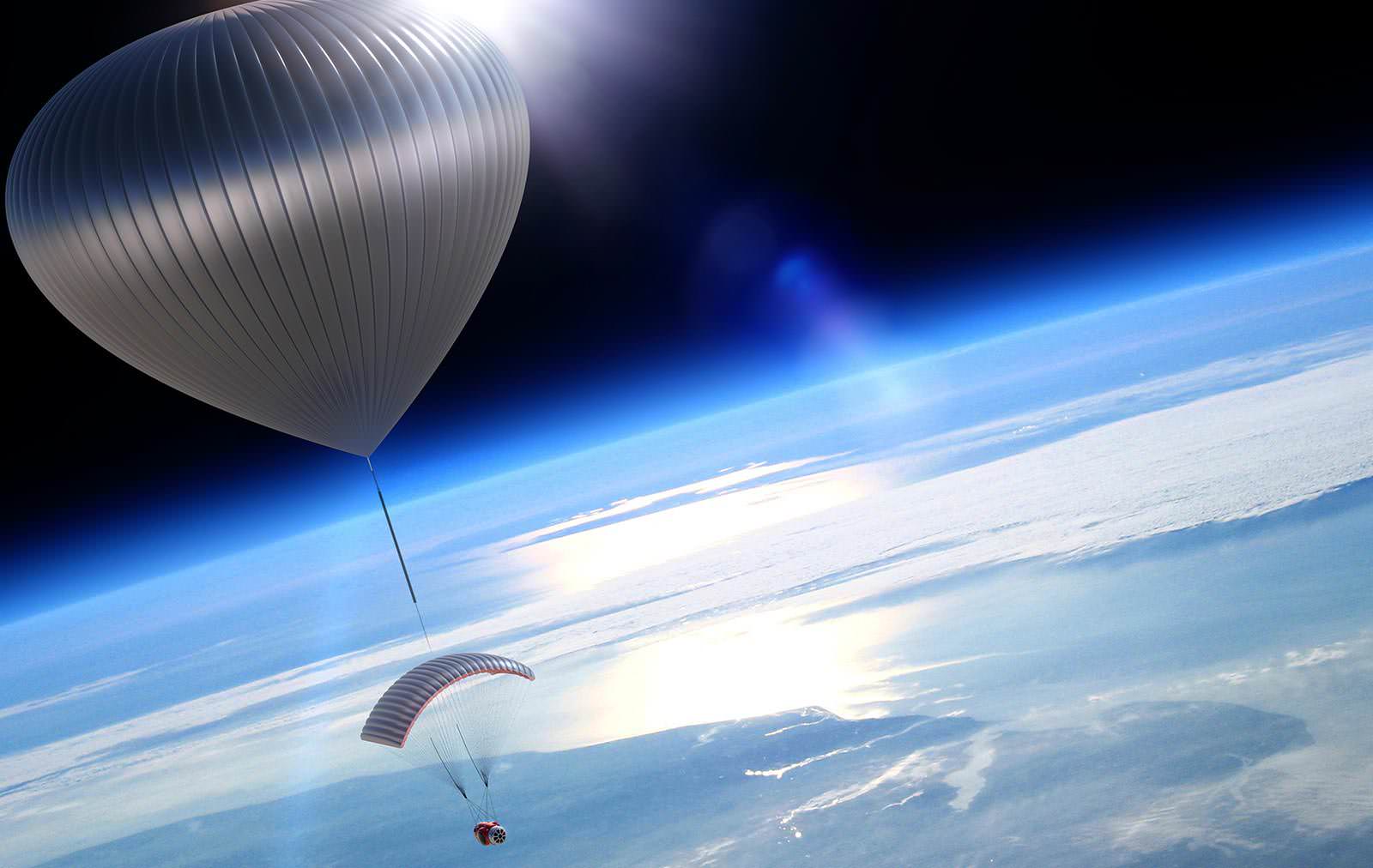
Doesn’t that look fun? A startup company is proposing to send customers 19 miles (30 kilometers) into the air via balloon, where they can linger for two hours and look at the curvature of the Earth and experience a black sky. While it’s not high enough to qualify as a spaceflight, the listed ticket price may be a little more affordable for space enthusiasts: $75,000.
Don’t get too excited yet — the project appears to be in very early stages, and no “first flight” date is listed yet. But there are some interesting notes for those looking for space and science experience in the company.
- Among the members of its executive is Alan Stern, the principal investigator for the New Horizons Pluto mission and NASA’s former associate administrator for the science mission directorate. (He’s also the CEO of the Golden Spike company that wants to offer commercial human missions to the moon.)
- The executive also includes Jane Poynter and Taber MacCallum, who were both members of Biosphere 2. More recently, they also took on senior positions in Inspiration Mars, a Dennis Tito-led project that aims to send humans past Mars. (The target launch date for that is Jan. 5, 2018.)
- The company proposing to build it is Paragon Space Development Corp. (which Poynter and MacCallum co-founded.) Paragon’s customers for thermal, environment and life support systems include a lot of name brands (including NASA). Paragon is also doing work for the Inspiration Mars project as well as Mars One, which aims to send colonists on a one-way trip to the Red Planet by 2023.

“Seeing the Earth hanging in the ink-black void of space will help people realize our connection to our home planet and to the universe around us, and will surely offer a transformative experience to our customers,” stated Poynter, who is CEO of World View. “It is also our goal to open up a whole new realm for exercising human curiosity, scientific research and education.”
World View’s announcement came after the Federal Aviation Administration “determined that World View’s spacecraft and its operations fall under the jurisdiction of the office of Commercial Space Flight,” the company added.
More information on their mission is available on the World View website. It’s a bit of a different track than Virgin Galactic and XCOR, who are offering rides into suborbital space for prices of $250,000 and $95,000, respectively. Neither company has an operational spacecraft yet, but they are in flight testing. Reports indicate they are hoping to get flights going next year.