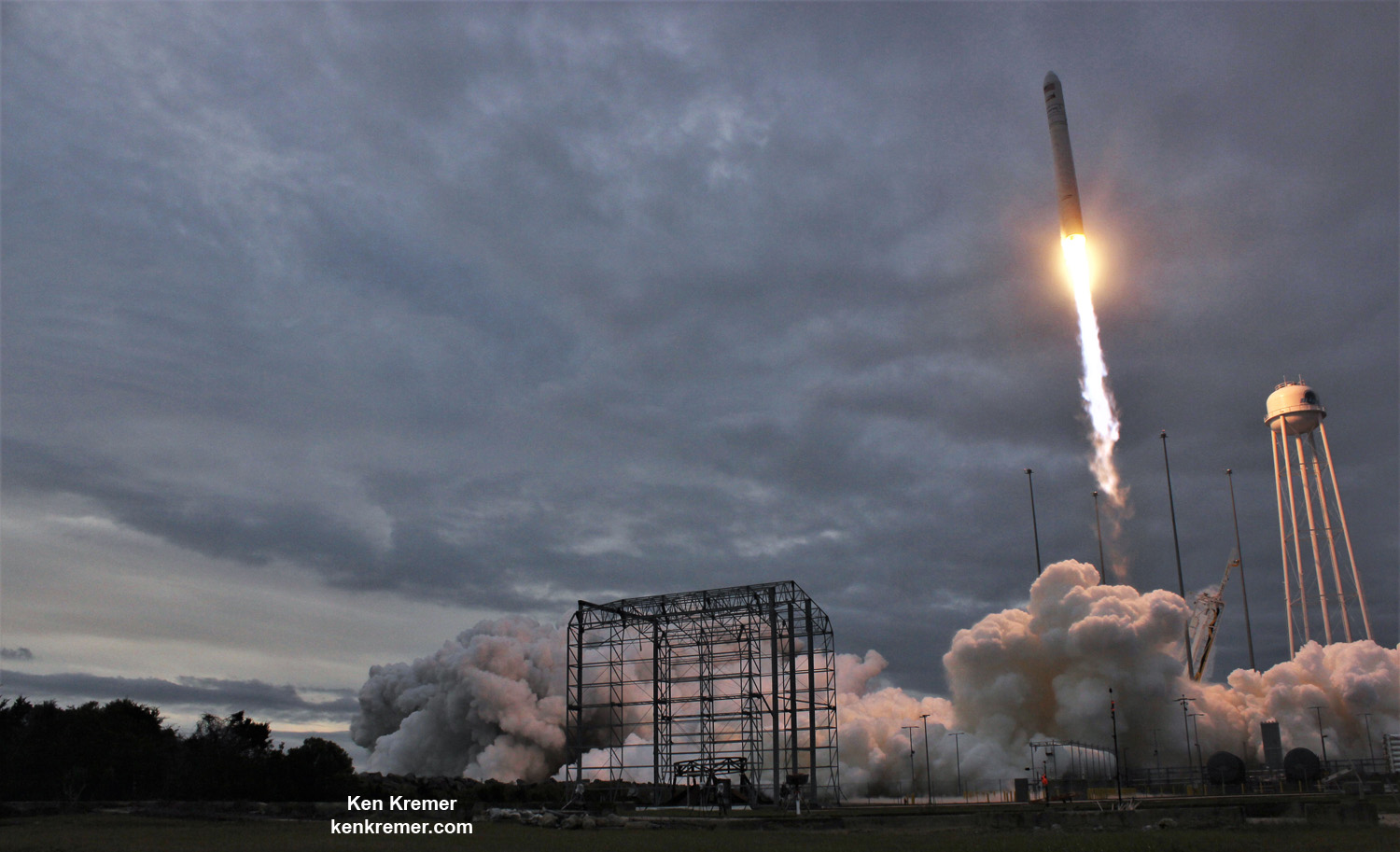
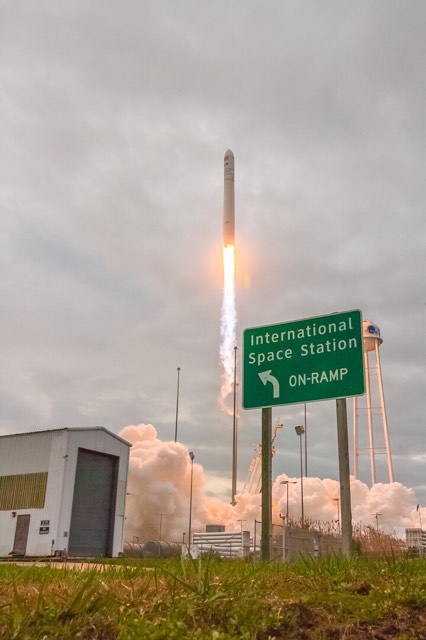
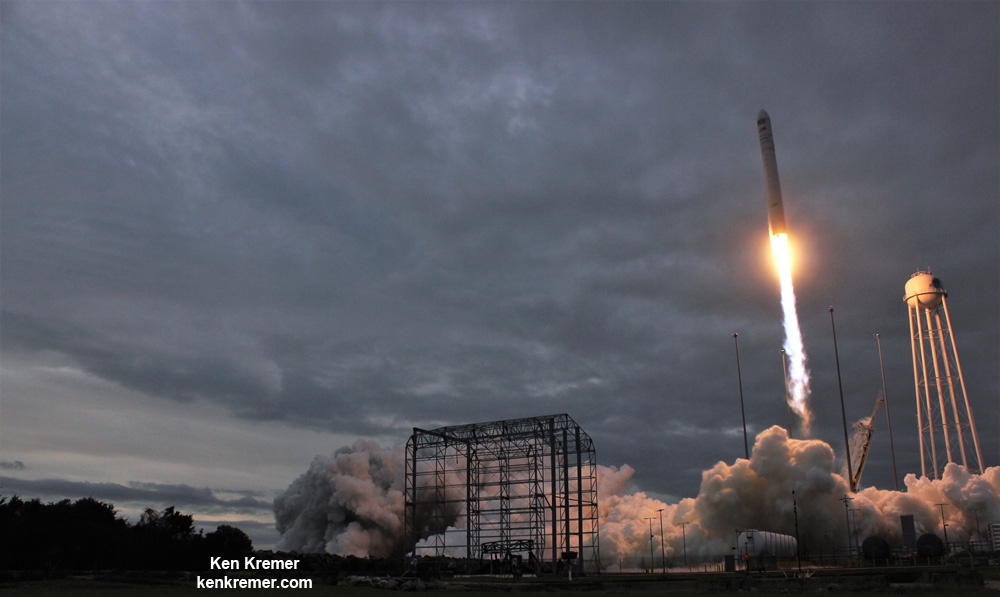
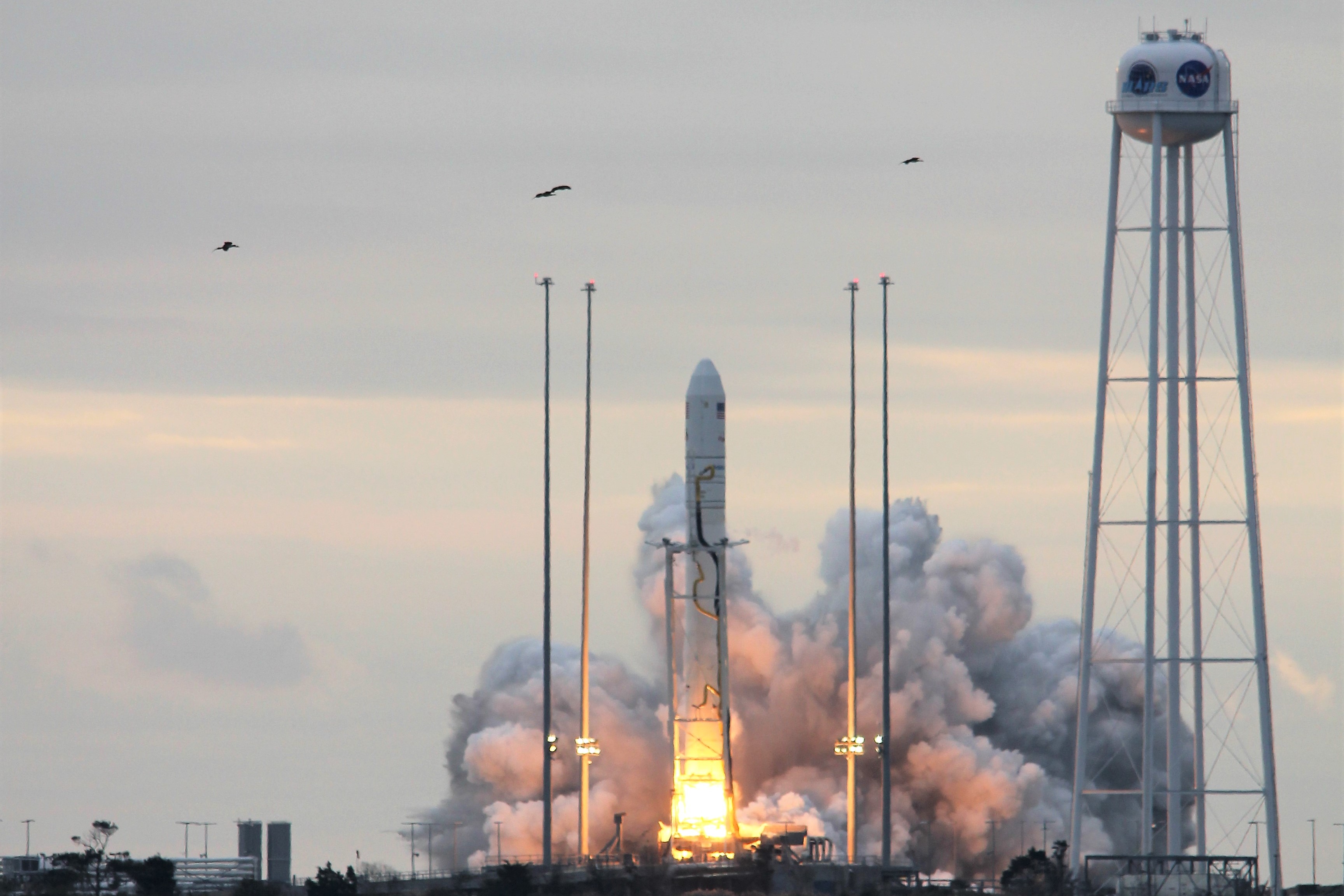
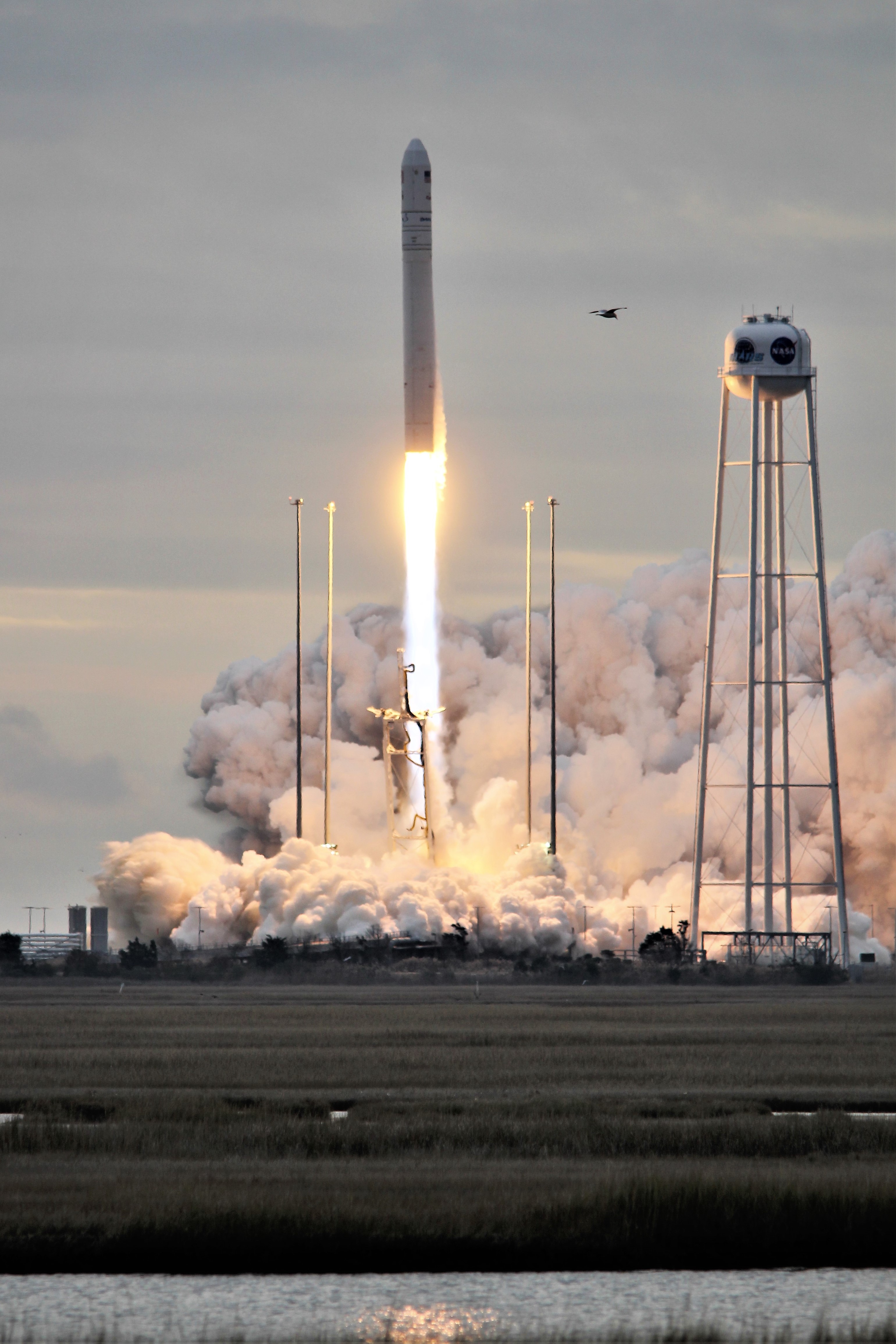
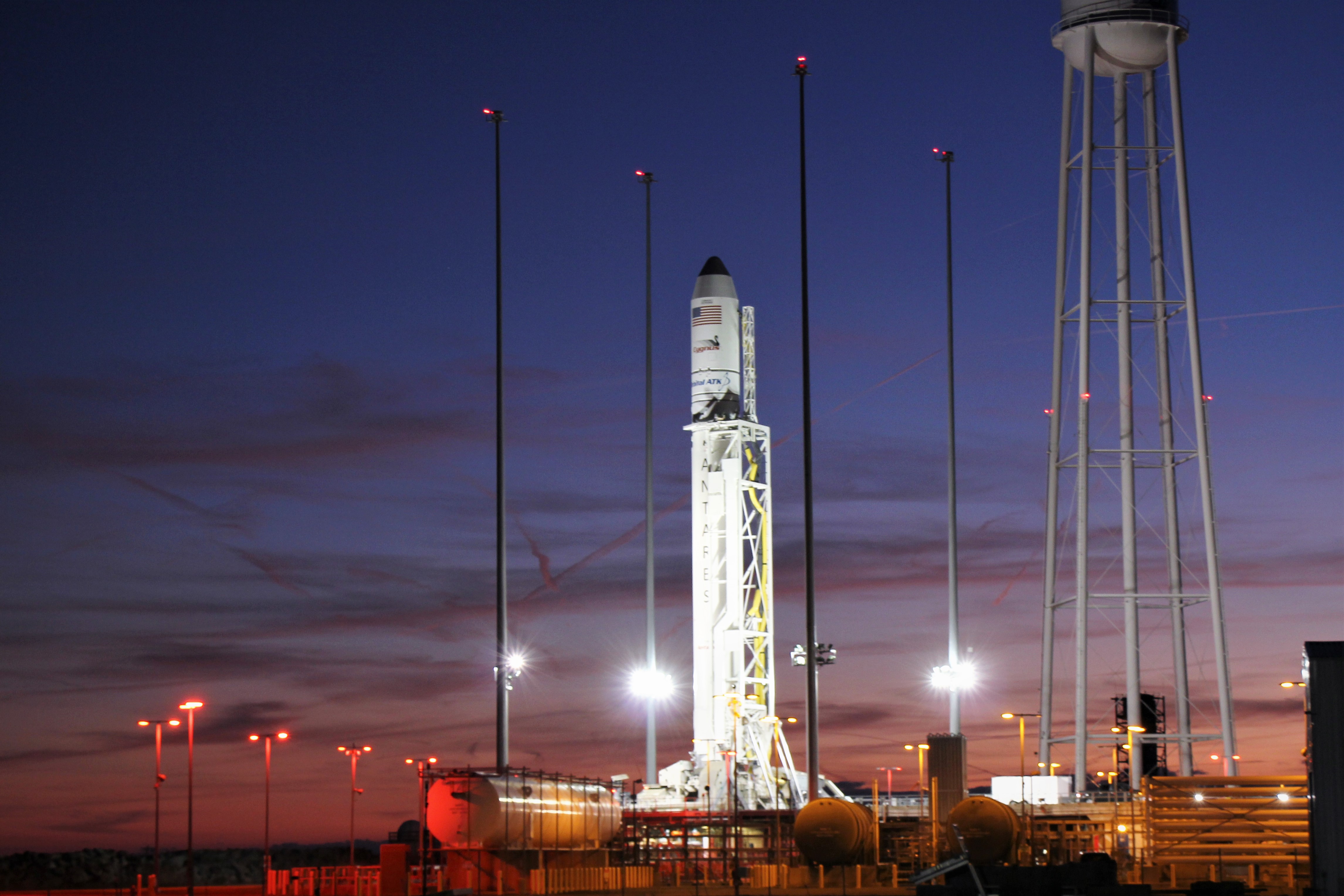
