[/caption]
Over the past decade, events have transpired on the ground that have both indirectly and directly impacted crews on orbit. With astronauts spending as long as six months in space on the International Space Station, some have had to deal with tragedies — both intimately personal and completely national — during a mission. NASA, for its part, has done everything it can do to prepare crews for life in space, and dealing with tragedies is factored into every flight.
When terrorists conducted the worst attack on American soil in U.S. history on September 11, 2001, there was a single U.S. astronaut orbiting high above on the ISS, left helpless to do anything but watch and photograph as his nation came under attack. Frank Culbertson, then commander of the orbiting outpost along with two Russian cosmonauts, spoke afterward of his sense of isolation as the country dealt with this tragedy.

A disaster a little closer to home struck on Feb. 1, 2003 – the space shuttle Columbia was lost on orbit with her crew of seven. Astronauts Donald Pettit and Kenneth Bowersox were on orbit on the ISS when Columbia broke apart in Earth’s atmosphere, returning from a non-space station mission. While the two crews were in space at the same time, astronauts Petit on the ISS and Willie McCool aboard Columbia played a friendly game of chess – separated by the void of space. Sadly, the game would never be finished. McCool and the rest of Columbia’s STS-107 lost their lives when the orbiter disintegrated in the skies above Texas. For Petit and Bowersox this cut them off from traditional forms of grieving as well as a way home.

With the orbiter fleet grounded, how would they change out crews? The 16 nations involved in the ISS project worked to balance things out until the shuttles were back in action. Post-Columbia, crew rotations among numerous other things would be changed. NASA would survive, but tragedies would still strike the NASA family.
When astronaut Dan Tani was stationed aboard the ISS in 2007 he received the terrible news that his mother was killed in an automobile accident. A NASA flight surgeon along with Tani’s wife contacted the astronaut while he was serving aboard the ISS.

