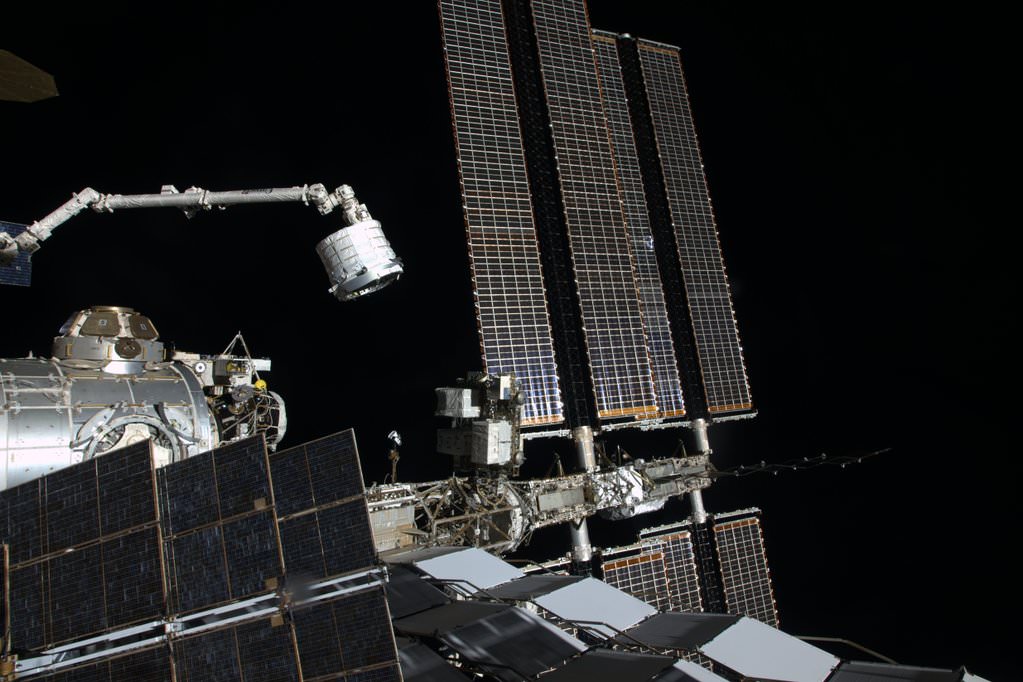
The International Space Station (ISS) grew in size today, April 16, following the successful installation of an experimental new room – the BEAM expandable habitat module.
Engineers at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston used the space station’s high tech robotic arm to pluck the small module known as the Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM) out from the unpressurized rear truck section of the recently arrived SpaceX Dragon cargo freighter, and added it onto the orbiting laboratory complex.
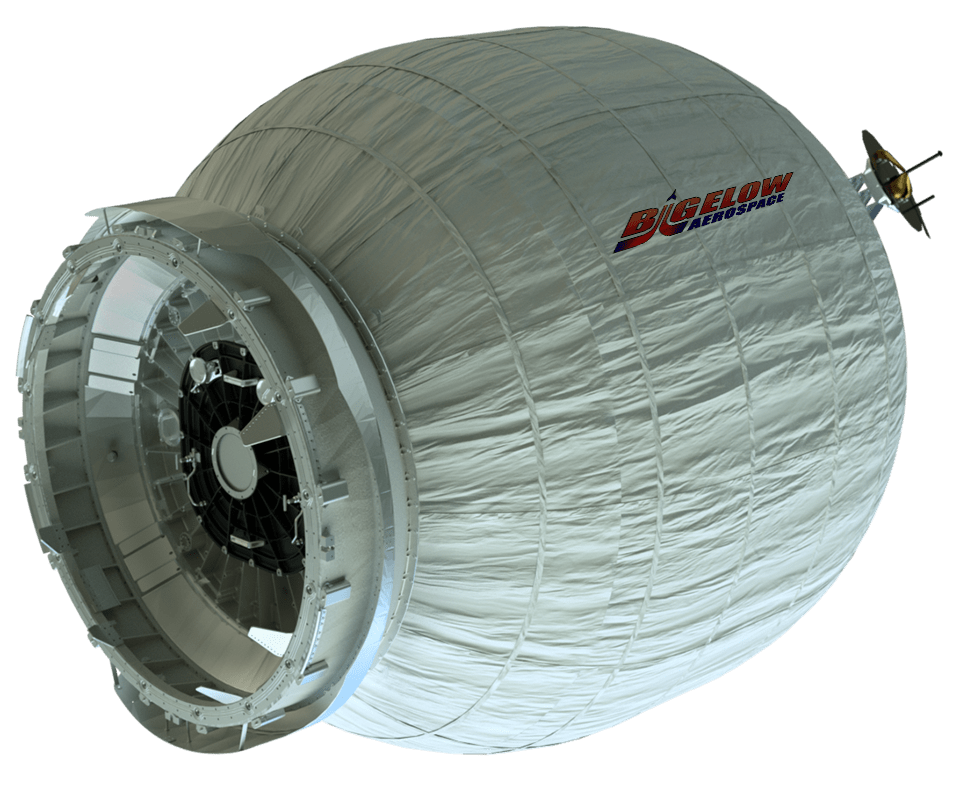
BEAM was manufactured by Las Vegas-based Bigelow Aerospace under a $17.8 million contract with NASA. It will remain joined to the station for at least a two-year test period.
The 3115 pound (1413 kg) BEAM will test the use of an expandable space habitat in microgravity with humans for the first time.
It was extracted from the Dragon’s trunk overnight with the robotic Canadarm2 and then installed on the aft port of the Tranquility module at 5:36 a.m. EDT over a period of about 4 hours. The station was flying over the Southern Pacific Ocean at the moment of berthing early Saturday.
NASA astronaut and ISS Expedition 47 crew member Tim Kopra snapped a super cool photo of BEAM in transit, shown above.