NASA WALLOPS FLIGHT FACILITY, VA – Astronauts aboard the International Space Station are now busily unloading nearly four tons of science experiments, research gear, station equipment and crew supplies – following the spectacular launch of the Orbital ATK Antares rocket earlier this week on Sunday Nov. 12 from Virginia’s eastern shore that propelled the Cygnus cargo freighter to an on time arrival two days later on Tuesday Nov. 14.
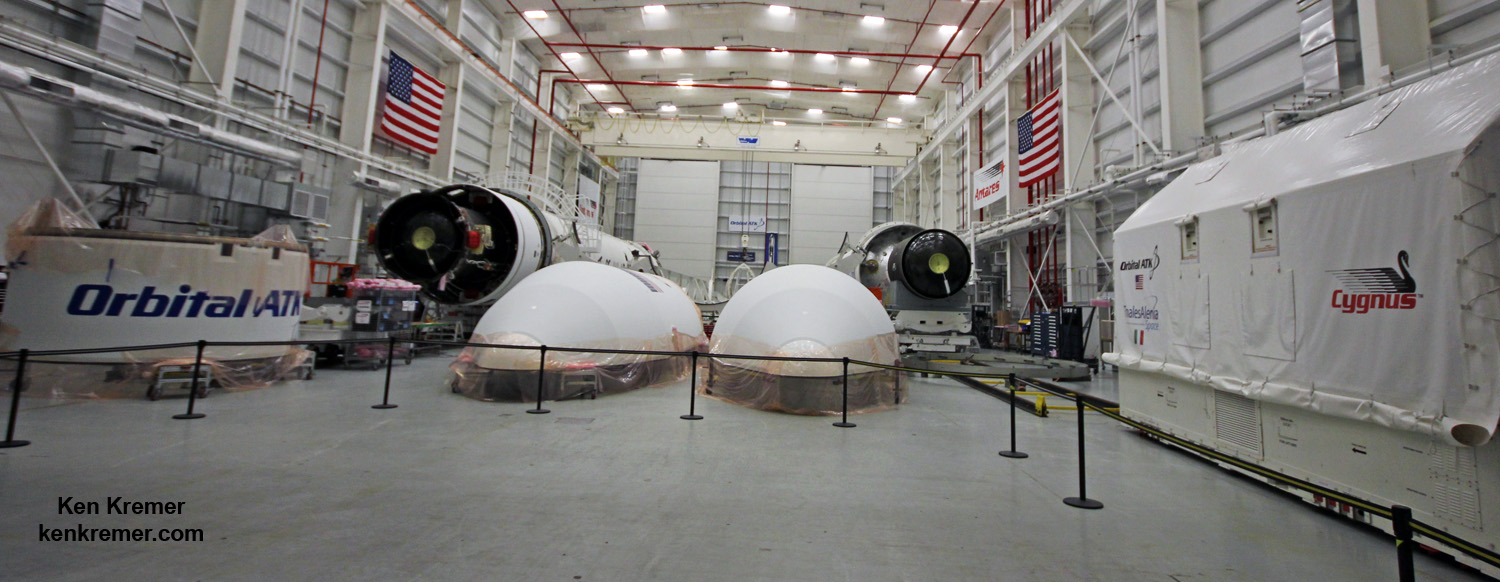
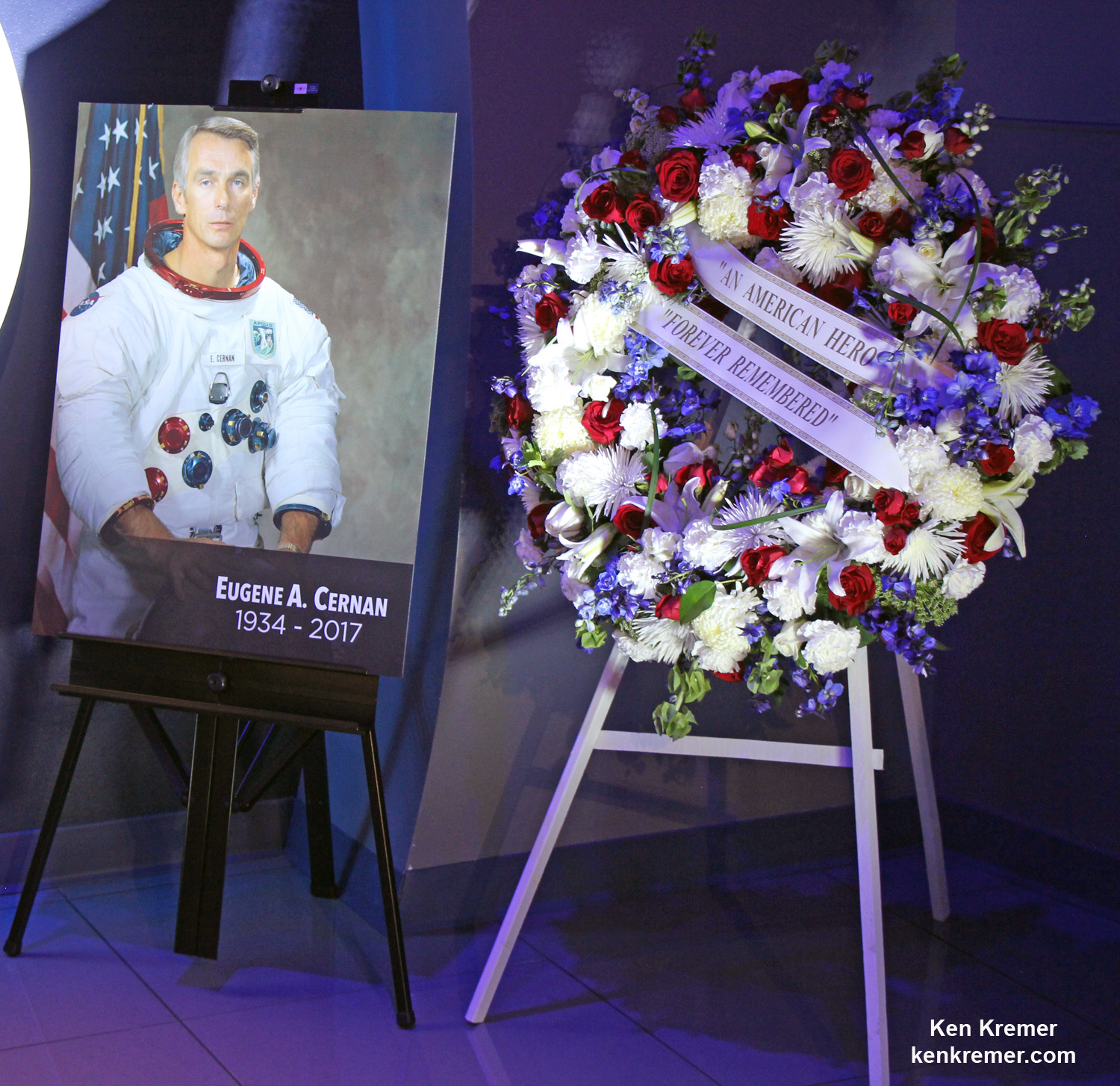
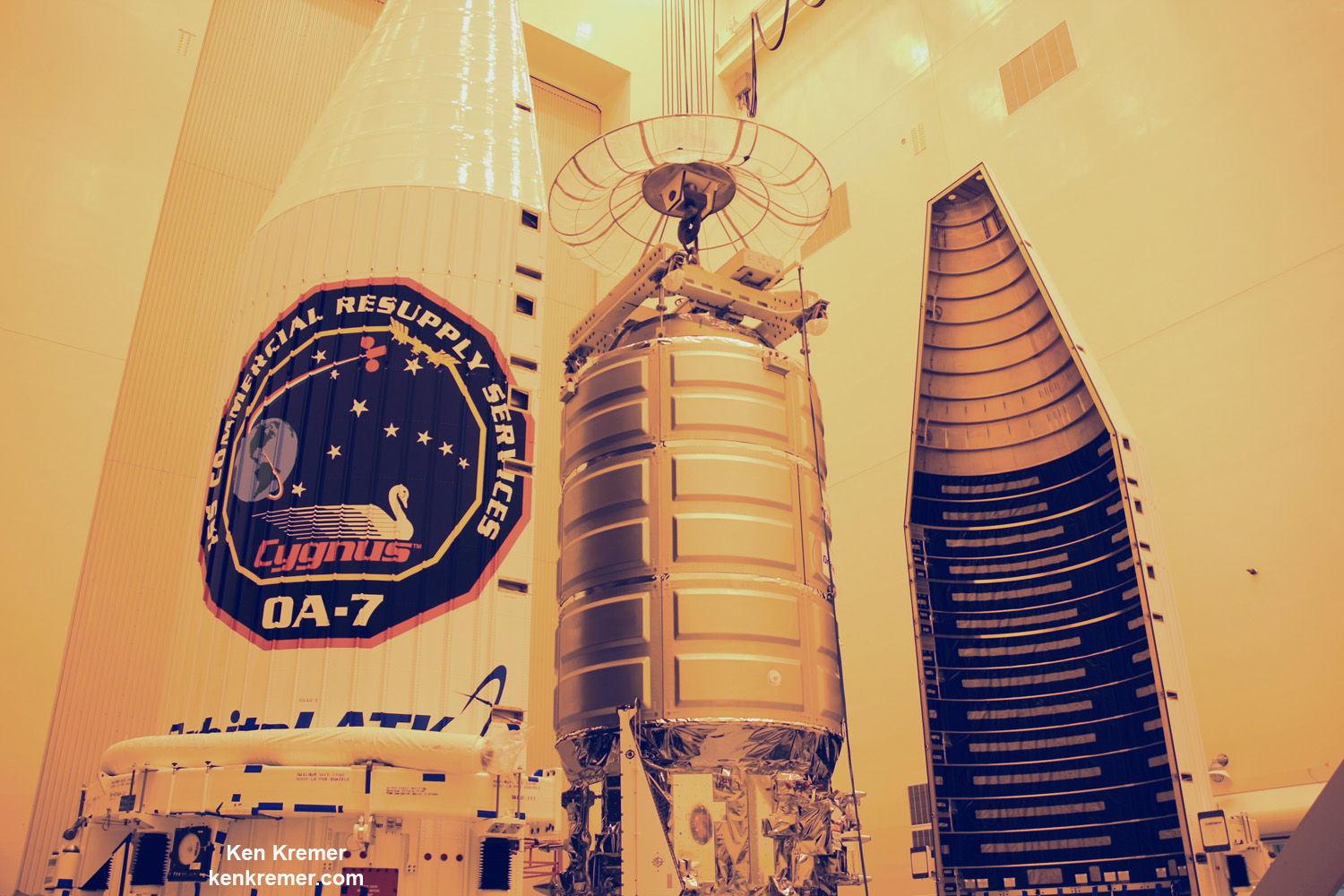
