[/caption]
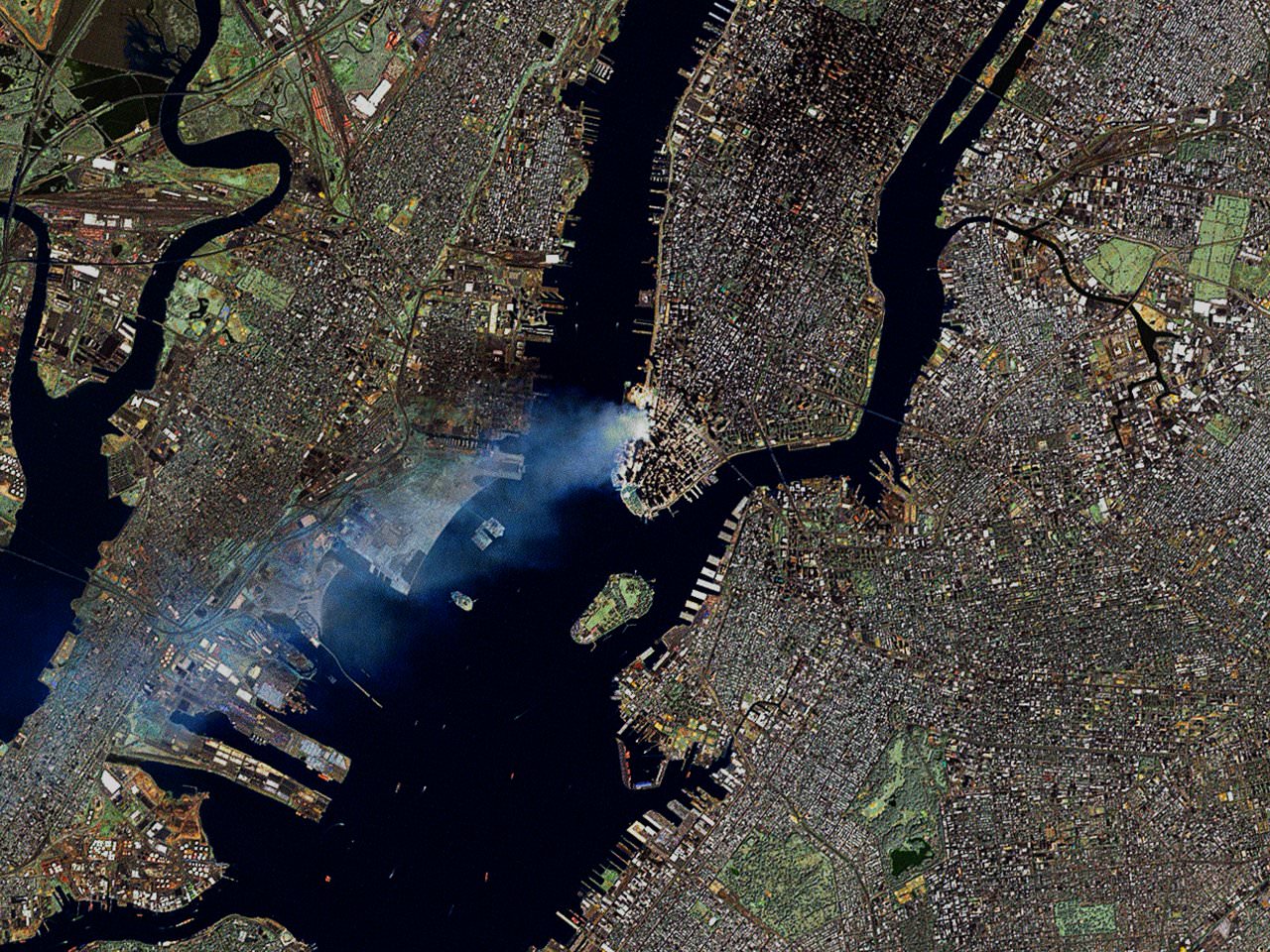
A decade ago, the 9/11 attacks killed close to three thousand people and with the chaos that ensued many more were left wondering what was going on, whether-or-not their loved ones were still alive – or what was coming next. One man in particular was more isolated than the rest of his fellow citizens on that horrific day – he was forced to watch, some 240 miles above the face of the planet – as his nation came under attack.
Frank Culbertson Jr. was the Expedition 3 Commander on the International Space Station when Islamic radicals slammed two planes into the World Trade Center in New York City and a third into the Pentagon in Washington D.C. A fourth hijacked plane, whose target was believed to be the Capitol Building in Washington D.C., was prevented from reaching its destination by passengers. The terrorists on board crashed that plane, United 93, near Shanksville, Pennsylvania.
“I think like most Americans, at first I did not know what was happening – I just knew that it was bad,” said Culbertson referring to the attacks. “It was very painful; it was like seeing a wound in the side of your country, your family and your friends.”

Culbertson’s crew mates, both Russian, were Soyuz Commander Vladimir Deshurov and Flight Engineer Mikhail Tyurin. They offered all the support they could. Tyurin went so far as to prepare Culbertson’s favorite Borscht dinner that evening. Both of them also gave him time, time to understand and come to terms with what had happened. Russian ground controllers also worked to be supportive of Culbertson during this period. Russia’s TsUP worked to uplink information to Culbertson with whatever information they could when U.S. assets were unable to do so.
Age-wise, the ISS was still a somewhat new enterprise at the time, it had only hosted a crew for about a year – but it was already showing that people from different nations, some of whom had been hostile to one another just a short time before – could work together.
Culbertson initially was not comfortable with expressing his thoughts and feelings about 9/11. With time however; he has shared some of his thoughts regarding that day. Through it all, Culbertson has decided to focus not on anger – but hope.

“I met a veteran at Williamsburg and once he found out what I did – he looked at me and said that what is happening on the International Space Station is one of the best things that we (the U.S.) were doing, we have to work internationally to find peaceful ways to solve our problems. It’s men and women like that, the young people that are in harm’s way working to prevent events like 9/11 from taking place – that are the real heroes.”
Culbertson found even more hope when he talked to the children who were close to the attacks when they occurred.
“I had the privilege of talking to a school that was just a couple blocks away from Ground Zero and meet those kids and teachers in person. They were close to Ground Zero – but they were optimistic about the future – and as they are our future – I think we are in good hands.”