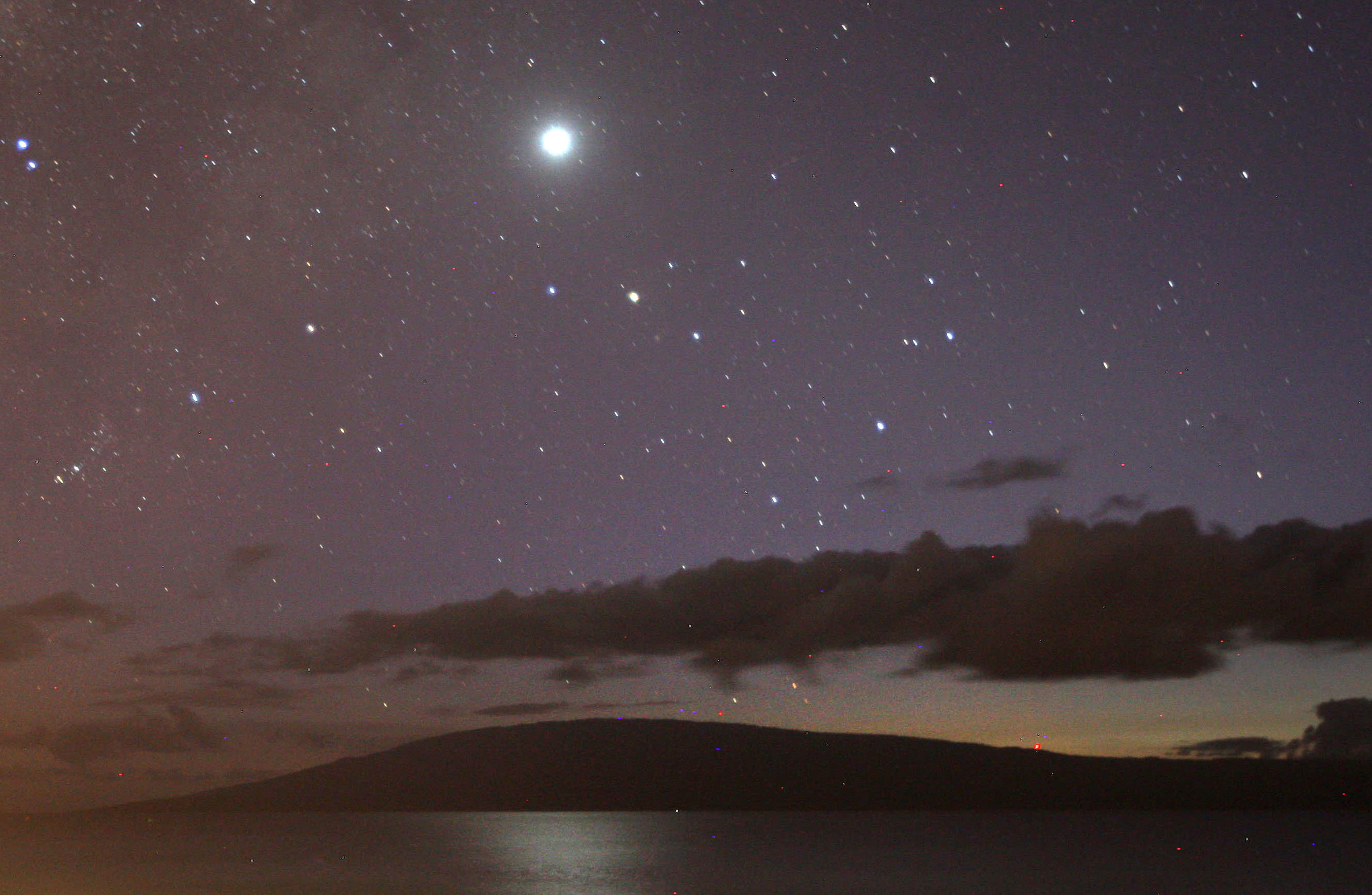
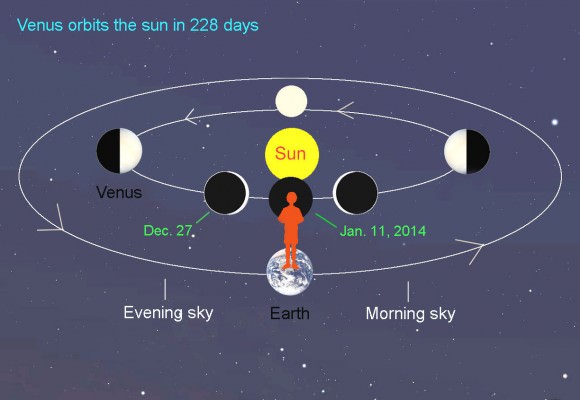
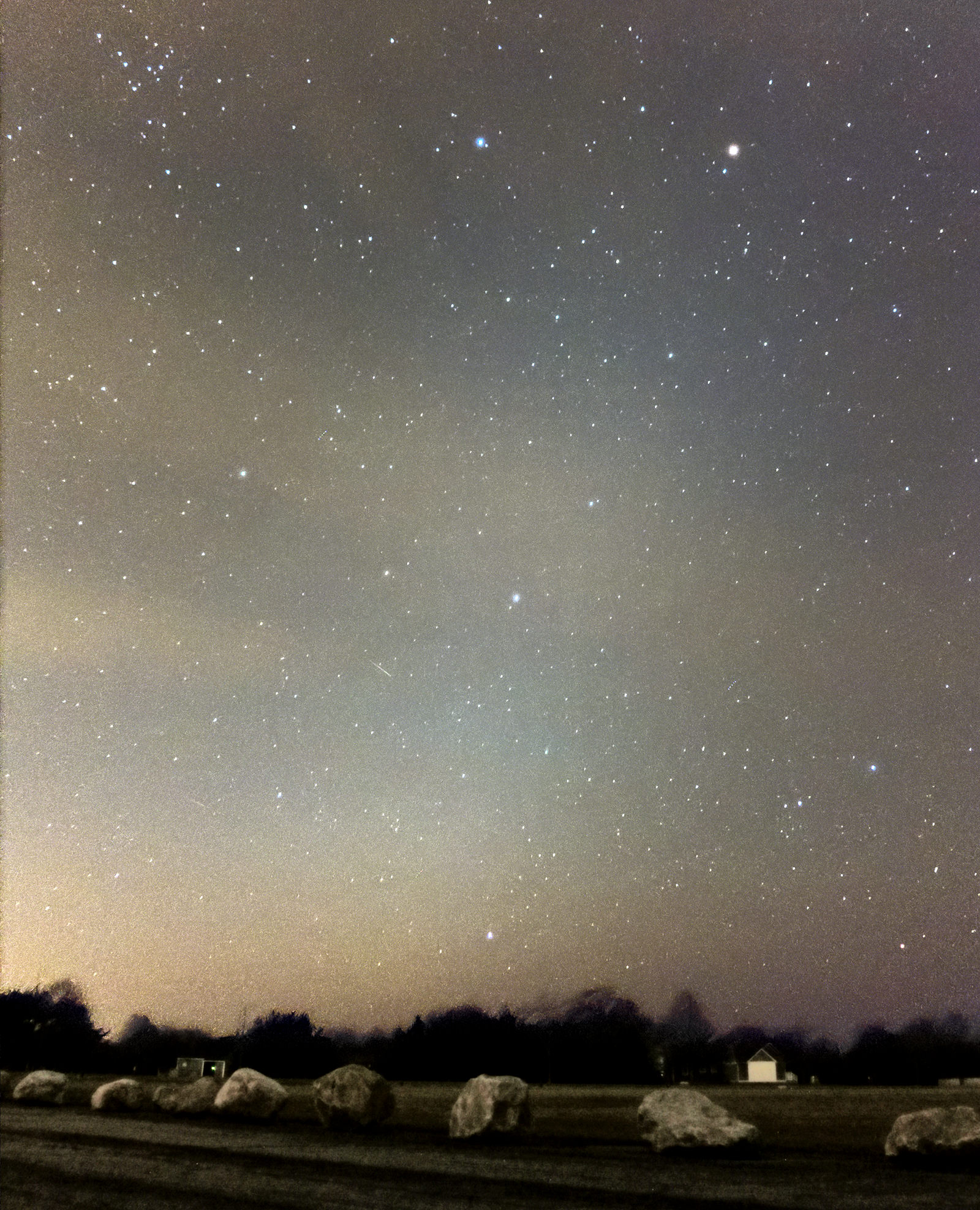
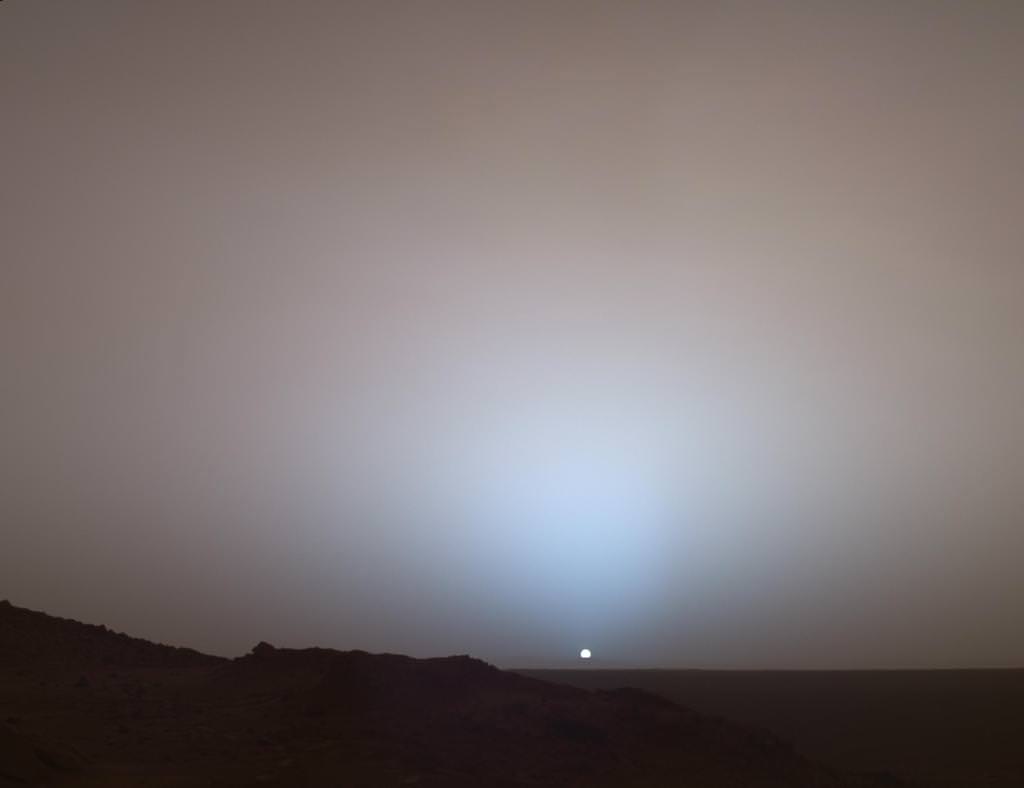
The result of sunlight reflected off fine particles of dust aligned along the plane of the Solar System, zodiacal light appears as a diffuse, hazy band of light stretching upwards from the horizon after sunset or before sunrise. Most people have never seen zodiacal light because it’s very dim, and thus an extremely dark sky is required. But thanks to recent dark sky regulations that were passed in the coastal Rhode Island town of Charlestown, this elusive astronomical phenomenon has become visible — to the particular delight of one local observatory.