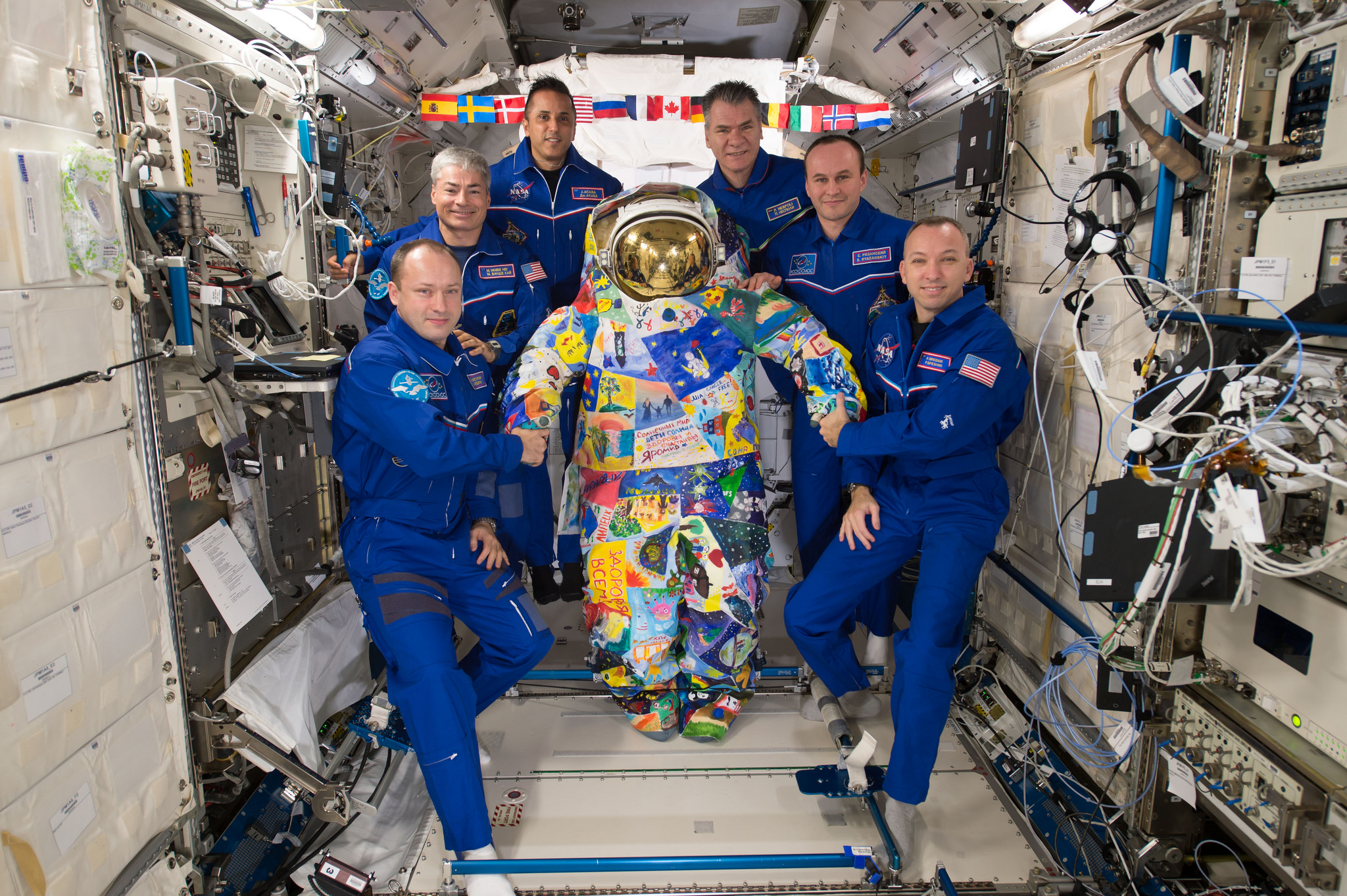
The Orbital ATK Cygnus spacecraft was christened the S.S. Gene Cernan and named in honor of NASA’s Apollo 17 lunar landing commander; Gene Cernan.
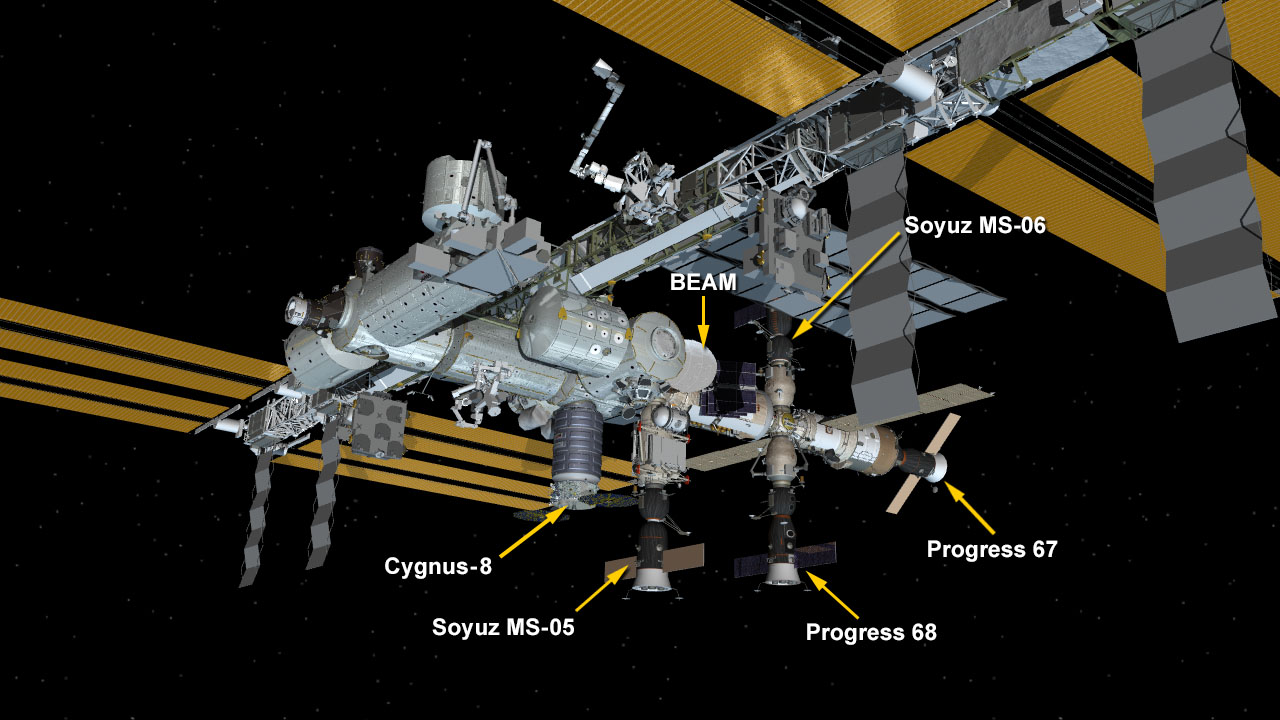
Among the goodies delivered by the newly arrived S.S. Gene Cernan Cygnus OA-8 supply run to resident the crew of six astronauts and cosmonauts from the US, Russia and Italy are ice cream, pizza and presents for the holidays. They are enjoying the fruits of the earthy labor of thousands of space workers celebrating the mission’s success.

