[/caption]
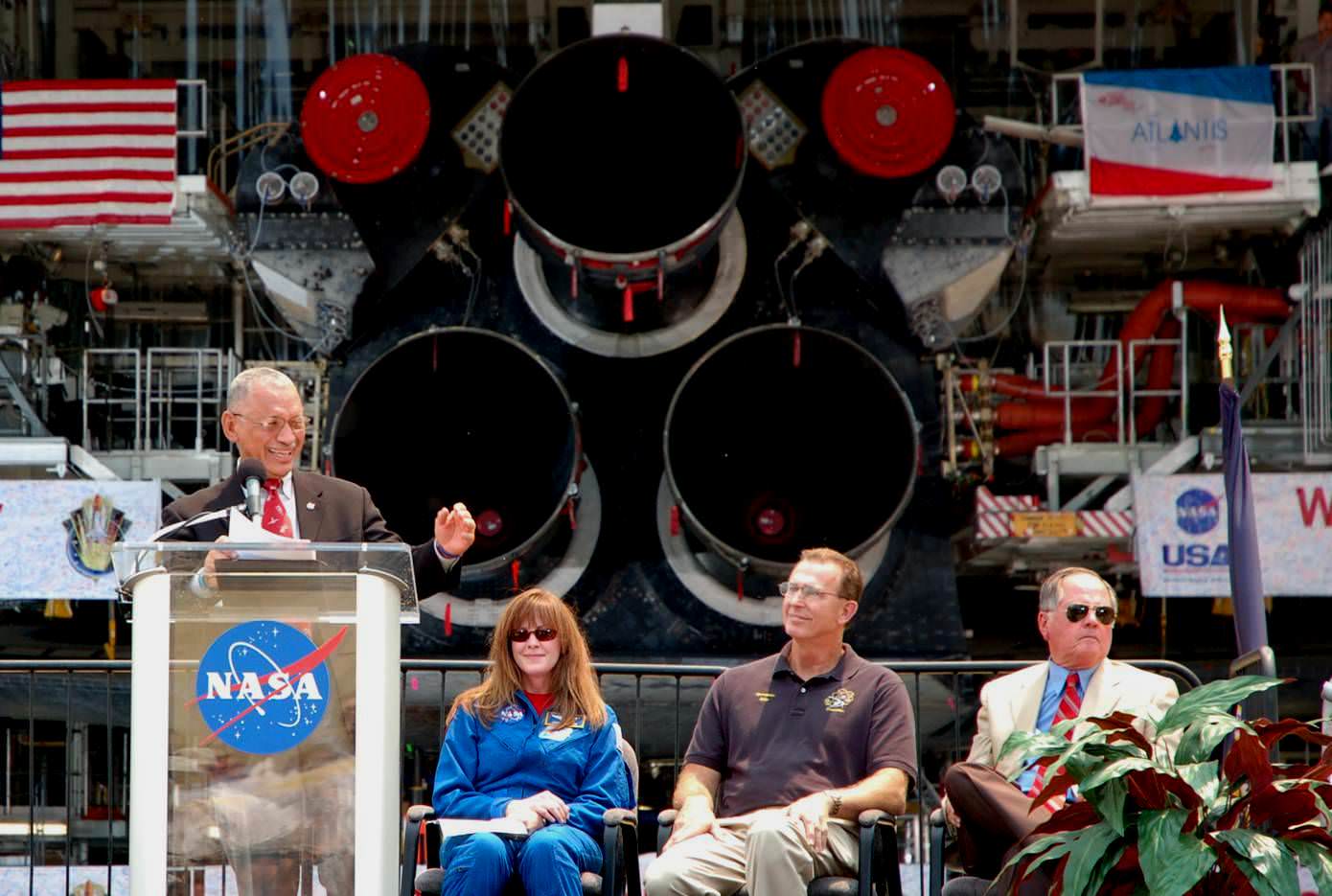
CAPE CANAVERAL – With the shuttle program’s end less than three months away, NASA took time to honor the program that has been the focal point of the agency’s manned space flight efforts for the past thirty years. At 1 p.m., NASA’s Administrator, Charles Bolden, along with Kennedy Space Center Director Robert Cabana, astronaut Janet Kavandi, shuttle Endeavour’s Vehicle Manager Mike Parrish and STS-1 Pilot Robert Crippen spoke to NASA employees and members of the media regarding the programs long history and its many achievements.
