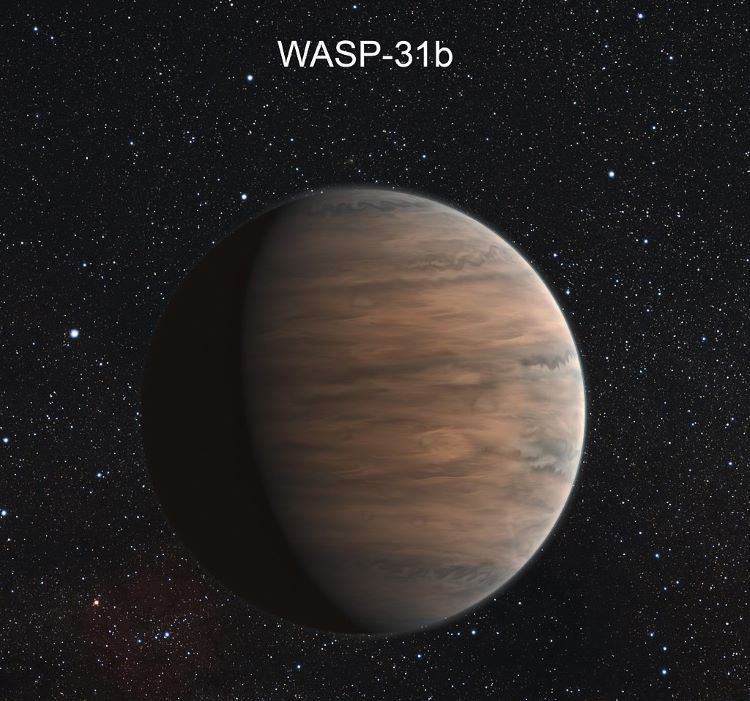
A recent study published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters examines a rare alloy molecule known as chromium hydride (CrH) and its first-time confirmation on an exoplanet, in this case, WASP-31 b. Traditionally, CrH is only found in large quantities between 1,200 to 2,000 degrees Kelvin (926.85 to 1,726.85 degrees Celsius/1700 to 3,140 degrees Fahrenheit) and used to ascertain the temperature of cool stars and brown dwarfs. Therefore, astronomers like Dr. Laura Flagg in the Department of Astronomy and Carl Sagan Institute at Cornell University refer to CrH as a “thermometer for stars”.
Continue reading “Astronomers Confirm First Exoplanet “Thermometer Molecule” that is Typically Used to Study Brown Dwarfs”Exploring Io’s Volcanic Activity via Hubble and Webb Telescopes
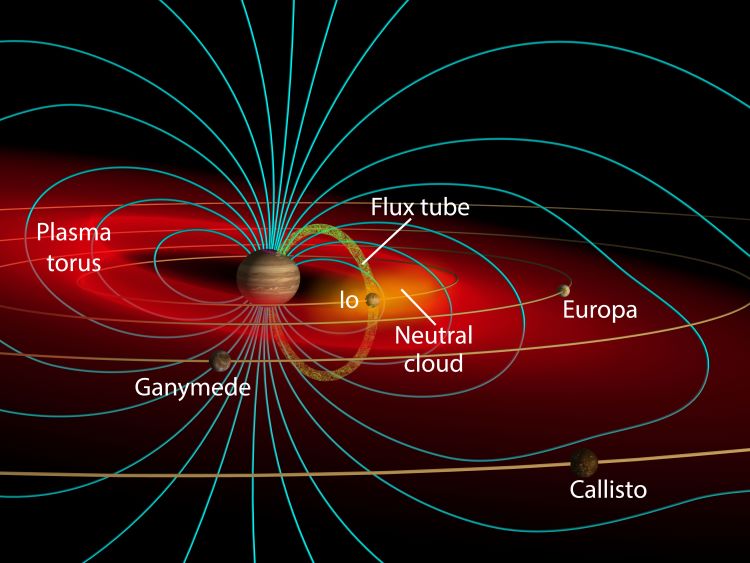
The two most powerful space telescopes ever built, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and Hubble Space Telescope, are about to gather data about the most volcanically body in the entire solar system, Jupiter’s first Galilean Moon, Io. This data will be used in combination with upcoming flybys of Io by NASA’s Juno spacecraft, which is currently surveying the Jupiter system and is slated to conduct these flybys later this year and early 2024. The purpose of examining this small, volcanic moon with these two powerful telescopes and one orbiting spacecraft is for scientists to gain a better understanding of how Io’s escaping atmosphere interacts with Jupiter’s surrounding magnetic and plasma environment.
