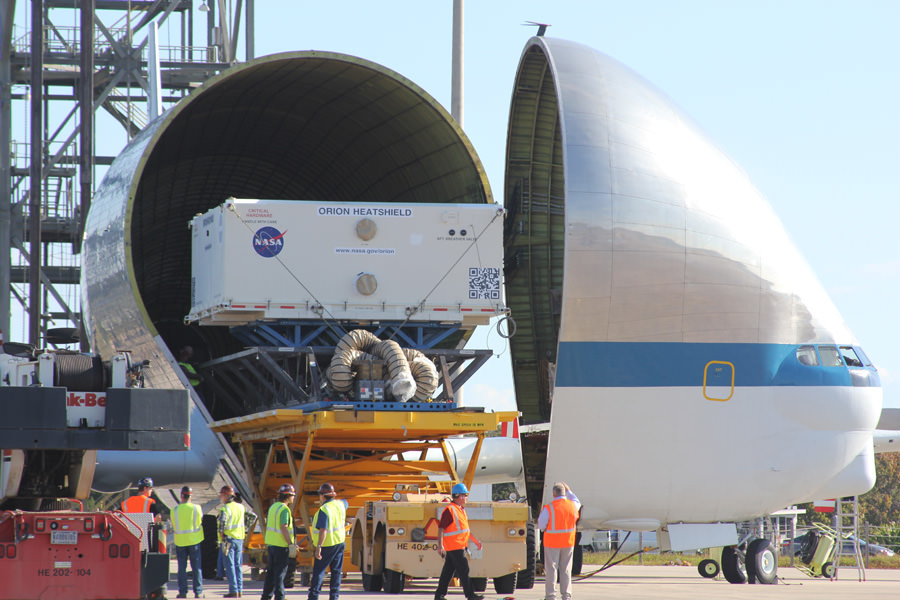
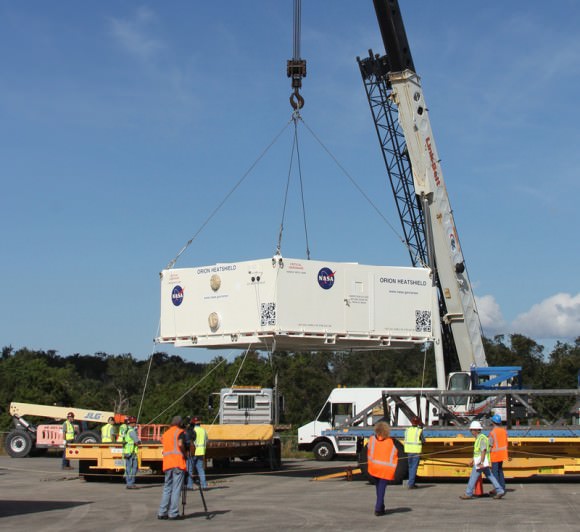
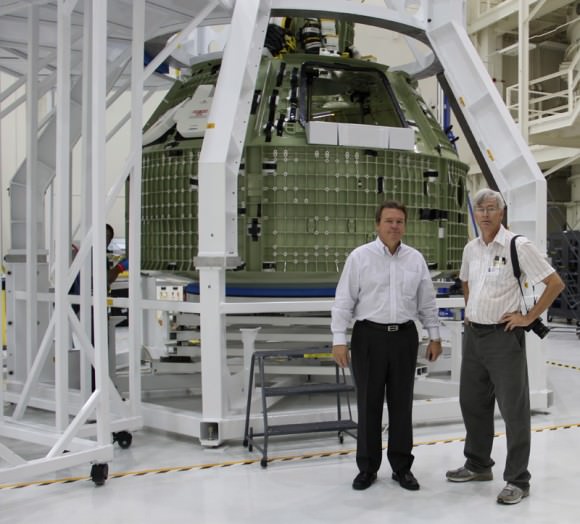
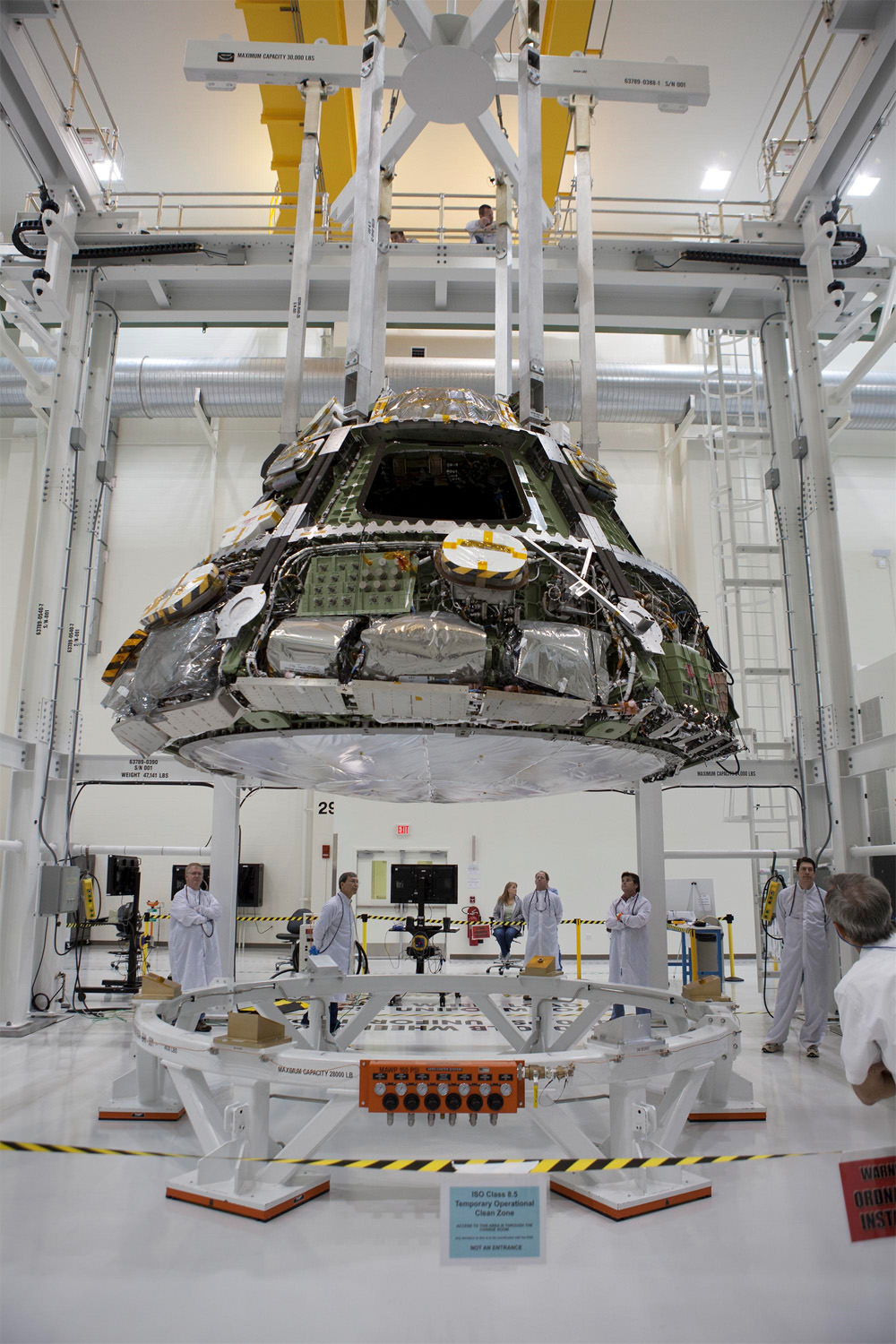
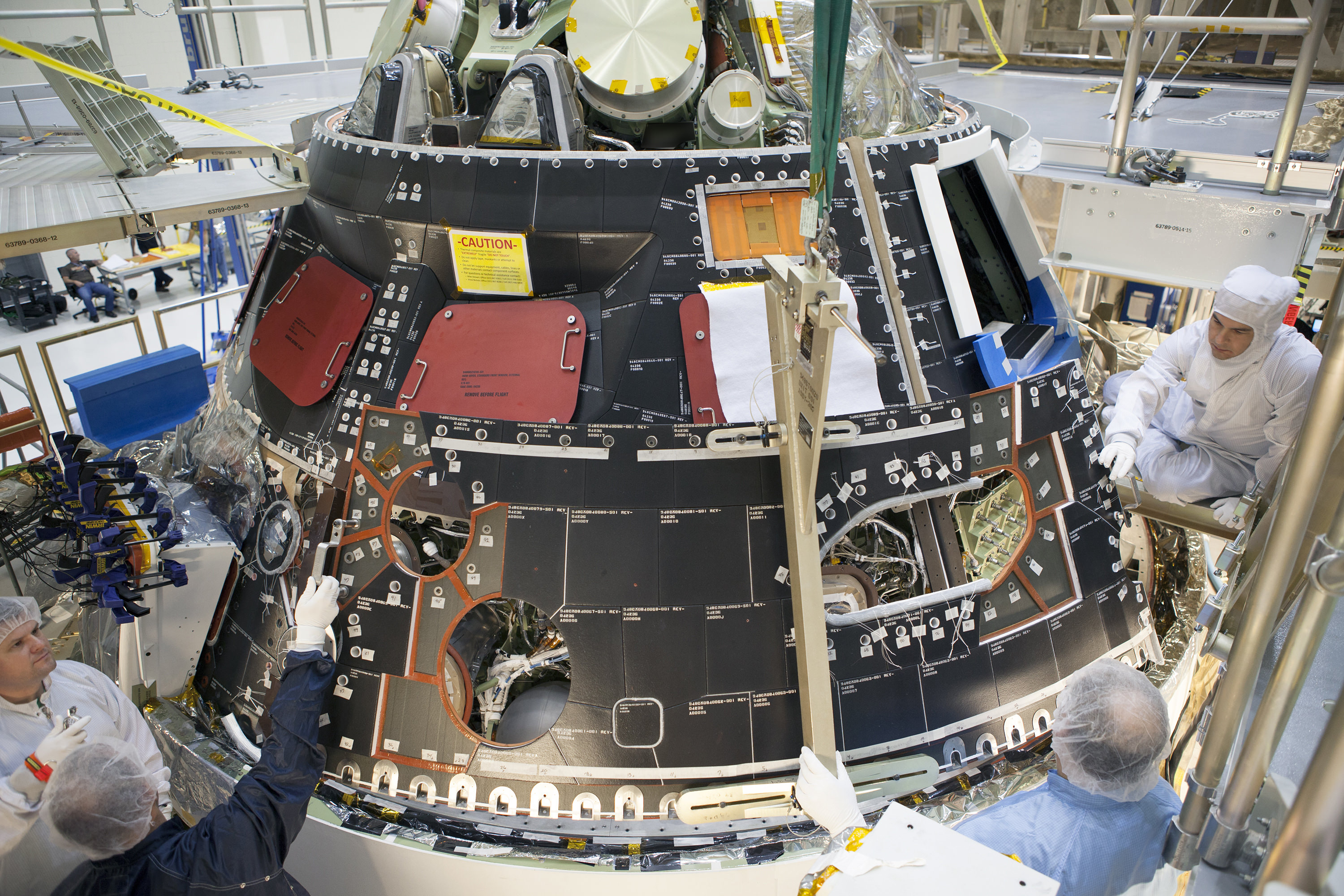
This past weekend technicians completed assembly of NASA’s first Orion crew module at the agency’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout (O & C) Facility at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida, signifying a major milestone in the vehicles transition from fabrication to full scale launch operations.
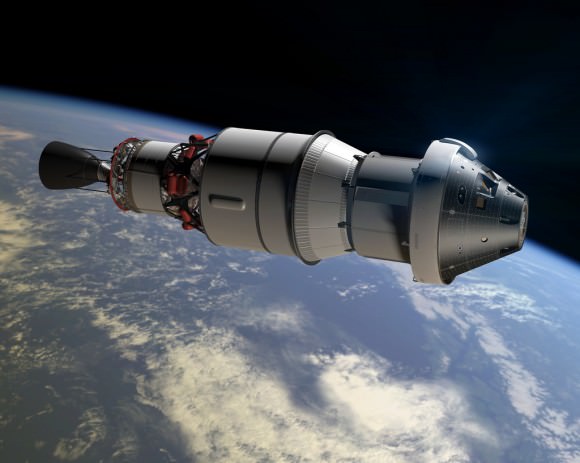
Orion is NASA’s next generation human rated vehicle and is scheduled to launch on its maiden uncrewed mission dubbed Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) in December 2014. It replaces the now retired space shuttle orbiters.