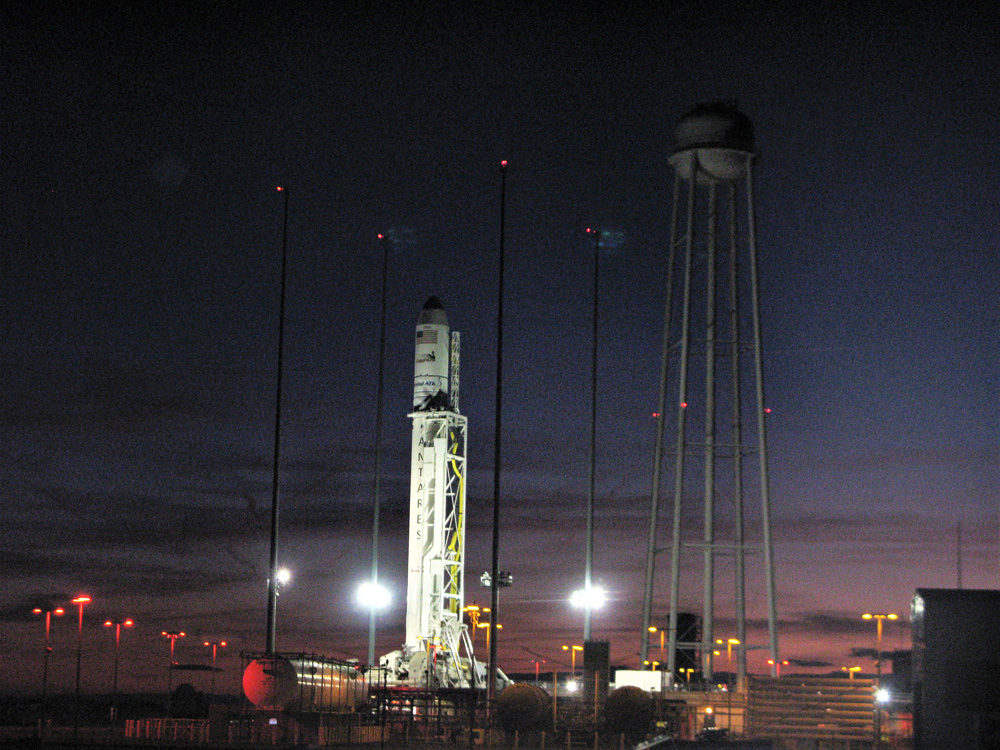
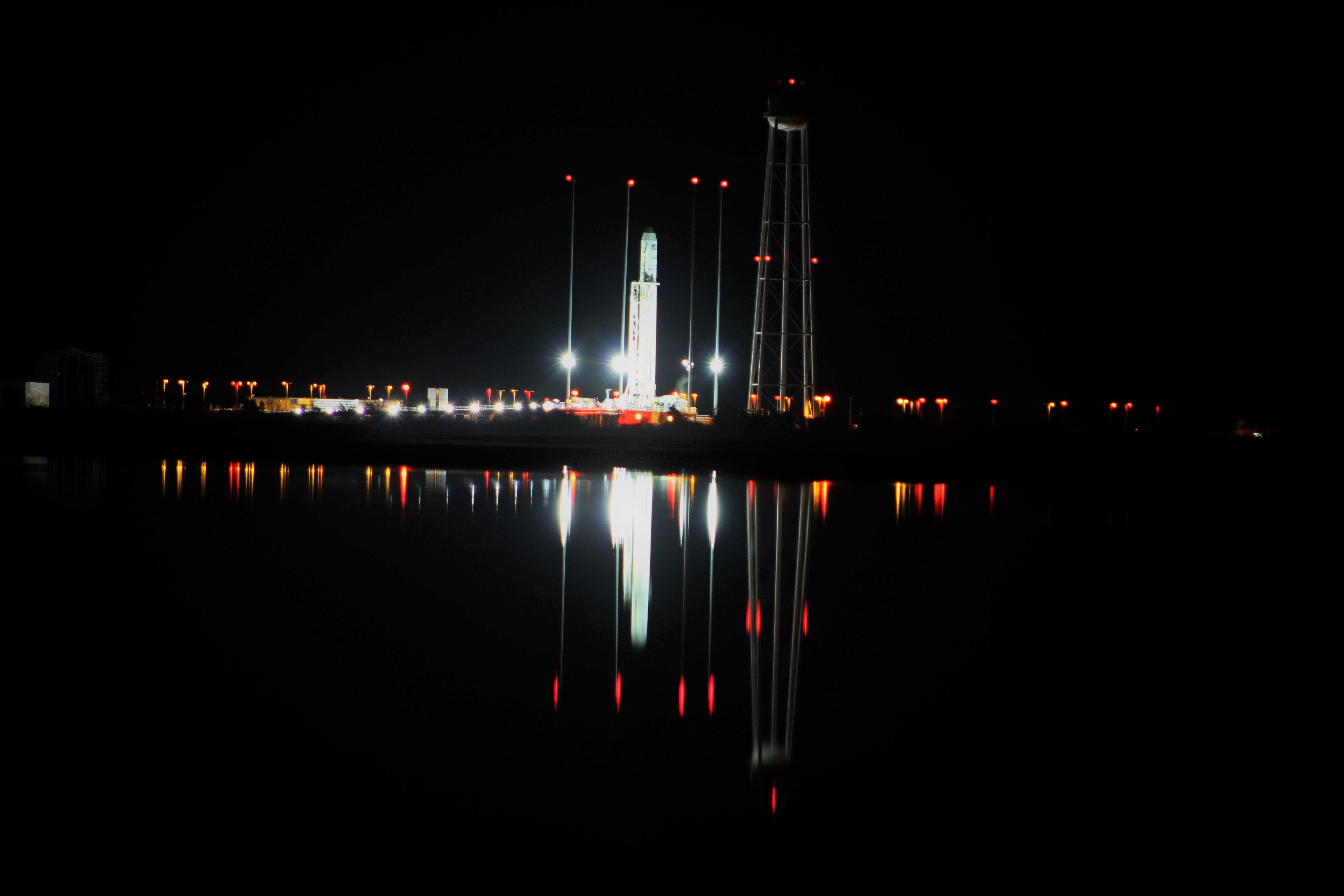
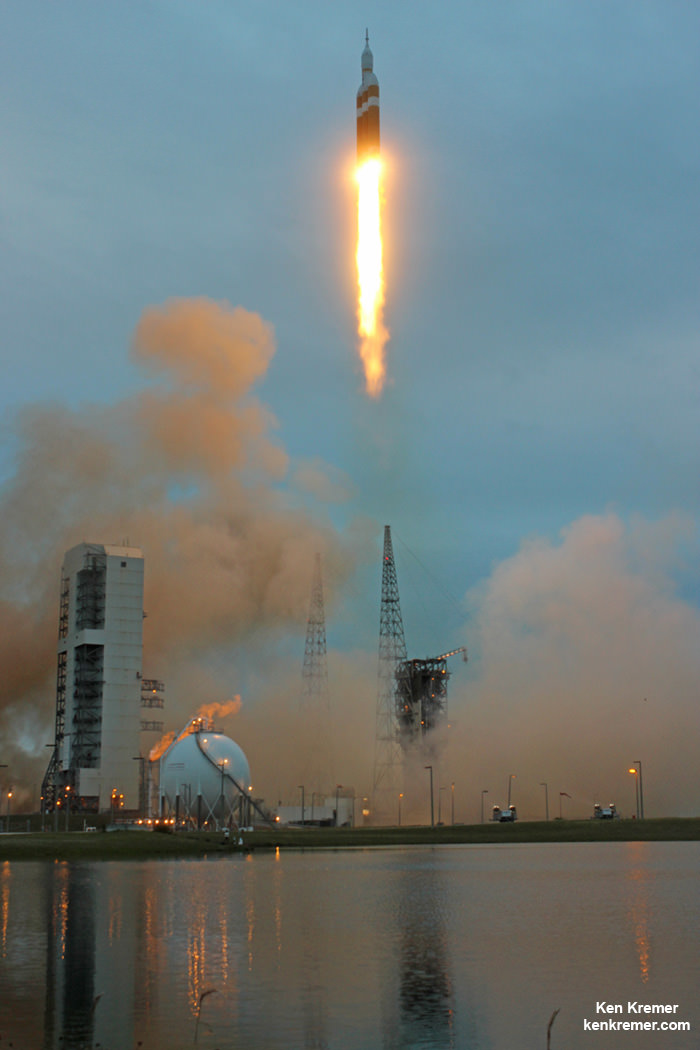
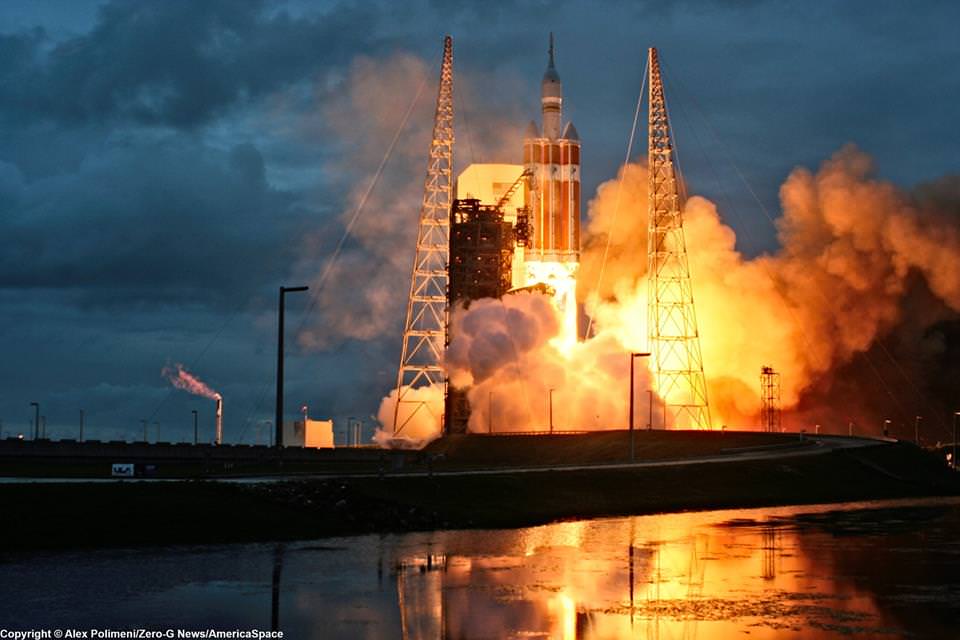
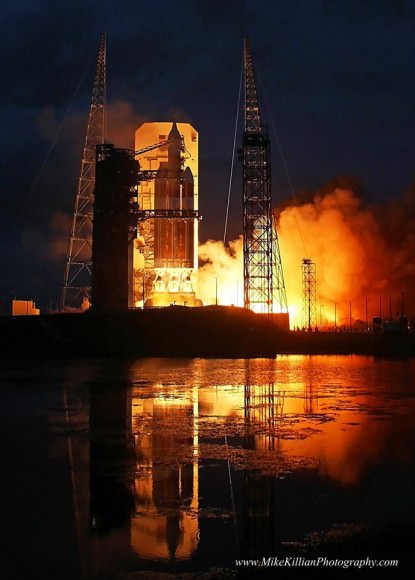
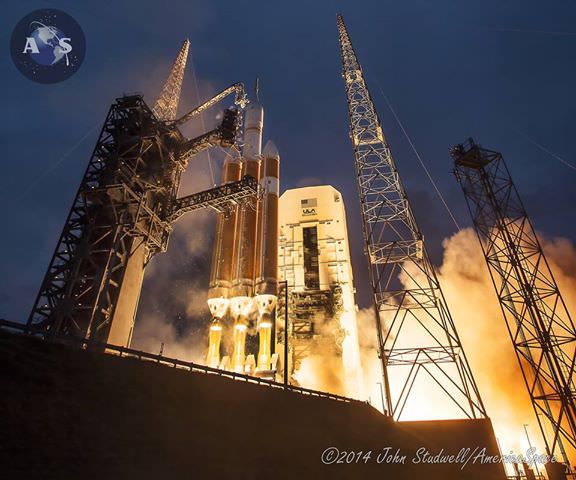
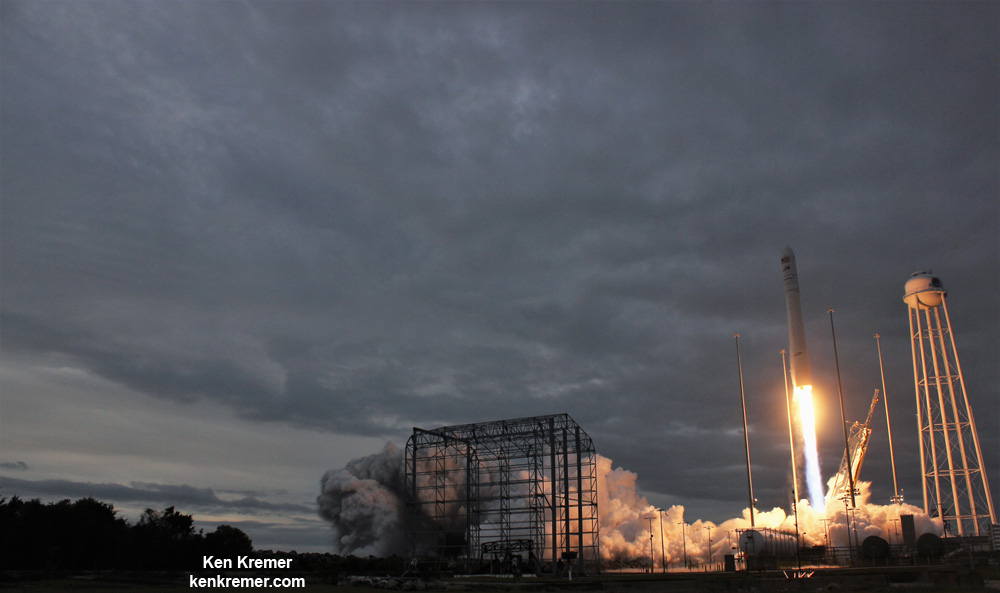
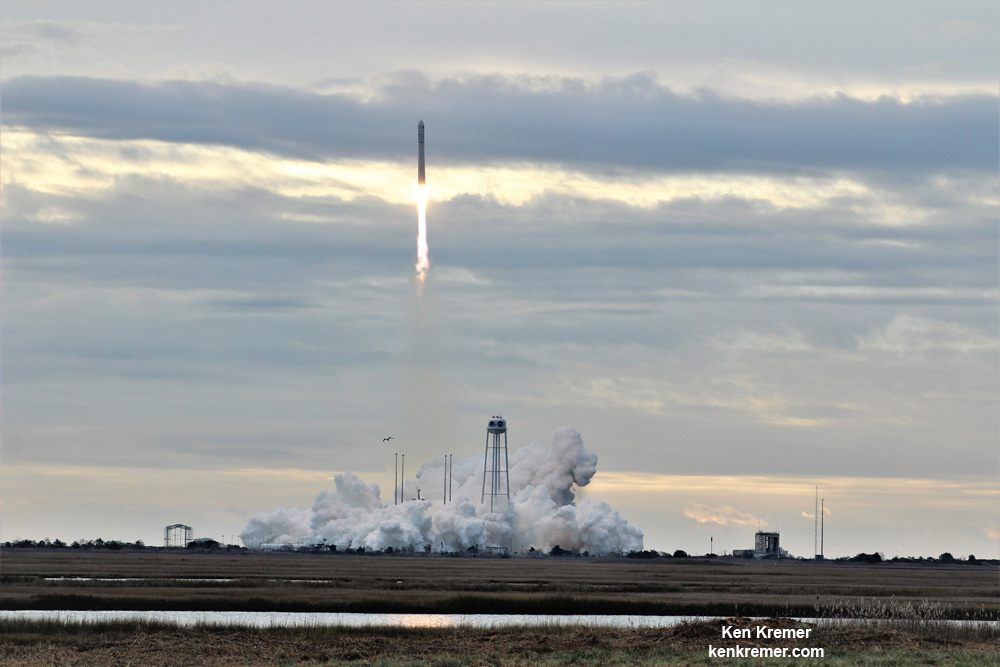
The journey began with the flawless liftoff of the two stage Antares rocket shortly after sunrise Sunday at 7:19 a.m. EST, Nov. 12, rocket from Pad-0A at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia.
Check out the expanding gallery of launch imagery and videos captured by this author and several space colleagues of Antares prelaunch activities around the launch pad and through Sunday’s stunningly beautiful sunrise blastoff.
After a carefully choreographed series of intricate thruster firings to raise its orbit in an orbital pursuit over the next two days, the Cygnus spacecraft on the OA-8 resupply mission for NASA arrived in the vicinity of the orbiting research laboratory.
