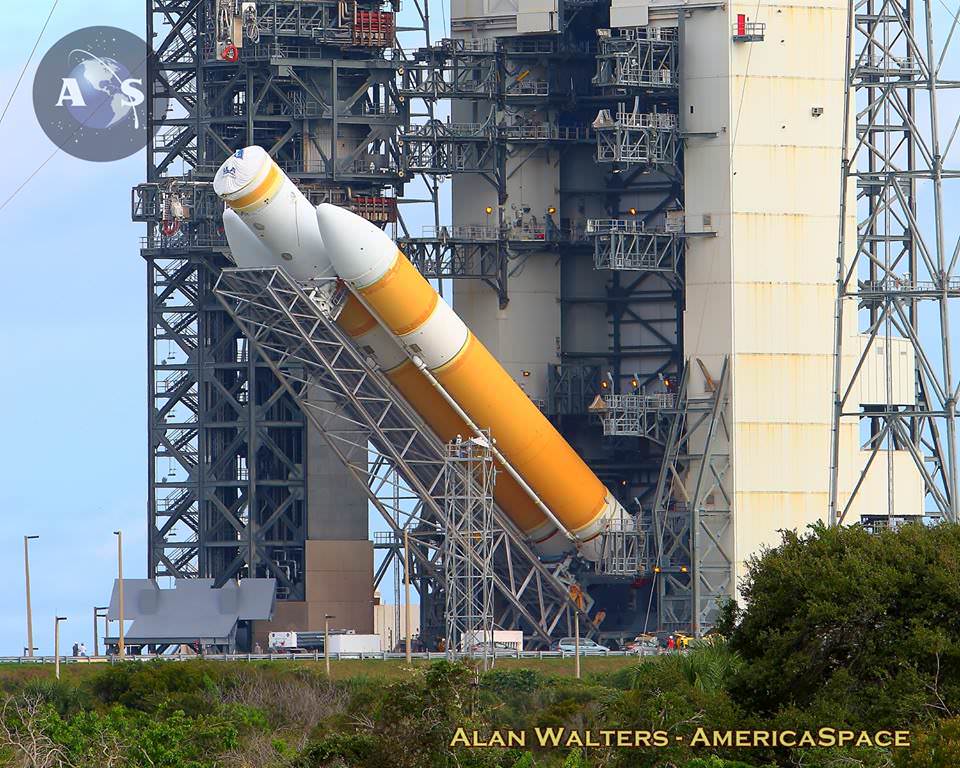
The world’s most powerful rocket – the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy – was moved to its Cape Canaveral launch pad overnight and raised at the pad today, Oct. 1, thereby setting in motion the final steps to prepare for blastoff of NASA’s new Orion capsule on its first test flight in just over two months.
All the pieces are ready and now it’s just a matter of attaching all those components together for the inaugural uncrewed liftoff of the state-of-the-art Orion spacecraft on its maiden mission dubbed Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) in December.
“We’ve been working toward this launch for months, and we’re in the final stretch,” said Kennedy Director Bob Cabana, in a NASA statement.
“Orion is almost complete and the rocket that will send it into space is on the launch pad. We’re 64 days away from taking the next step in deep space exploration.”
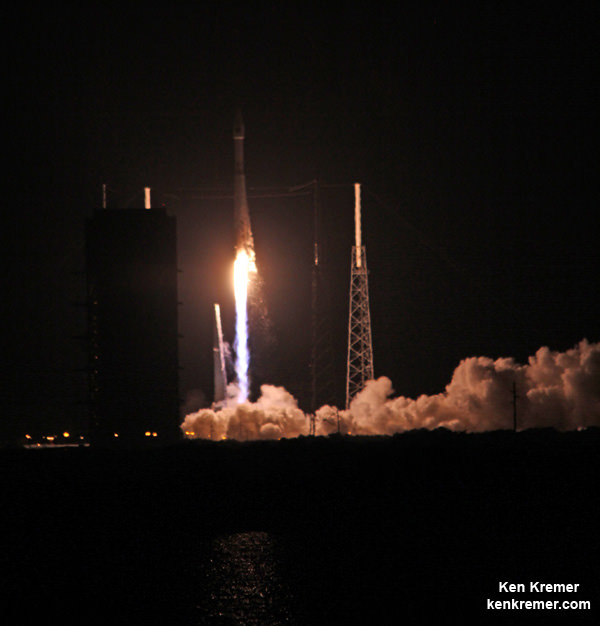
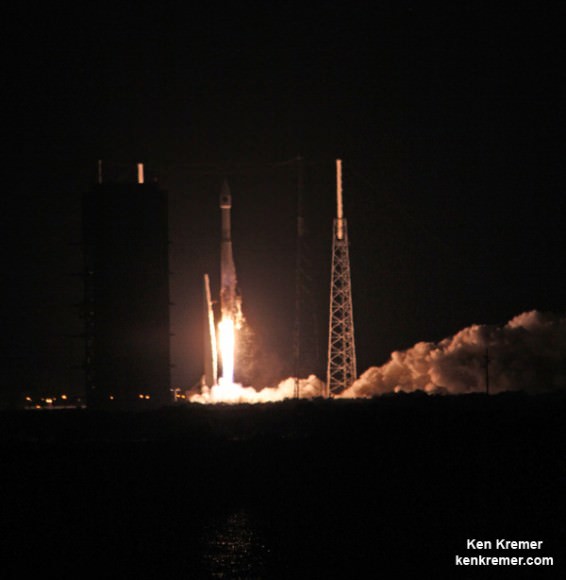
The triple barreled Delta IV Heavy topped by the Orion EFT-1 capsule is slated to blastoff on December 4, 2014, from Space Launch Complex 37 (SLC-37) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

After a nearly two day delay due to drenching rain storms, the Delta IV Heavy integrated first and second stages were transported horizontally overnight Wednesday starting around 10 p.m. from the processing hanger inside ULA’s Horizontal Integration Facility (HIF) to the nearby launch complex and servicing gantry at Pad 37.