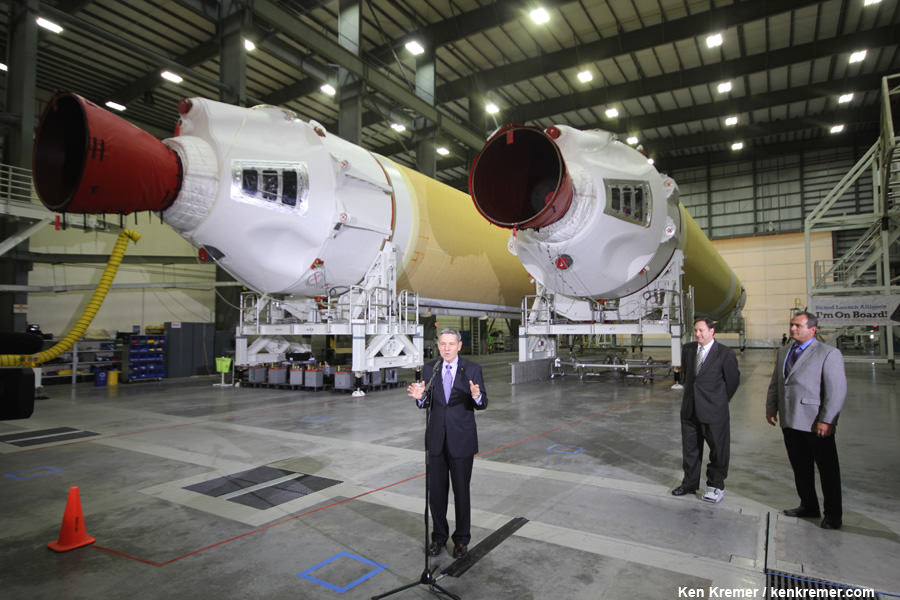
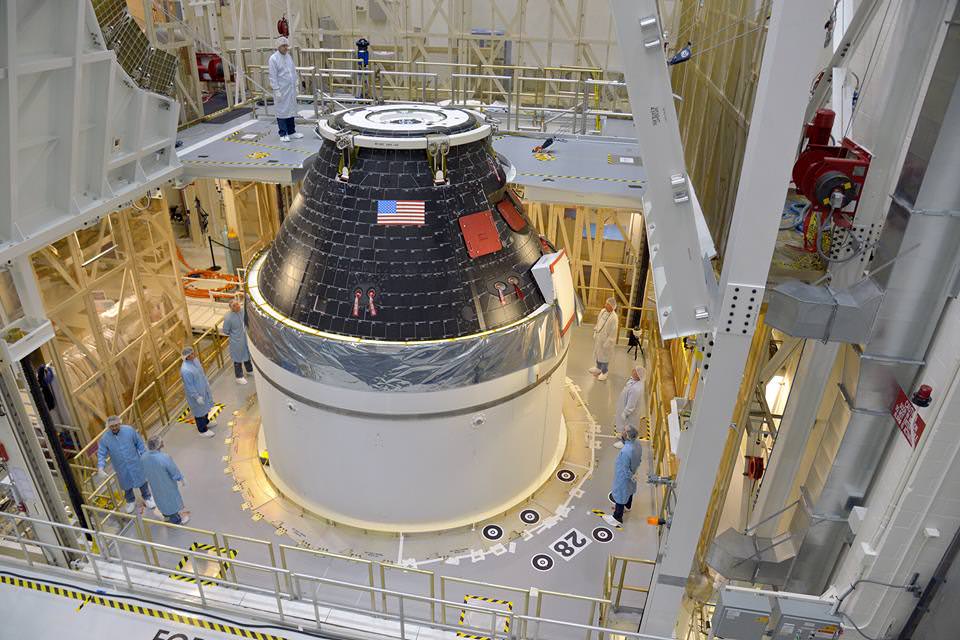
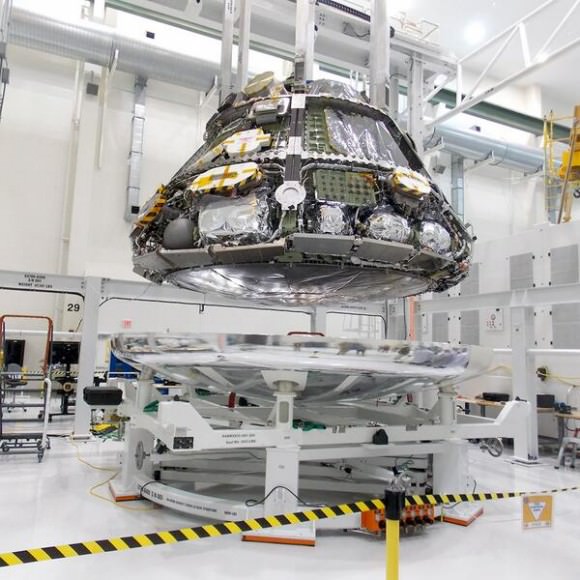
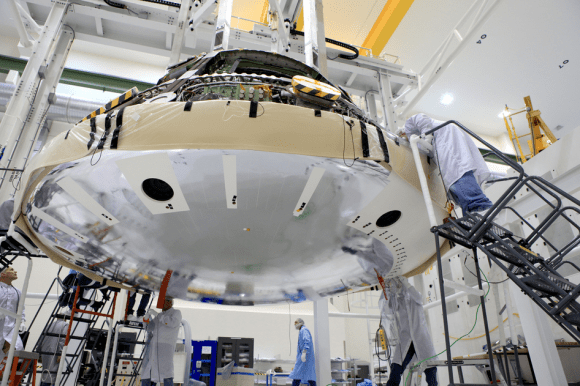
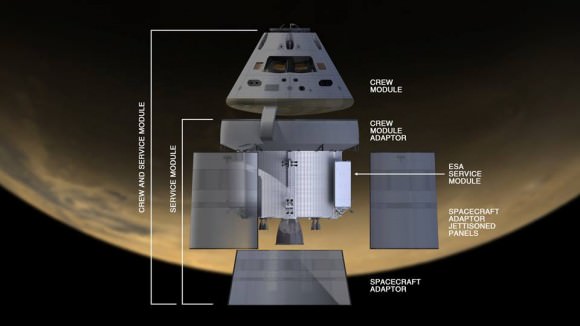
The black Orion crew module (CM) sits stacked atop the white service module (SM) in the O & C high bay photos, shown above and below.
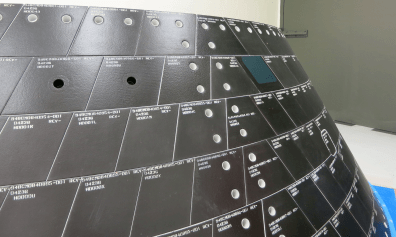
The black area is comprised of the thermal insulating back shell tiles. The back shell and heat shield protect the capsule from the scorching heat of re-entry into the Earth’s atmosphere at excruciating temperatures reaching over 4000 degrees Fahrenheit (2200 C) – detailed in my story here.