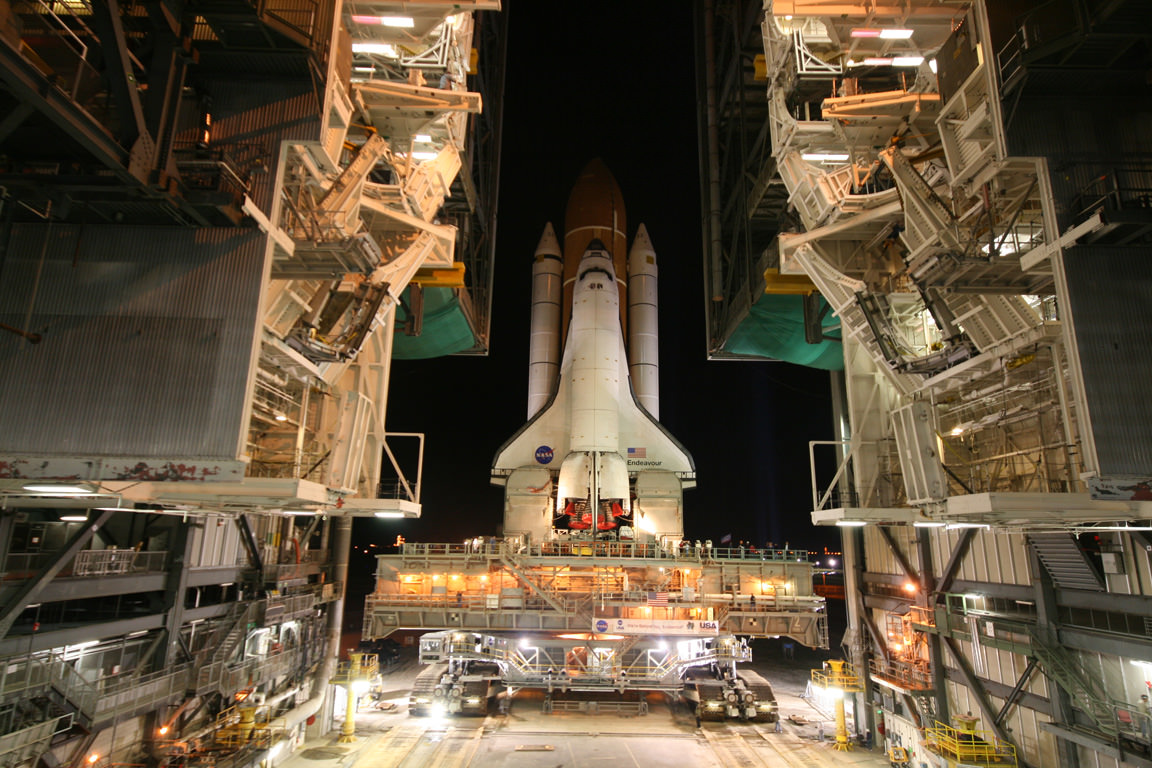
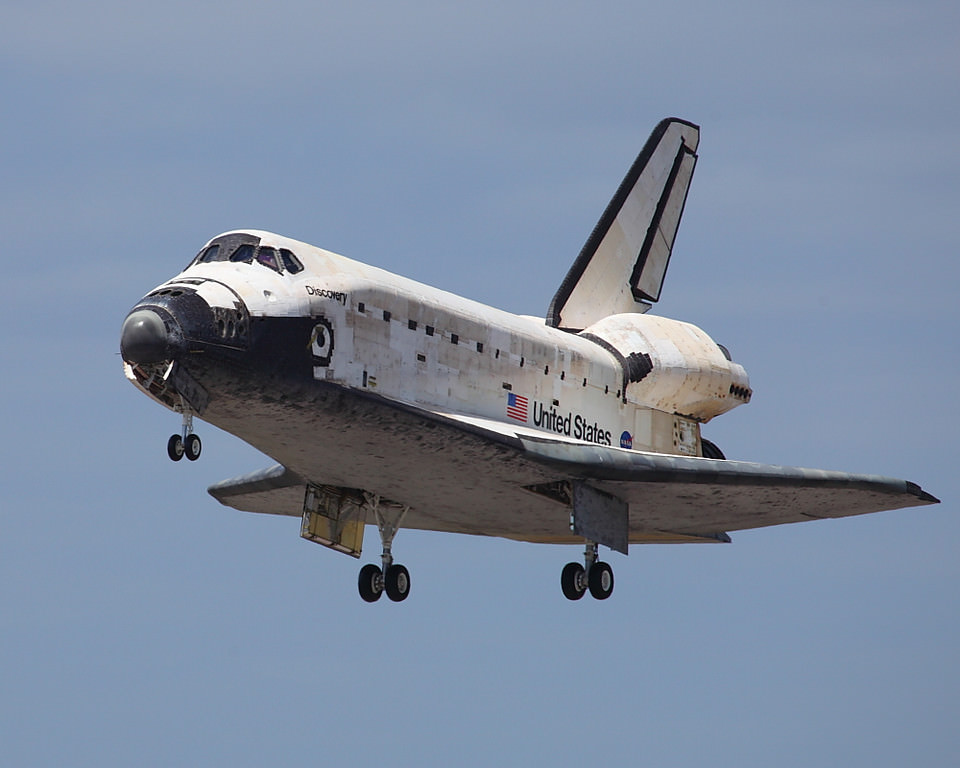
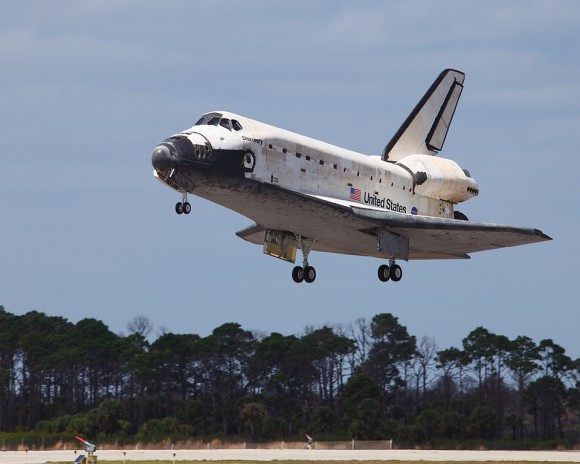
However, the most important announcement of the day was where the remaining shuttles will go when the program draws to a close. It was announced that the space shuttle Enterprise, a test article of the shuttle design, will move from its current home at the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Virginia to the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York. The Udvar-Hazy Center will be home for Discovery, which finished its last mission in March. Endeavour, which is being readied for its final flight at the end of this month, will go to the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Atlantis, which is currently scheduled to fly the last shuttle mission in June, will go to the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida.

Although Bolden and Cabana are former astronauts, they were joined by one of the two men that flew the very first shuttle mission, STS-1 – Robert Crippen. This mission is viewed as one of the most risky test flights in history. If something had gone wrong during the first mission’s launch, Crippen and Commander John Young would have had to eject from Columbia – through the vehicle’s fiery plume. However, everything worked according to plan and Columbia landed at Edwards Air Force Base in California two days later.
The weight of the day’s events had an obvious impact on Bolden and Crippen, both of whom were visibly emotional during the presentation. Crippen’s comments detailed the feelings of many in that this is a bitter-sweet anniversary. Those in attendance supported the four-time shuttle veteran with loud applause when it was announced that Atlantis would remain at Kennedy Space Center.

“Stay focused, “said Bolden during his comments, referring to the gap in manned space flight that is about to take place. “It’s been a rough day.”
There was also a guest appearance from the current members of the International Space Station who called in from on orbit. They apologized for not being able to attend – before they acknowledged it was thanks to the hard work of those present that they couldn’t be there. Astronauts Cady Coleman, Ron Garan were joined by ESA astronaut Paolo Nespoli as well as cosmonauts Dmitry Kondratyev, Andrey Borisenko and Alexander Samokutyaev. The station’s crew spoke about how the shuttle program made this international effort possible.

On April 12, 1981, the space shuttle Columbia roared into orbit on the first mission of the shuttle program. The first crew only had two astronauts on board, Apollo veteran John Young and rookie astronaut Robert Crippen. The first flight of the shuttle program took place 20 years to the day that the first human rode fire into orbit – Yuri Gagarin.