BEAM was carried to orbit in a compressed form inside the Dragon’s truck following the April 8 blast off from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 4:43 p.m. EDT on the Dragon CRS-8 resupply mission for NASA to the ISS.
BEAM is a prototype inflatable habitat that could revolutionize the method of construction of future habitable modules intended for use both in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) as well as for deep space expeditions Beyond Earth Orbit (BEO) to destinations including the Moon, Asteroids and Mars.
The advantage of expandable habitats is that they offer a much better volume to weight ratio compared to standard rigid metallic structures such as all of the current ISS pressurized modules.
It is constructed of lighter weight reinforced fabric rather that metal. This counts as the first test of an expandable module and investigators want to determine how it fares with respect to protection again solar radiation, space debris and the temperature extremes of space.
Furthermore they also take up much less space inside the payload fairing of a rocket during launch.
Watch this animation showing how Canadarm2 transports BEAM from the Dragon spacecraft to a side berthing port on Tranquility where it will soon be expanded.

Current plans call for the module to be expanded in late May with air. It will expand to nearly five times from its compressed size of 8 feet in diameter by 7 feet in length to roughly 10 feet in diameter and 13 feet in length. Once inflated it will provide 565 cubic feet (16 m3) of habitable volume.
Exactly how it will expand is also an experiment and could happen in multiple ways. Therefore the team will exercise great caution and carefully monitor the inflation and check for leaks.

The astronauts will first enter BEAM about a week after the expansion. Thereafter they will visit it about 2 or 3 times per year for several hours to retrieve sensor data and assess conditions, say NASA officials.
Visits could perhaps occur even frequently more if NASA approves. says Bigelow CEO Robert Bigelow.
BEAM is an extraordinary test bed in itself.