Technicians and engineers from prime contractor Lockheed Martin subsequently covered the crew module with protective foil. The CM/SM stack was then lifted and moved for the installation of the Orion-to-stage adapter ring that will mate them to the booster rocket.

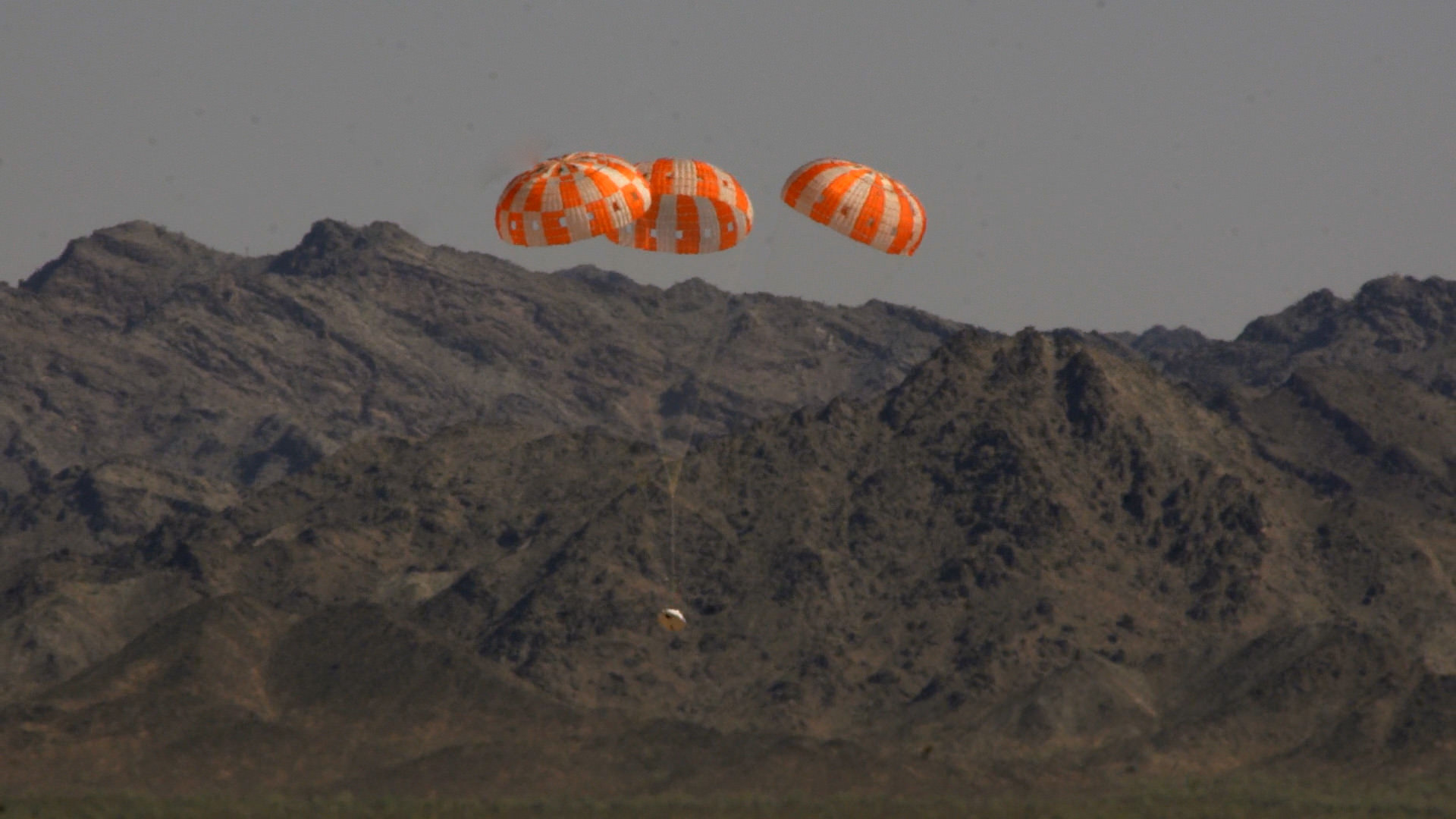
At the conclusion of the EFT-1 flight, the detached Orion capsule plunges back and hits the Earth’s atmosphere at 20,000 MPH (32,000 kilometers per hour).
“That’s about 80% of the reentry speed experienced by the Apollo capsule after returning from the Apollo moon landing missions,” Scott Wilson, NASA’s Orion Manager of Production Operations at KSC, told me during an interview at KSC.
