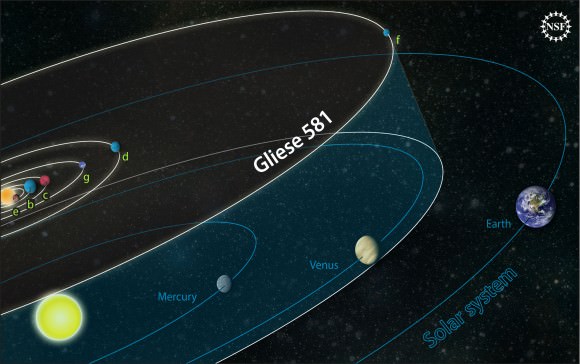
Two potentially habitable planets in the Gliese 581 system are just false signals arising out of starstuff, a new study said. Gliese 581d and 581g are (study authors said) instead indications of the star’s activity and rotation. It’s the latest twist in a long tale about the system as astronomers struggle to understand how many planets could be orbiting the star.
“Our improved detection of the real planets in this system gives us confidence that we are now beginning to sufficiently eliminate Doppler signals from stellar activity to discover new, habitable exoplanets, even when they are hidden beneath stellar noise,” stated Paul Robertson, a postdoctoral fellow at Penn State University, in a press release.
“While it is unfortunate to find that two such promising planets do not exist, we feel that the results of this study will ultimately lead to more Earth-like planets.”
Planets were first announced around the system in 2007 (by a research team led by Geneva’s Stephane Udry) including Gliese 581d. The system has been under heavy scrutiny since a team led by Steven Vogt of the University of Santa Cruz announced Gliese 581g in September 2010. Both 581d and 581g were considered to be in the “habitable” region around the dwarf star they orbited, meaning the spot that’s not too far or close to the star for liquid water to exist.

About two weeks after the discovery, another team led by Geneva University’s Francesco Pepe said it could not find indications of Gliese 581g in data from HARPS (High Accuracy Radial Velocity Planet Searcher), a telescope instrument frequently used at the European Southern Observatory to confirm exoplanets. It also cast doubt on the existence of Gliese 581f, announced by a team led by Geneva’s Michel Mayor in 2009. Other researchers examined the system, too, with mixed results.
Two years later, Vogt led another research team saying that analysis of an “extended dataset” from HARPS did show Gliese 581g. But in a press release at the time from the Planetary Habitability Laboratory at the University of Puerto Rico at Arecibo, its director (Abel Mendez) said the discovery would continue to be controversial. At the time he added the planet to the list of potentially habitable exoplanets the laboratory maintains. As of yesterday, both 581d and 581g are crossed off.
The uncertainty arises from the delicacy of looking for signals of small planets around much larger stars. Astronomers typically find planets through watching them pass across the face of a star, or measuring the tug that they exert on their parent star during their orbit. It is the nature of the tug on Gliese 581 that is so interesting astronomers.
“These ‘Doppler shifts’ can result from subtle changes in the star’s velocity caused by the gravitational tugs of orbiting planets,” wrote Penn State in the press release yesterday. “But Doppler shifts of a star’s ‘absorption lines’ also can result from magnetic events like sunspots originating within the star itself — giving false clues of a planet that does not actually exist.”
The researchers now say that only three planets exist around this star. It’s impossible to fully represent the debate in a single short news article, so we encourage you to look at some of the original literature. Here is a list of papers related to Gliese 581g and another for Gliese 581d. The new paper is available online in Science.
Also, here are some past Universe Today stories about the system:
- More Evidence that Gliese 581 Has Planets in the Habitable Zone (Dec. 14, 2007)
- Nearly Earth-sized Planet, Possible Watery World Spotted Near Another Star (April 21, 2009)
- New Earth-sized Exoplanet is in Star’s Habitable Zone (Sept. 29, 2010)
- Could Chance for Life on Gliese 581g Actually Be “100%”? (Sept. 30, 2010)
- Buzz About Gliese 581g: Doubts of Its Existence; Aliens Signals Detected (Oct. 2, 2010)
- The Habitability of Gliese 581d (Oct. 19, 2010)
- Update on Gliese 581d’s Habitability (May 6, 2011)
- First SETI Search of Gliese 581 Finds No Signs of ET (June 5, 2012)