How do crazy but neat ideas such as the Mars crane make it to space? It’s through years, sometimes decades, of development to try to solve a problem in space exploration. NASA has an entire program devoted to far-out concepts that are at least a decade from making it into space, and has just selected five projects for a second round of funding.
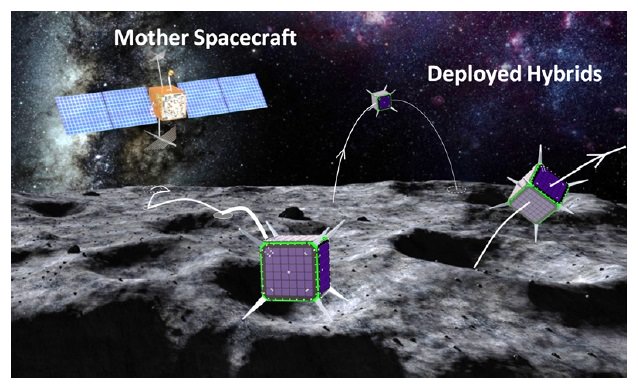
One of them is a robotic swarm of spacecraft that we’ve written about before on Universe Today. Flying out from a mothership, these tiny spacecraft would be able to tumble across the surface of a low-gravity moon or asteroid.
“The systematic exploration of small bodies would help unravel the origin of the solar system and its early evolution, as well as assess their astrobiological relevance,” stated its principal investigator, Stanford University’s Marco Pavone, in a 2012 story. “In addition, we can evaluate the resource potential of small bodies in view of future human missions beyond Earth.”
The concept, called “Spacecraft/Rover Hybrids for the Exploration of Small Solar System Bodies“, is among the selectees in the second phase of the NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts program. Each will receive up to $500,000 to further develop their concept during the next two years. While Phase I studies are considered to show if a project is feasible, Phase II begins to narrow down the design.
“This was an extremely competitive year for NIAC Phase II candidates,” stated Jay Falker, the program’s executive at NASA Headquarters. “But the independent peer review process helped identify those that could be the most transformative, with outstanding potential for future science and exploration.”
This is the rest of the selected concepts:
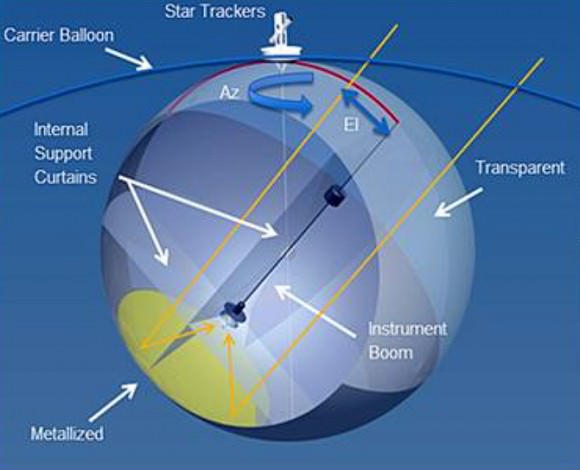
10 meter Sub-Orbital Large Balloon Reflector (Christopher Walker, University of Arizona): A telescope that uses part of a balloon as a reflector. The telescope would fly high in the atmosphere, perhaps doing examinations of Earth’s atmosphere or performing telecommunications or surveillance.
Deep mapping of small solar system bodies with galactic cosmic ray secondary particle showers (Thomas Prettyman, Planetary Science Institute): Using subatomic particles to map asteroids, comets and other smaller objects in the solar system.
Low-Mass Planar Photonic Imaging Sensor (Ben S.J. Yoo, University of California, Davis): A new way of thinking about telescopes that would use a low-mass planar photonic imaging sensor. This could be useful for missions to the outer solar system.
Orbiting Rainbows (Marco Quadrelli, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory): Using “an orbiting cloud of dust-like matter” for astronomical imaging by taking advantage of the spots where light passes through.
Source: NASA