Combined Hubble (optical) and VLA (radio) images show enormous radio jets shooting out from the galaxy Hercules A
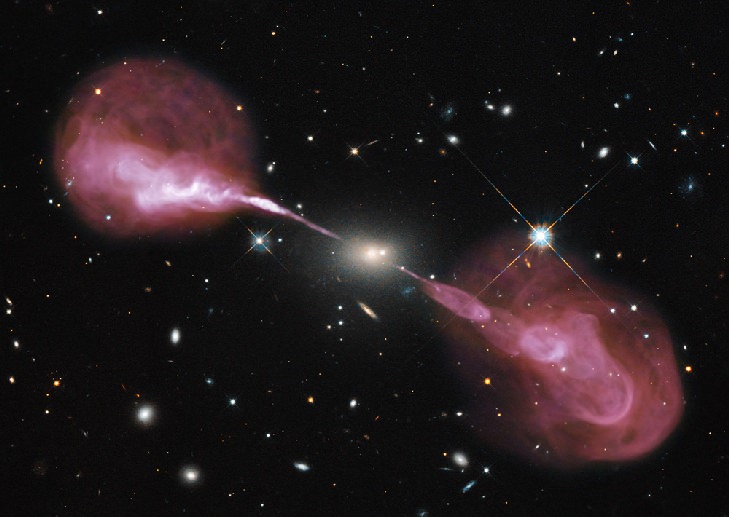
Talk about pouring your heart out! Astronomers using Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 and the recently-upgraded Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) radio telescope in New Mexico have identified gigantic jets of plasma, subatomic particles and magnetic fields blasting out of the center of Hercules A, a massive galaxy 2 billion light-years away.
The image above is a combination of optical images from Hubble and radio data gathered by the multi-dish VLA. If our eyes could see in the high-energy spectrum of radio, this is what Hercules A — the otherwise ordinary-looking elliptical galaxy in the center — would really look like.
(Of course, if we could see in radio our entire sky would be a very optically busy place!)
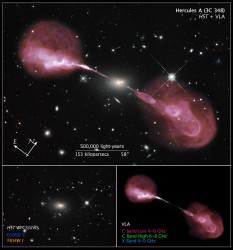 Also known as 3C 348, Hercules A is incredibly massive — nearly 1,000 times the mass of our Milky Way galaxy with a similarly scaled-up version of a supermassive black hole at its center. Due to its powerful gravity and intense magnetic field Hercules A’s monster black hole is firing superheated material far out into space from its rotational poles. Although invisible in optical light, these jets are bright in radio wavelengths and are thus revealed through VLA observations.
Also known as 3C 348, Hercules A is incredibly massive — nearly 1,000 times the mass of our Milky Way galaxy with a similarly scaled-up version of a supermassive black hole at its center. Due to its powerful gravity and intense magnetic field Hercules A’s monster black hole is firing superheated material far out into space from its rotational poles. Although invisible in optical light, these jets are bright in radio wavelengths and are thus revealed through VLA observations.
Traveling close to the speed of light, the jets stretch for nearly 1.5 million light-years from both sides of the galaxy. Ring-shaped structures within them suggest that occasional strong outbursts of material have occurred in the past.
Announced on November 29, these findings illustrate the combined imaging power of two of astronomy’s most valuable and cutting-edge tools: Hubble and the newly-updated VLA. The video below shows how it was all done… check it out.
Read more on the NRAO press release here.
Image credits: NASA, ESA, S. Baum and C. O’Dea (RIT), R. Perley and W. Cotton (NRAO/AUI/NSF), and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA). Source: NRAO.