The next step in Orion’s multi stage journey to the launch pad follows later this week with transport of the CM/SM stack to another KSC facility named the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHFS) for fueling, before moving again for the installation of the launch abort system (LAS) in yet another KSC facility.

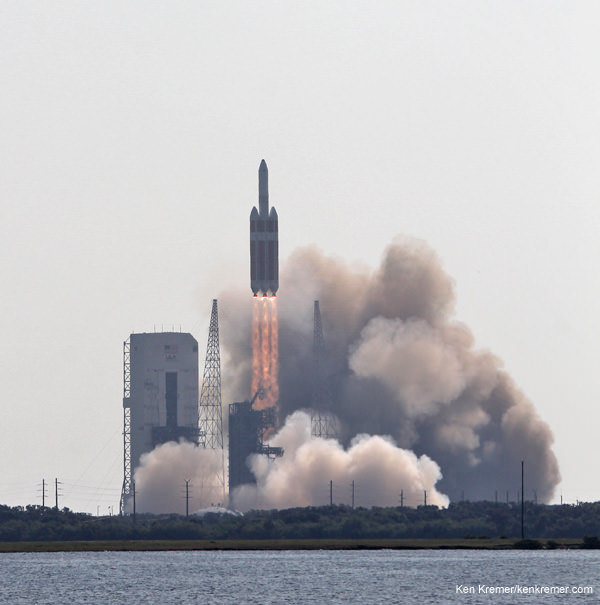
The Orion EFT-1 test flight is slated to soar to space atop the mammoth, triple barreled United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral, Florida, on Dec. 4, 2014 .