Continue reading “Exploring Io’s Volcanic Activity via Hubble and Webb Telescopes”Ancient Cracked Mud Found on Mars

A recent study published in Nature examines how mud cracks observed on Mars by NASA’s Curiosity rover could provide insight into how life on the Red Planet could have formed in its ancient past. On Earth, mud cracks have traditionally been linked to cycles of wet and dry environments that assisted in developing the complex processes responsible for microbial life to take hold. This study was conducted by an international team of researchers and holds the potential to help scientists better understand the geological and chemical processes that might have existed in Mars’ ancient past, up to billions of years ago.
Continue reading “Ancient Cracked Mud Found on Mars”40th Rocket Lab Electron Mission, “We Love The Nightlife”, Launches From New Zealand with Reused Engine
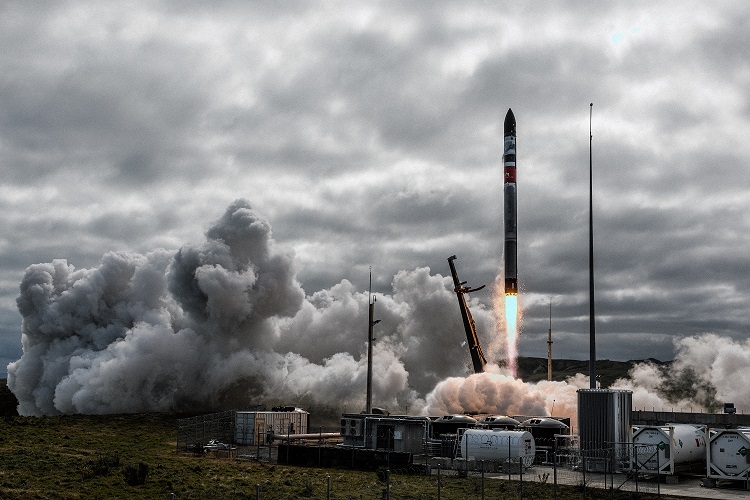

Private space company, Rocket Lab, launched its 40th Electron mission on their lauded Electron rocket, dubbed “We Love The Nightlife”, on August 24th at 11:45am New Zealand Standard Time (August 23rd at 7:45pm EST), which also marks the 7th launch of 2023, all successful. The purpose of the mission was to deliver the next-generation Acadia satellite for Capella Space to a circular orbit above the Earth at 640 km (400 miles), which was executed flawlessly. Acadia is part of Capella’s synthetic aperture radar (SAR) constellation and is the first of four Acadia satellites that Rocket is currently contracted to launch for Capella.
Continue reading “40th Rocket Lab Electron Mission, “We Love The Nightlife”, Launches From New Zealand with Reused Engine”Dr. Tracy Becker Honored with 2023 Carl Sagan Medal for Science Communication

This year’s prestigious Carl Sagan Medal, also known as the “Sagan Medal” and named after the late astronomer, Dr. Carl Sagan, has been awarded to Dr. Tracy Becker, who is a planetary scientist in the Space Science Division of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) in San Antonio, Texas. The Sagan Medal recipient is chosen by the Division for Planetary Sciences of the American Astronomical Society (AAS) and is meant to acknowledge planetary scientists who are not only active in science communication with the general public but have taken enormous strides in helping the general public better understand, and get excited for, the field of planetary science.
