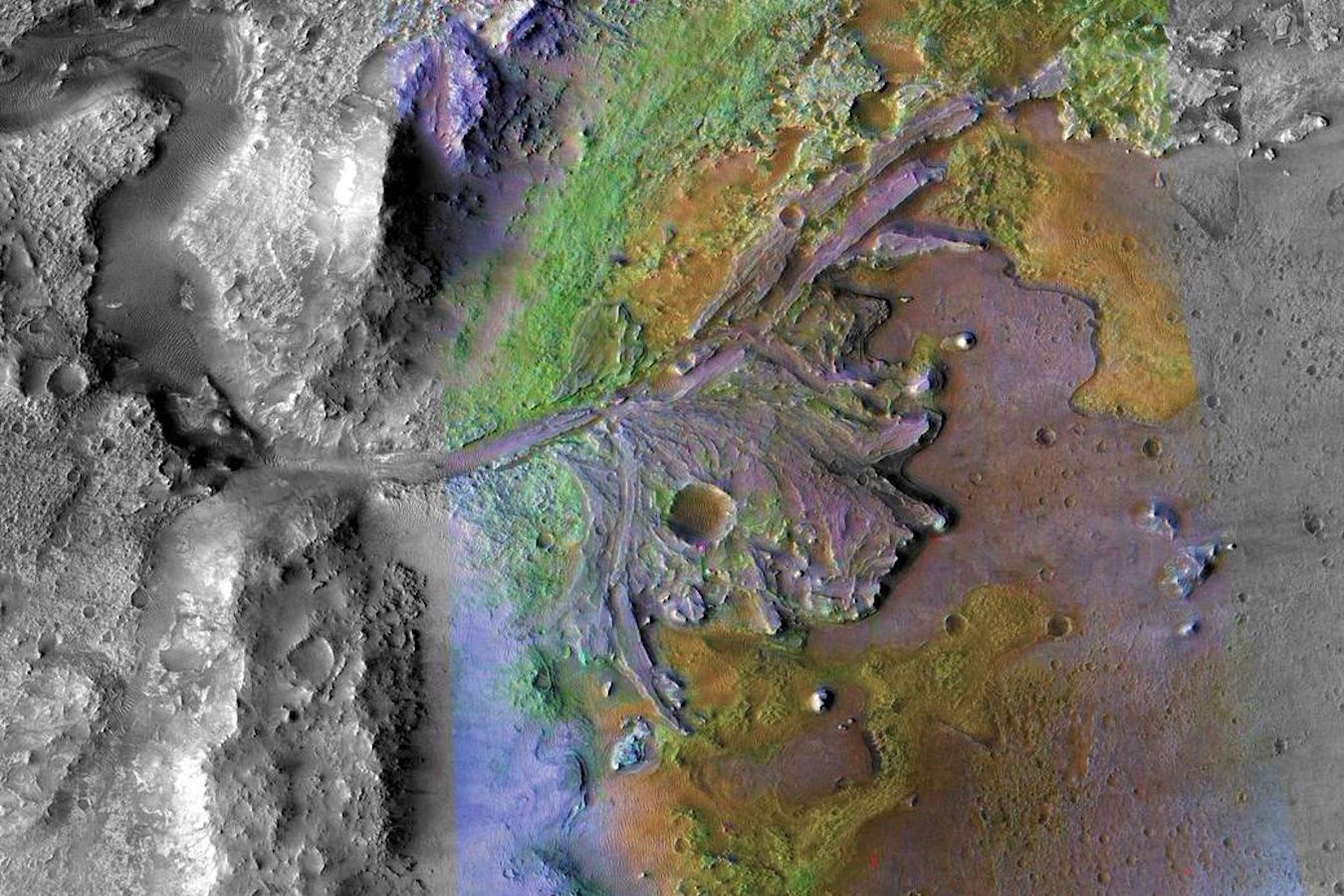
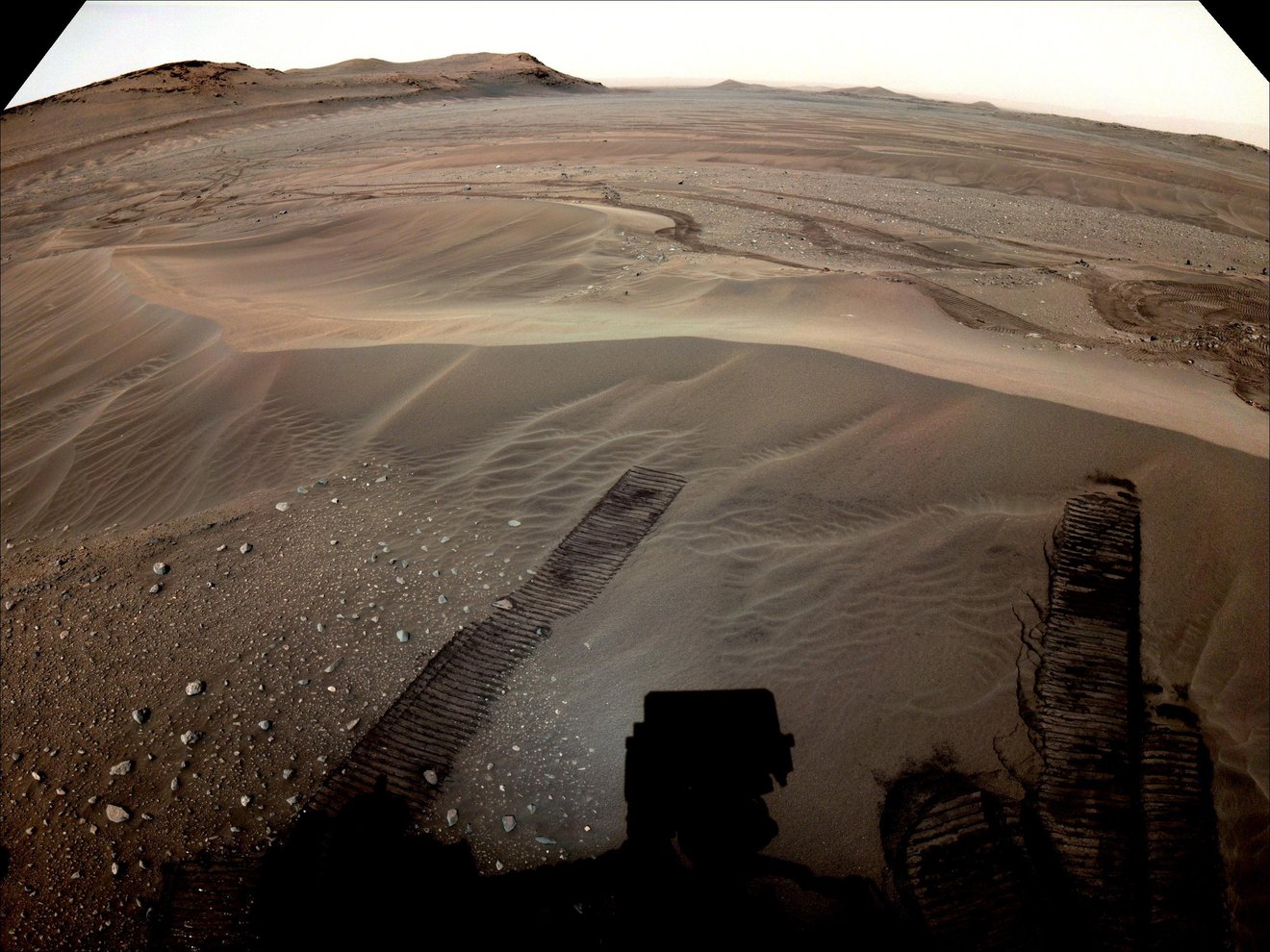
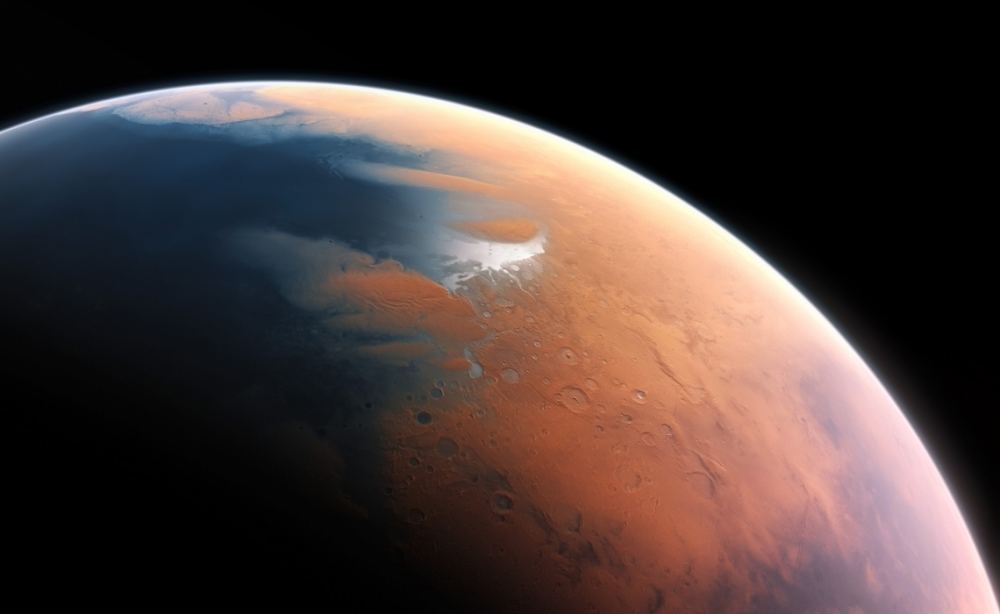
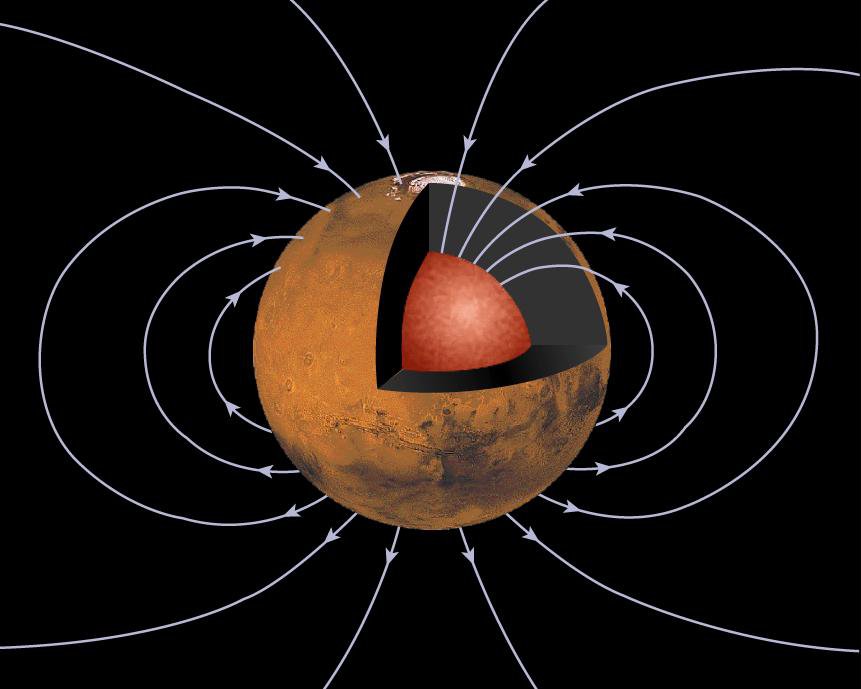
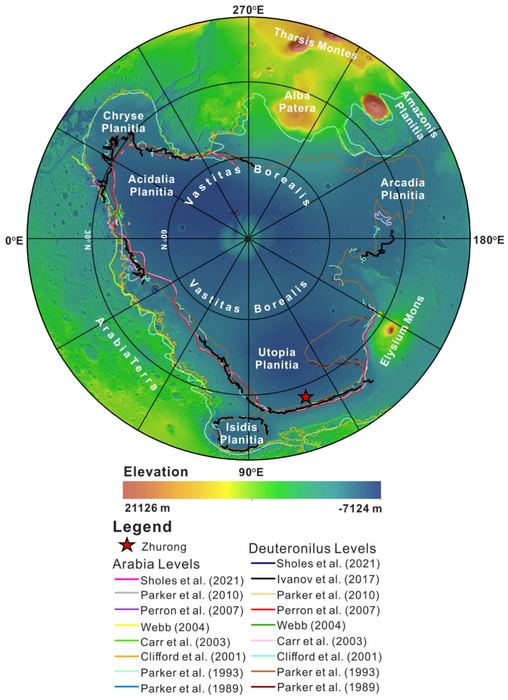
NASA is actively working to return surface samples from Mars in the next few years, which they hope will help us better understand whether ancient life once existed on the Red Planet’s surface billions of years ago. But what about atmospheric samples? Could these provide scientists with better information pertaining to the history of Mars? This is what a recent study presented at the 55th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference hopes to address as a team of international researchers investigated the significance of returning atmospheric samples from Mars and how these could teach us about the formation and evolution of the Red Planet.
Continue reading “Could Martian atmospheric samples teach us more about the Red Planet than surface samples?”Could Martian atmospheric samples teach us more about the Red Planet than surface samples?