Early this morning, the rocket was hoisted up into its launch configuration. Several of my space photo-journalist colleagues were on hand. See their photos herein.
From now until launch technicians will conduct the final processing, testing and checkout of the Delta IV Heavy booster. They will also carry out “a high fidelity rehearsal to include fully powering up the booster and loading the tanks with fuel and oxidizer,” according to ULA.
“This is a tremendous milestone and gets us one step closer to our launch later this year,” said Tony Taliancich, ULA’s director of East Coast Launch Operations, in a ULA statement.
“The team has worked extremely hard to ensure this vehicle is processed with the utmost attention to detail and focus on mission success.”
“The Delta IV Heavy is the world’s most powerful launch vehicle flying today, and we are excited to be supporting our customer for this critical flight test to collect data and reduce overall mission risks and costs for the program,” said Taliancich.

NASA’s Orion Program manager Mark Geyer told me in a recent interview that the Orion spacecraft, built by prime contractor Lockheed Martin, will be transported to the pad around November 10 or 11. Then the Orion will be hoisted and attached to the top of the Delta IV Heavy rocket at the base of its service module.
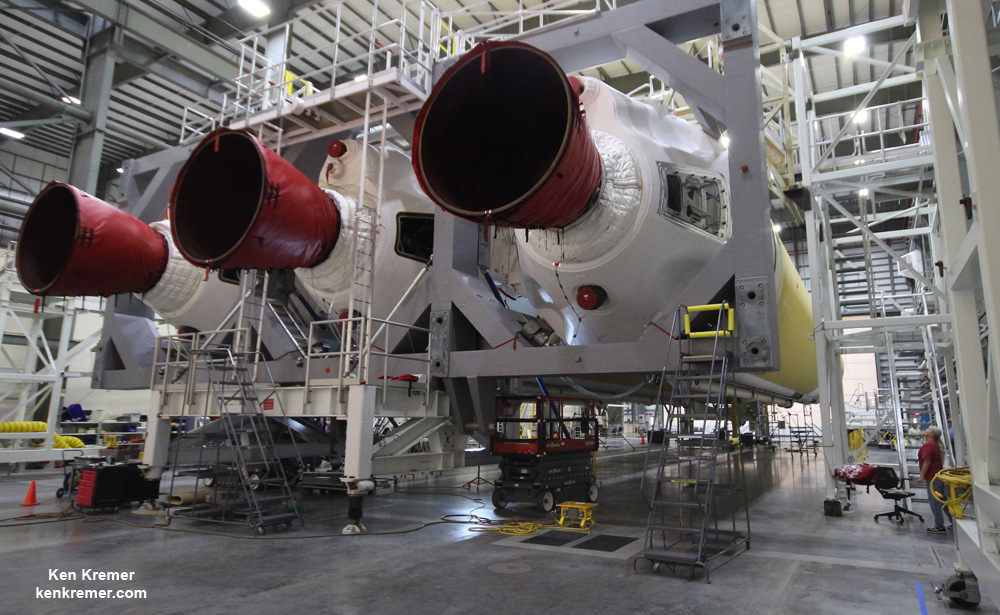
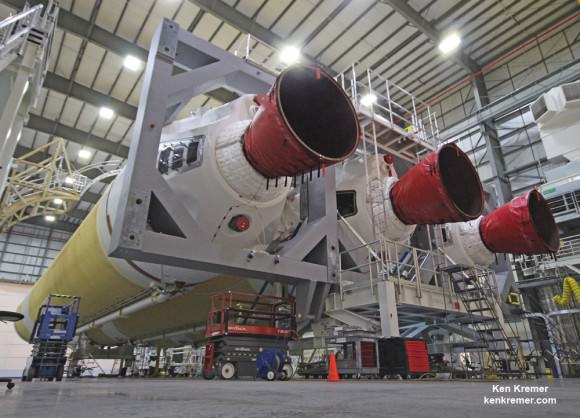
The Delta IV Heavy first stage is comprised of a trio of three Common Booster Cores (CBCs).

