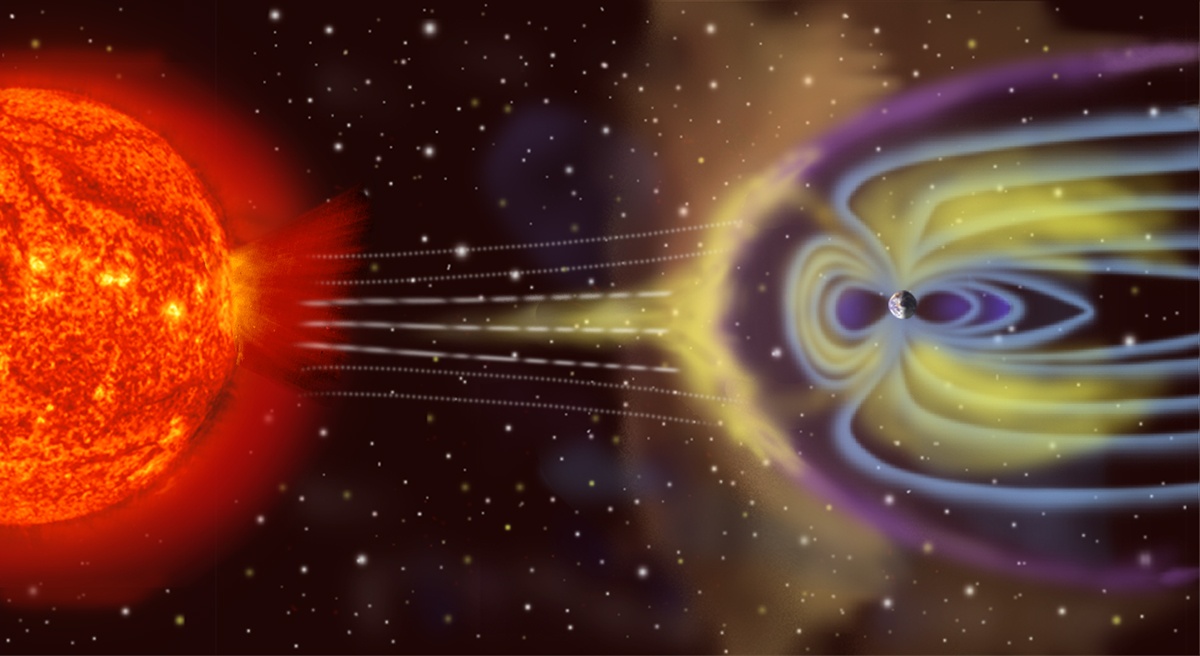
“A great fire appeared in the sky to the North, and lasted three nights,” wrote a Portuguese scribe in early March, 1582. Across the globe in feudal Japan, observers in Kyoto noted the same fiery red display in their skies too. Similar accounts of strange nighttime lights were recorded in Leipzig, Germany; Yecheon, South Korea; and a dozen other cities across Europe and East Asia.
It was a stunning event. While people living at high latitudes were well aware of auroras in 1582, most people living closer to the equator were not. The solar storm that year was unlike anything in living memory, and it was so strong it brought the aurora to latitudes as low as 28 degrees (in line with Florida, Egypt, and southern Japan). People this close to the equator had no frame of reference for such dazzling nighttime displays, and many took it as a religious portent.
Continue reading “A Very Powerful Solar Storm Hit the Earth Back in 1582”