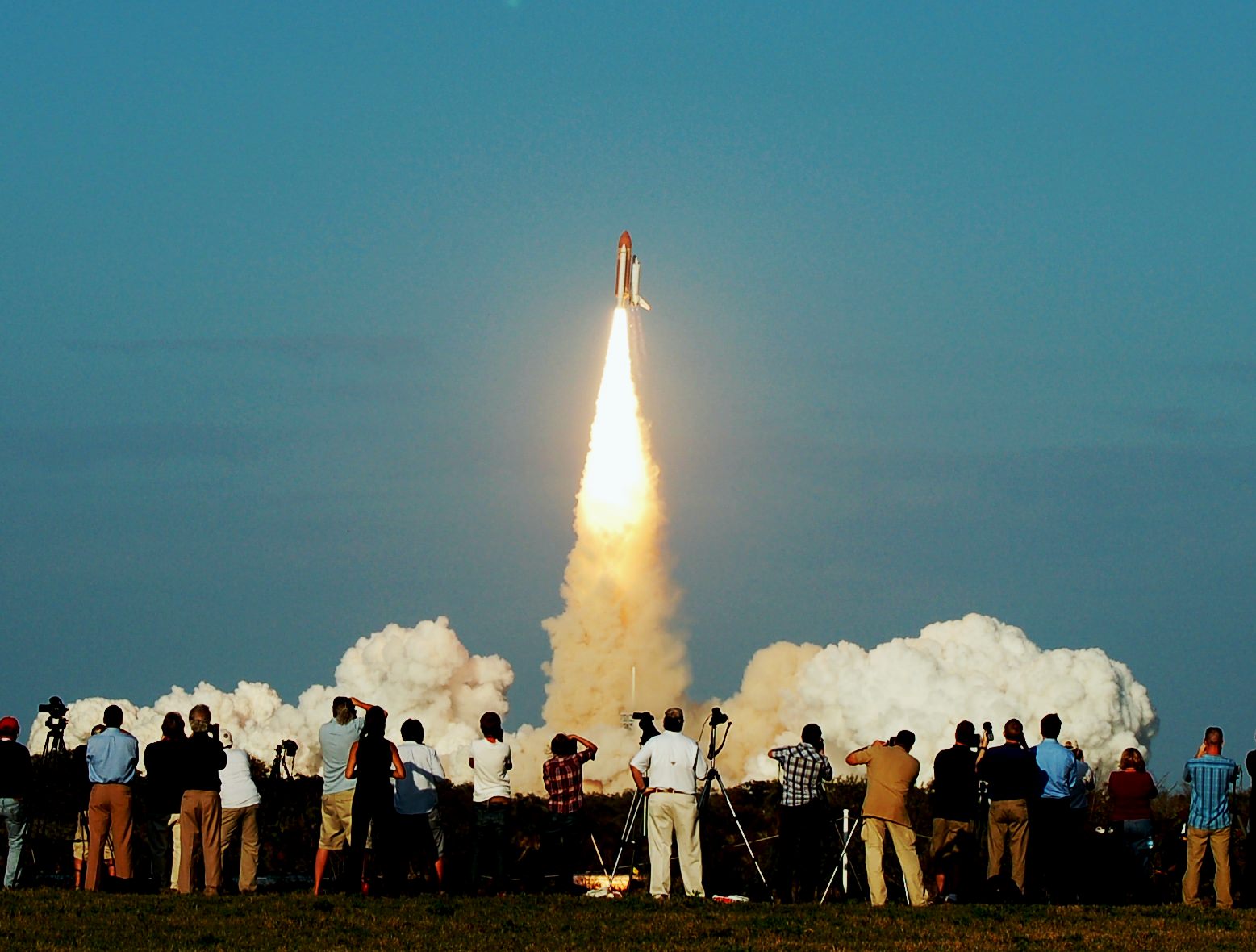
There are currently only two shuttle flights remaining, Endeavour is slated to conduct its 25th and final mission, STS-134, at the end of this month and Atlantis will launch the final mission on June 28. Once this mission is over, NASA will have to rely on Russia for access to the International Space Station until small, commercial firms; those supported under President Obama’s new plans for NASA can produce a launch system to fill the void.
“I would have been happy to get any of the orbiters here at KSC,” said Robert Crippen when interviewed. “Getting Atlantis makes this a very good day.”