Continue reading “Dr. Tracy Becker Honored with 2023 Carl Sagan Medal for Science Communication”Watch an Actual Exoplanet Orbit its Star for 17 Years
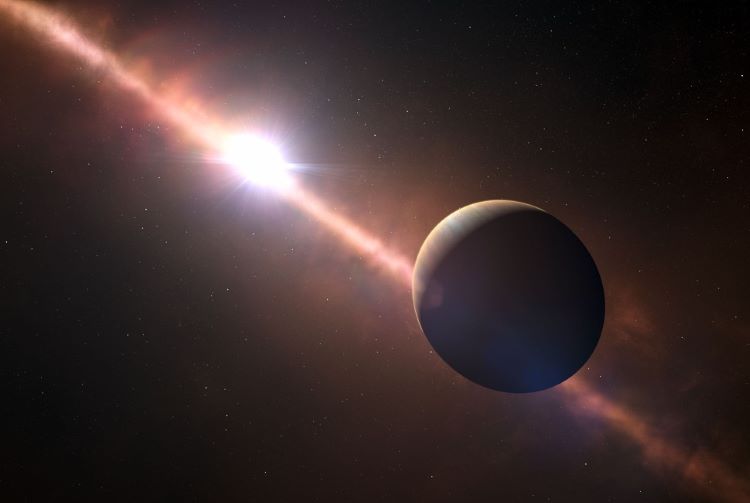

Searching for exoplanets is incredibly difficult given their literal astronomical distances from Earth, which is why a myriad of methods have been created to find them. These include transit, redial velocity, astrometry, gravitational microlensing, and direct imaging. It is this last method that was used to recently create a time-lapse video that compresses a mind-blowing 17 years of the partial orbit of exoplanet, Beta Pictoris b, into 10 seconds. The data to create the video was collected between 2003 and 2020, it encompasses approximately 75 percent of the total orbit, and marks the longest time-lapse video of an exoplanet ever produced.
Continue reading “Watch an Actual Exoplanet Orbit its Star for 17 Years”This Jupiter-Sized Exoplanet is Unusual for Several Reasons
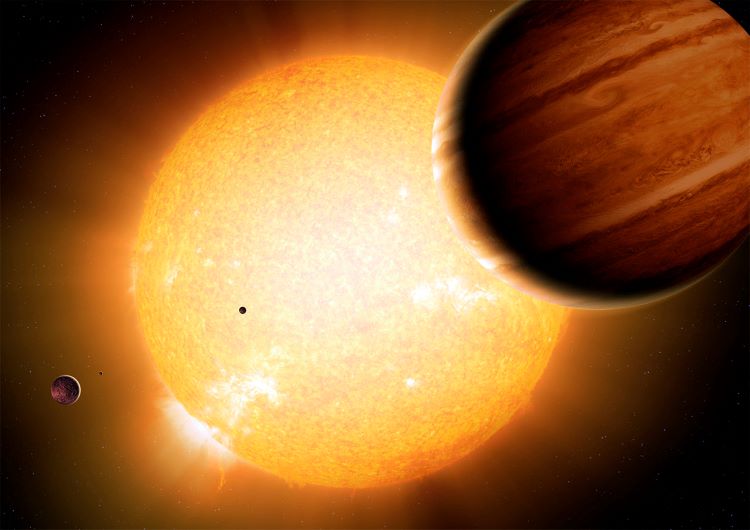

In a recent study published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, a team of international researchers examined exoplanet TOI-4860 b, which is located approximately 80 parsecs (261 light-years) from Earth and has an orbital period of approximately 1.52 days around a low-mass star, or a star smaller than our Sun. Exoplanets orbiting so close to their parent stars aren’t uncommon and commonly known as “hot Jupiters”.
However, TOI-4860 b is unique due its relative size compared to its parent star, along with its lower surface temperatures compared to “hot Jupiters” and possessing large amounts of heavy elements. These attributes are why researchers are classifying TOI-4680 b as a “warm Jupiter”, and could challenge traditional planetary systems formation models while offering new insights into such processes, as well.