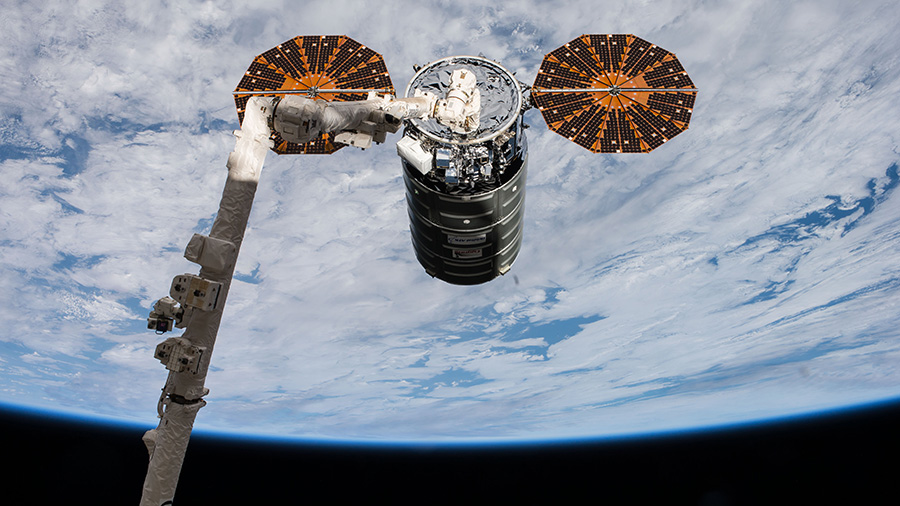

Expedition 53 Flight Engineer Paolo Nespoli of ESA (European Space Agency) assisted by NASA astronaut Randy Bresnik then deftly maneuvered the International Space Station’s 57.7-foot-long (17.6 meter-long) Canadarm2 robotic arm to grapple and successfully capture the Cygnus cargo freighter at 5:04 a.m., Tuesday Nov. 14.
The station was orbiting 260 statute miles over the South Indian Ocean at the moment Nespoli grappled the S.S. Gene Cernan Cygnus spacecraft with the Canadian-built robotic arm.
Ground controllers at NASA’s Mission Control at the Johnson Space Center in Texas, then maneuvered the arm and robotic hand grappling Cygnus towards the exterior hull and berthed the cargo ship at the Earth-facing port of the stations Unity module.
The berthing operation was completed at 7:15 a.m. after all 16 bolts were driven home for hard mating as the station was flying 252 miles over the North Pacific in orbital night.

The Cygnus spacecraft dubbed OA-8 is Orbital ATK’s eighth contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA to the International Space Station under the unmanned Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) program to stock the station with supplies on a continuing and reliable basis.
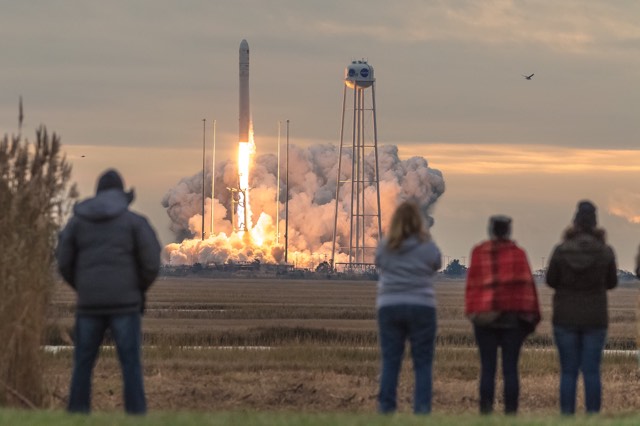

Altogether over 7,400 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware launched to the orbital laboratory and its crew of six for investigations that will occur during Expeditions 53 and 54.
The S.S. Gene Cernan manifest includes equipment and samples for dozens of scientific investigations including those that will study communication and navigation, microbiology, animal biology and plant biology. The ISS science program supports over 300 ongoing research investigations.
Apollo 17 was NASA’s final lunar landing mission. Gere Cernan was the last man to walk on the Moon.

Among the experiments flying aboard Cygnus are the coli AntiMicrobial Satellite (EcAMSat) mission, which will investigate the effect of microgravity on the antibiotic resistance of E. coli, the Optical Communications and Sensor Demonstration (OCSD) project, which will study high-speed optical transmission of data and small spacecraft proximity operations, the Rodent Research 6 habitat for mousetronauts who will fly on a future SpaceX cargo Dragon.
Cygnus will remain at the space station until Dec. 4, when the spacecraft will depart the station and release 14 CubeSats using a NanoRacks deployer, a record number for the spacecraft.
It will then be commanded to fire its main engine to lower its orbit and carry out a fiery and destructive re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean as it disposes of several tons of trash.

The Cygnus OA-8 manifest includes:
Crew Supplies 2,734.1 lbs. / 1,240 kg
Science Investigations 1631.42 lbs. / 740 kg
Spacewalk Equipment 291.0 lbs. / 132 kg
Vehicle Hardware 1,875.2 lbs. / 851 kg
Computer Resources 75.0 lbs. / 34 kg
Total Cargo: 7,359.0 lbs. / 3,338 kg
Total Pressurized Cargo with Packaging: 7,118.7 lbs. / 3,229 kg
Unpressurized Cargo (NanoRacks Deployer): 240.3 lbs. / 109 kg
Under the Commercial Resupply Services-1 (CRS-1) contract with NASA, Orbital ATK will deliver approximately 66,000 pounds (30,000 kilograms) of cargo to the space station. OA-8 is the eighth of these missions.
The Cygnus OA-8 spacecraft is Orbital ATK’s eighth contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA to the International Space Station under the unmanned Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) program to stock the station with supplies on a continuing basis.
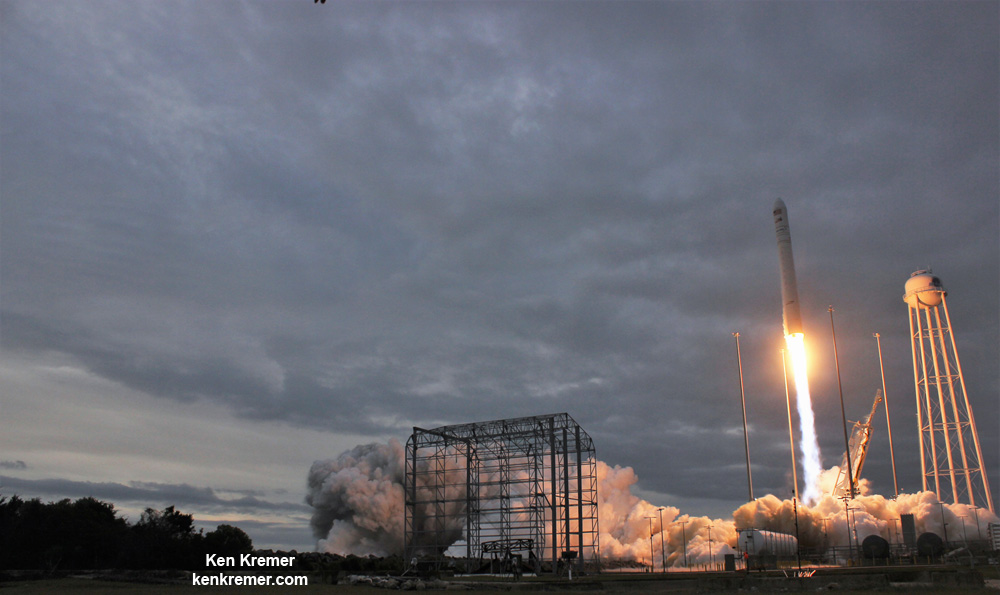

Beginning in 2019, the company will carry out a minimum of six cargo missions under NASA’s CRS-2 contract using a more advanced version of Cygnus.

Watch for Ken’s continuing Antares/Cygnus mission and launch reporting from on site at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility, VA during the launch campaign.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.