The state-of-the-art Orion spacecraft will carry America’s astronauts on voyages venturing farther into deep space than ever before – past the Moon to Asteroids, Mars and Beyond!

NASA is simultaneously developing a monster heavy lift rocket known as the Space Launch System or SLS, that will eventually launch Orion on its deep space missions.
The maiden SLS/Orion launch on the Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) unmanned test flight is now scheduled for no later than November 2018 – read my story here.
SLS will be the world’s most powerful rocket ever built.
The two-orbit, four and a half hour EFT-1 flight will lift the Orion spacecraft and its attached second stage to an orbital altitude of 3,600 miles, about 15 times higher than the International Space Station (ISS) – and farther than any human spacecraft has journeyed in 40 years.

The EFT-1 mission will test the systems critical for EM-1 and future human missions to deep space that follow.
The Orion EFT-1 capsule has come a long way over the past two years of assembly.
The bare bones, welded shell structure of the Orion crew cabin arrived at KSC in Florida from NASA’s Michoud facility in New Orleans in June 2012 and was officially unveiled at a KSC welcoming ceremony on 2 July 2012, attended by this author.
“Everyone is very excited to be working on the Orion. We have a lot of work to do. It’s a marathon not a sprint to build and test the vehicle,” said Jules Schneider, Orion Project manager for Lockheed Martin at KSC, during an exclusive 2012 interview with Universe Today inside the Orion clean room at KSC.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Orion, SLS, Boeing, Sierra Nevada, Orbital Sciences, SpaceX, commercial space, Curiosity, Mars rover, MAVEN, MOM and more Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
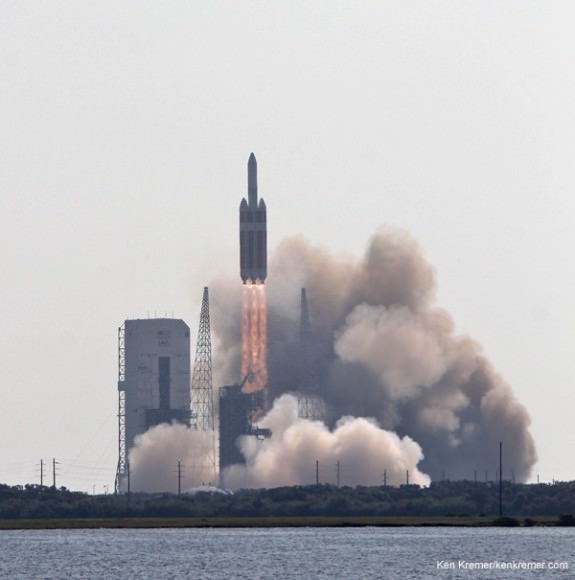















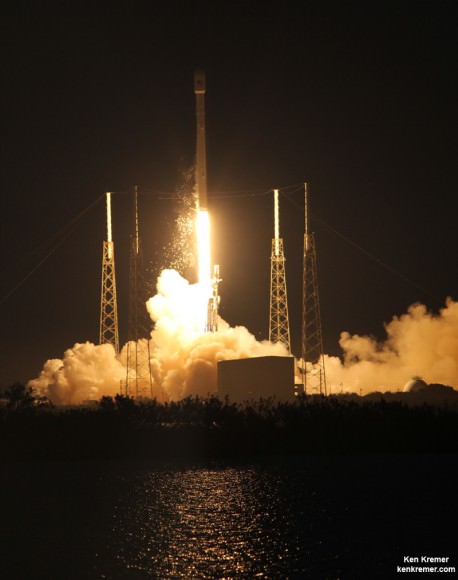
 Delta 4 Heavy rocket and super secret US spy satellite roar off Pad 37 on June 29, 2012 from Cape Canaveral, Florida. NASA’s Orion EFT-1 capsule will blastoff atop a similar Delta 4 Heavy Booster in December 2014. Credit: Ken Kremer- kenkremer.com[/caption]
Delta 4 Heavy rocket and super secret US spy satellite roar off Pad 37 on June 29, 2012 from Cape Canaveral, Florida. NASA’s Orion EFT-1 capsule will blastoff atop a similar Delta 4 Heavy Booster in December 2014. Credit: Ken Kremer- kenkremer.com[/caption]