Frosty Drew Observatory is a small, privately-run observatory featuring a Meade Schmidt Cassegrain LX200 16″ telescope mounted on an alt-azimuth pier inside a dome that stands among the sports fields, parking areas, and nature trails of Ninigret Park and Wildlife Refuge in southern Rhode Island. Being a good distance from urban centers and developed areas, the skies there are some of the darkest in the state. But situated along the eastern seaboard of the United States, even Charlestown’s coast lies beneath a perpetual haze of light pollution.
A new town ordinance, passed in 2012, helped to darken the skies a notch. And while watching comet ISON one evening, astronomer Scott MacNeill became aware of the results.
The following is an excerpt from a Jan. 7 article by Cynthia Drummond of The Westerly Sun, reprinted with permission:
Scott MacNeill was in Ninigret Park, his telescope trained on the comet “Ison,” when he saw something he had never seen before: a celestial phenomenon called “zodiacal light.” After several decades of being obscured by light pollution, the feature was visible again, thanks to the town’s “dark sky” ordinance.
At first, MacNeill, an astronomer and the assistant director of the Frosty Drew observatory, didn’t believe what he was seeing. The cone of light, which he initially thought was light pollution, turned out to be a faint, white glow that astronomers at the observatory hadn’t glimpsed in recent memory.

“To see it in New England, period, is amazing, Zodiacal light is a common marker for the quality of a dark sky location.”
– Scott MacNeill, Astronomer, Frosty Drew Observatory
“I was sitting back for a minute, just looking at the sky, and I said ‘wait a minute. This is the southeast, and to the southeast is the ocean. What is coming up in the southeast?’ And then I noticed the cone. And I’m like ‘no way. That can’t be zodiacal light.’ I’ve heard so many stories about the days of old at Frosty Drew when you used to see zodiacal light here,” he said.
MacNeill credits Charlestown’s dark sky ordinance with reducing light pollution to the point where zodiacal light can be seen again. The ordinance, adopted in October 2012, regulates commercial outdoor lighting in order to improve the town’s dark sky for star-gazers, and to protect residents, wildlife and light-sensitive plants from the effects of light pollution.
One of the provisions of the ordinance requires that new lighting fixtures be designed to focus downward so light does not radiate up into the sky. Lighting installed before the ordinance was passed is exempt from the new regulations.
Building and Zoning Official Joe Warner explained that after the ordinance passed, two major sources of light pollution near the observatory were modified so they would be less polluting.
“At Ninigret Wildlife Refuge, some of the pole lights were changed to dark sky compliant lighting. The Charlestown Ambulance barn also replaced their lights with dark sky compliant lights,” he said.
Charlestown has been recognized as one of the only dark spots on the New England coast — a rare treat for people who enjoy looking at the night sky.
(Read the full article on The Westerly Sun’s website here.)
_________________
It’s fantastic to see results like this both occurring and being publicized, as dark skies have become quite rare in many populated areas of the world. People who live in or near major metropolitan areas — even in the surrounding sprawling suburbs — often never truly get a dark sky, not such that the dimmer stars, the Milky Way, meteor showers — and yes, the zodiacal light — can be readily seen on an otherwise clear night. The view of a star-filled night sky that has been a part of the human existence for millennia has steadily been doused by the murky glow of artificial lighting. Luckily groups like the International Dark Sky Association are actively trying to change that, but change isn’t always welcome — or quick.
At least, in one Rhode Island town anyway, a small victory has been won for the night.
(HT to Brown University’s Ladd Observatory in Providence for the heads-up on this story.)


































![MER10-SpiritAndOpportunity_ByTheNumbers[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/MER10-SpiritAndOpportunity_ByTheNumbers1-580x423.jpg)