Each CBC measures 134 feet in length and 17 feet in diameter. They are equipped with an RS-68 engine powered by liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen propellants producing 656,000 pounds of thrust. Together they generate 1.96 million pounds of thrust.
The Delta IV Heavy became the world’s most powerful rocket upon the retirement of NASA’s Space Shuttle program and is the only vehicle that is sufficiently powerful to launch the Orion EFT-1 spacecraft.
The first CBC booster was attached to the center booster in June. The second one was attached in early August.

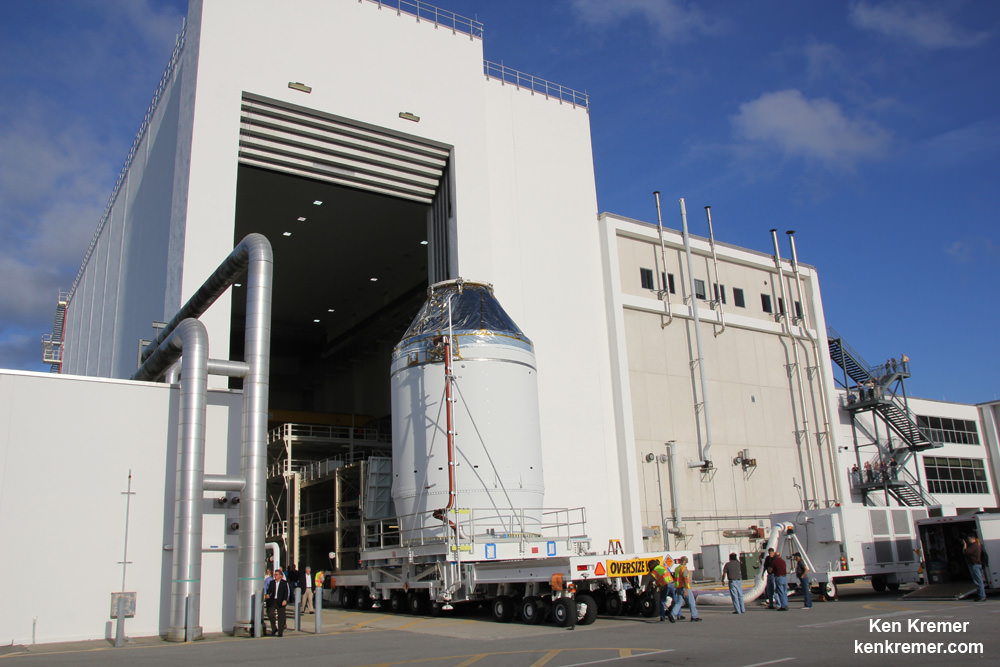
I recently visited the HIF during a media tour after the three CBCs had been joined together as well as earlier this year after the first two CBCs arrived by barge from their ULA assembly plant in Decatur, Alabama, located about 20 miles west of Huntsville. See my photos herein.
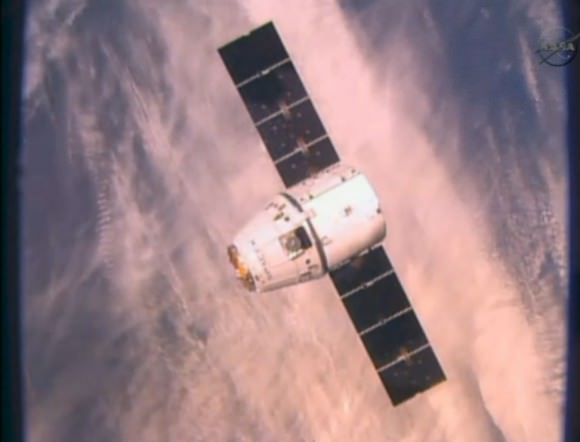
I was also on hand at KSC when the Orion crew module/service module (CM/SM) stack was rolled out on Sept. 11, 2014, on a 36 wheeled transporter from its high bay assembly facility in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building.
It was moved about 1 mile to the KSC fueling facility named the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHFS). Read my Orion move story – here.
Fueling of Orion was completed over the weekend and it has now been moved to the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) for the installation of its last component – the Launch Abort System (LAS).
Orion’s next stop is SLC-37.
The two-orbit, four and a half hour EFT-1 flight will lift the Orion spacecraft and its attached second stage to an orbital altitude of 3,600 miles, about 15 times higher than the International Space Station (ISS) – and farther than any human spacecraft has journeyed in 40 years.
NASA is simultaneously developing a monster heavy lift rocket known as the Space Launch System or SLS, that will eventually launch Orion on its deep space missions.
The maiden SLS/Orion launch on the Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) unmanned test flight is now scheduled for no later than November 2018 – read my story here.
SLS will be the world’s most powerful rocket ever built and the assembly of its core stage has begun at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Read my story – here.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Orion, SLS, Boeing, Sierra Nevada, Orbital Sciences, SpaceX, commercial space, Curiosity, Mars rover, MAVEN, MOM and more Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.