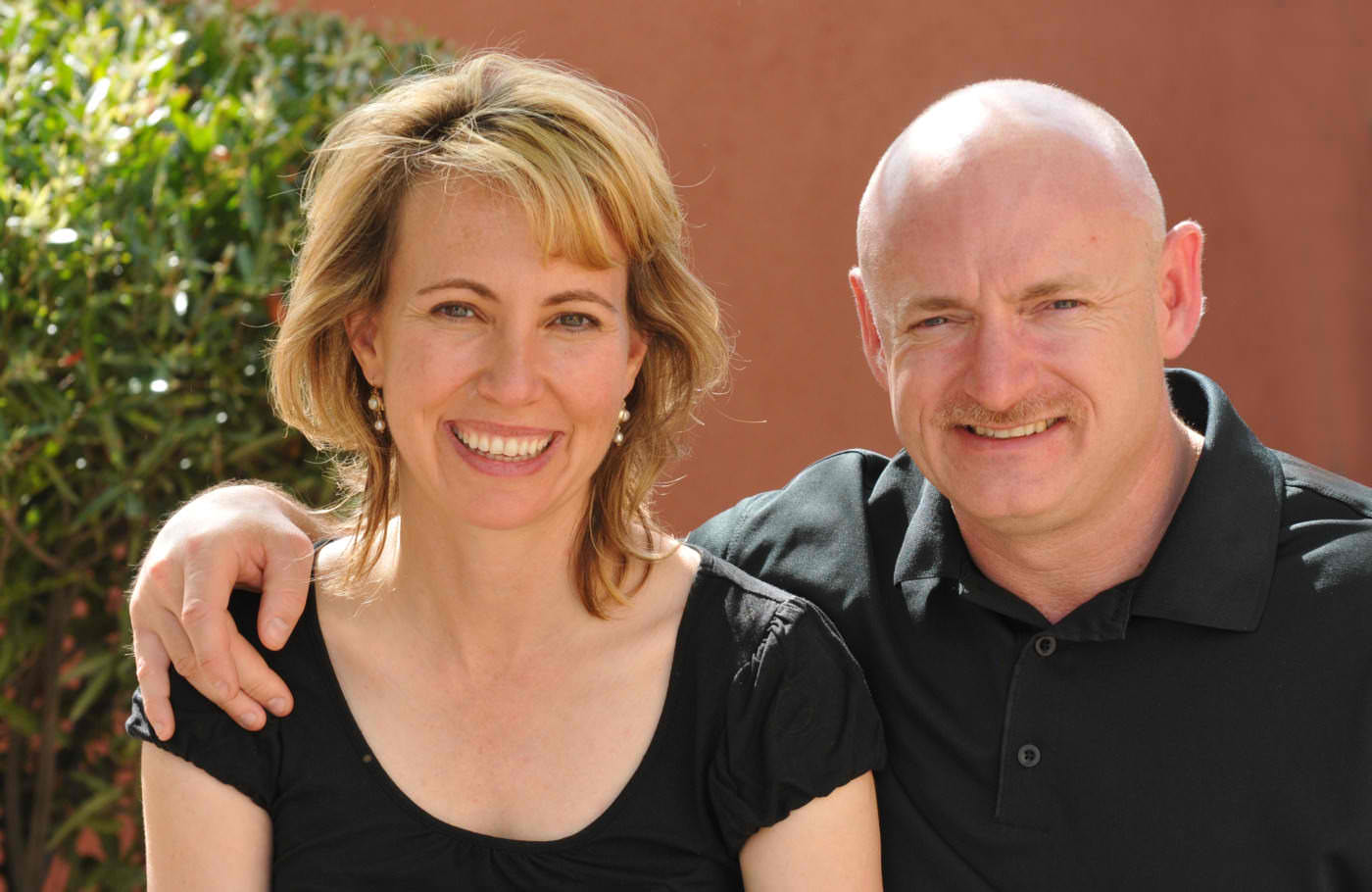
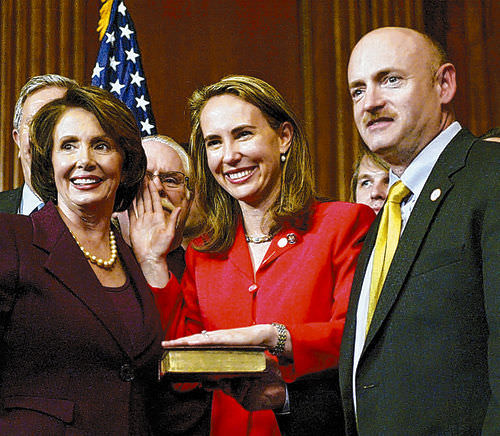
With the recent tragedy in Tucson, Arizona, NASA once again had to focus on emergency contingencies. This time a commander for an upcoming shuttle mission, Mark Kelly, had to be notified that his wife, Rep. Gabrielle Giffords, had been seriously injured in a mass shooting while meeting with her constituents at an event called “Congress on your Corner.” NASA had to contact both Mark Kelly and his brother Scott, who was on-orbit aboard the ISS. NASA also had to deal with the potential that Mark might not be able to launch with his crewmates on Endeavour’s final mission – STS-134. As such, a backup commander was announced, four-time shuttle veteran Rick Sturckow.
“NASA’s goal is mission success and crew safety. Although NASA does not train crewmembers as backups for its shuttle crews or ISS crews, it has enough trained crewmembers that substitutions late in the training flow for medical or personal emergencies can succeed,” said Tom Jones Ph.D a four-time shuttle veteran and author of Sky Walking: An Astronaut’s Memoir. “NASA has replaced at least three crewmembers within a few months to launch since the Apollo era. They also moved an ISS crewmember in training to an earlier crew to replace a crewmember dealing with medical problems. Once in space, NASA will notify astronauts of family problems back on the ground if they have asked for such notification in discussions before launch.”
NASA works to ensure the safety and privacy of its astronauts during times like this. This point was emphasized during a recent press conference held to update the media about repairs conducted to the shuttle, Discovery. William Gerstenmaier; administrator for Space Operations stated emphatically from the outset – that this was not the appropriate time to discuss these issues. One wayward reporter tried anyway, taking the question at a different angle and to another member of the interview panel – John Shannon. Shannon made sure that the reporter understood and that NASA stood as one – behind Mark Kelly and his family.
There is no way that NASA can predict every single possible scenario – but the agency does the best it can.
“Crew members are informed as soon as possible of any family emergencies or other urgent news and issues. In advance of their mission, crew members meet with astronaut office management to discuss individual preferences regarding notification of such emergencies,” said Kylie Clem a public affairs officer with NASA. “NASA provides psychological support for all astronauts, including those in space. A NASA Flight Surgeon, psychological services and family support services are all available for Scott and Mark’s families. The astronaut office is a close knit organization.”
Not all the news NASA has relayed to its astronauts has been tragic. Astronaut Mike Fincke welcomed his daughter Tarali Paulina into the world from orbit in 2004 and astronaut Randy Bresnik did the same for his daughter, Abigail Mae Bresnik, while part of the STS-129 mission in 2009. In all cases, NASA works to ensure that, regardless of the situation, its astronauts will find out their most personal news – in the best way possible – given the circumstances.