Continue reading “This Jupiter-Sized Exoplanet is Unusual for Several Reasons”Interpreting Dune Patterns: Insights from Earth and Mars
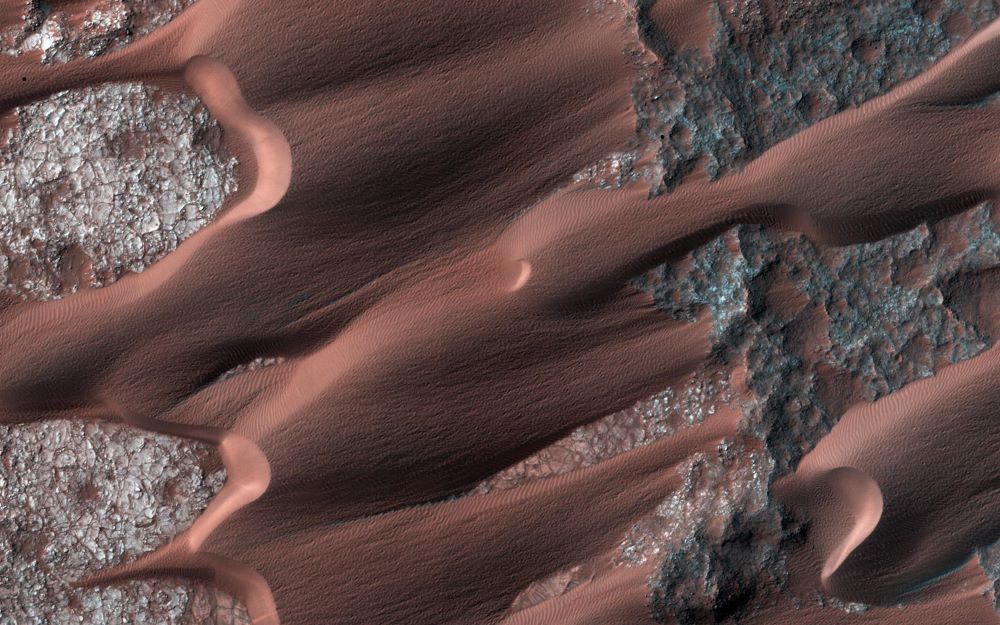

A recent study published in the journal Geology attempts to interpret the patterns of dunes, which are sand mounds frequently formed by aeolian (wind) processes and range in size from small ripples observed on beaches to massive structures observed in the desert. Specifically, the researchers focused on patterns of dune crestlines, which are the top of the dunes. Different dune crestline patterns might appear as mundane features, but their formations are often the result of a myriad of influences, including climate change, surface processes, and atmospheric phenomena.
Continue reading “Interpreting Dune Patterns: Insights from Earth and Mars”China’s Chang’e-7 Will Deploy a Hopper that Jumps into a Crater in Search of Water Ice
Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Chinese National Space Administration recently published a study in the journal Space: Science & Technology outlining how the upcoming Chang’e-7 mission, due to launch in 2026, will use a combination of orbital observations and in-situ analyses to help identify the location, amount, and dispersion of water-ice in the permanently-shadowed regions (PSRs) of the Moon, specifically at the lunar south pole.
Continue reading “China’s Chang’e-7 Will Deploy a Hopper that Jumps into a Crater in Search of Water Ice”Jupiter’s Moons Get the JWST Treatment
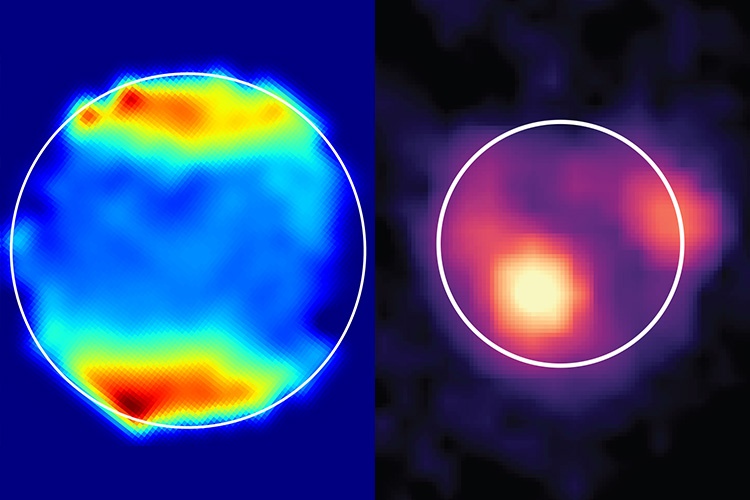
A pair of studies published in JGR: Planets and Science Advances discuss new findings from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) regarding Jupiter’s first and third Galilean Moons, Io and Ganymede, and more specifically, how the massive Jupiter is influencing activity on these two small worlds. For Io, whose mass is about 21 percent larger than Earth’s Moon, the researchers made the first discovery of sulfur monoxide (SO) gas on the volcanically active moon. For Ganymede, which is the largest moon in the solar system and boasts twice the mass of the Earth’s Moon, the researchers made the first discovery of hydrogen peroxide, which exists in Ganymede’s polar regions.
Continue reading “Jupiter’s Moons Get the JWST Treatment”