But Robert Bigelow hopes that BEAM can be used to conduct science experiments after maybe a six month shakedown cruise, if all goes well, and NASA approves a wider usage.
Bigelow Aerospace has already taken in the next step in expandable habitats.
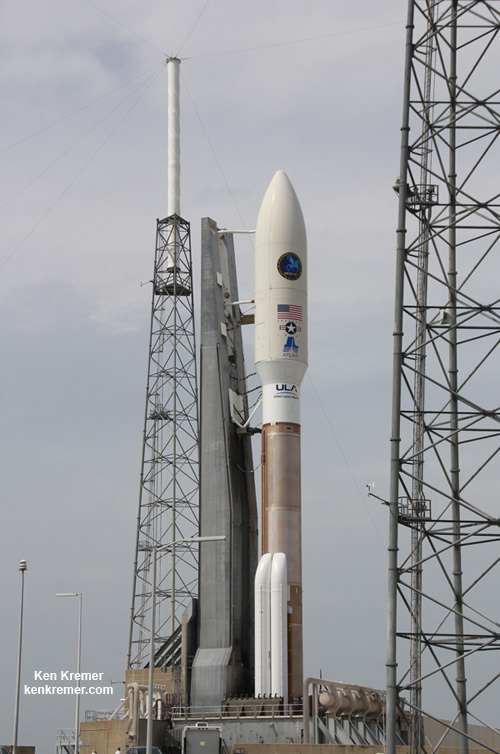
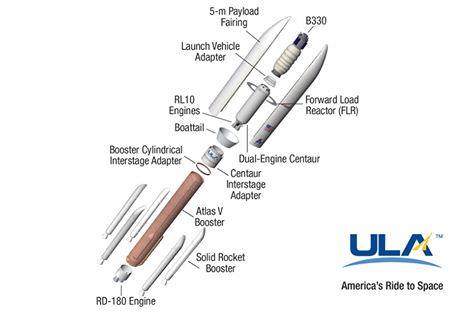
Earlier this week, Bigelow and rocket builder United Launch Alliance (ULA) announced they are joining forces to develop and launch the B330 expandable commercial habitat module in 2020 on an Atlas V. It is about 20 times larger and far more capable. Details in my story here.
Robert Bigelow says he hopes that NASA will approve docking of the B330 at the ISS.
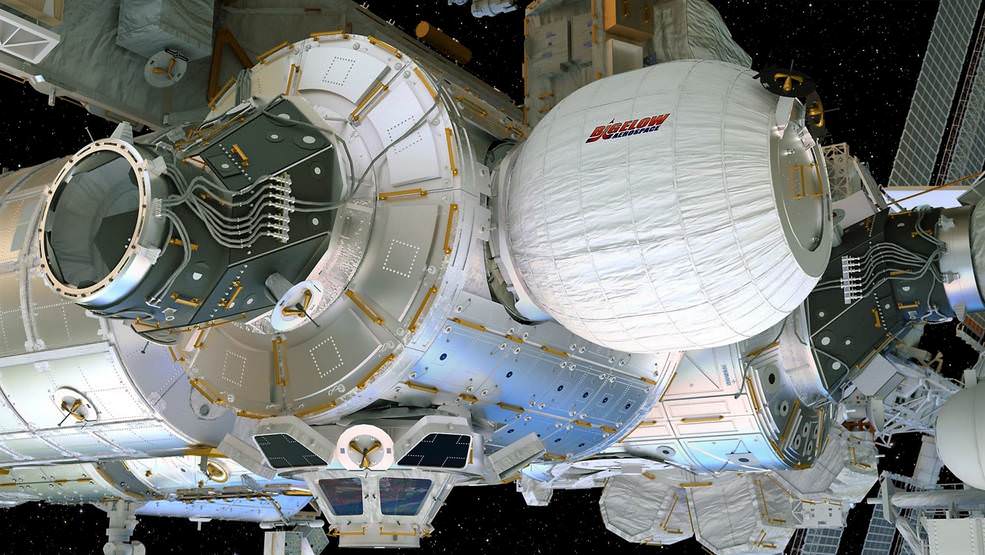

Credits: Bigelow Aerospace
The SpaceX Dragon spacecraft delivered almost 7,000 pounds of cargo.
CRS-8 counts as the company’s eighth flight to deliver supplies, science experiments and technology demonstrations to the ISS for the crews of Expeditions 47 and 48 to support dozens of the approximately 250 science and research investigations in progress.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
………….
Learn more about SpaceX, NASA Mars rovers, Orion, SLS, ISS, Orbital ATK, ULA, Boeing, Space Taxis, NASA missions and more at Ken’s upcoming outreach events:
Apr 17: “NASA and the Road to Mars Human Spaceflight programs”- 1:30 PM at Washington Crossing State Park, Nature Center, Titusville, NJ – http://www.state.nj.us/dep/parksandforests/parks/washcros.html